Table of Contents
- 1 What is Communication?
- 2 Definitions of Communication
- 3 Functions of Communication
-
4 Importance of Communication
- 4.1 Basis of Decision-Making and Planning
- 4.2 Smooth and Efficient Working
- 4.3 Motivation to Work
- 4.4 Job Satisfaction
- 4.5 Commitment to Organizational Objectives
- 4.6 Coordination
- 4.7 Adaptability to External Environment
- 4.8 Internal Functioning of an Enterprise
- 4.9 Healthy Industrial Relations
- 4.10 Helps in Performing Managerial Roles
- 4.11 Facilitates Leadership
- 4.12 Facilitates control
- 4.13 Training and Development
- 4.14 Substance to Organizational Existence
- 5 Principles of Communication
- 6 Process of Communication
- 7 Types of Communication
- 8 Elements of Communication
- 9 FAQ Related to Communication
What is Communication?
Simply defined, communication is the act of transmitting information, ideas, and attitudes from one person to another. It is the process of transmitting a message from a source to an audience through a channel.
For example, in a conversation, which is the most common type of communication, the person who speaks is the source and the person who listens is the audience. What is transmitted by the person who speaks is the message and the spoken voice carried through the air is the channel.

In other words, The word communication is derived from the Latin word ‘communicate, which means to share, impart, Ban and Hawkins define communication as the process of sending and receiving messages through channels that establish common meaning between a source and receiver.
According to Joseph A. Devito, communication refers to “the act by one or more persons, of sending and receiving messages, distorted by noise, within a context, with some effect and with some opportunity for feedback.
Definitions of Communication
These are some definitions of communication given by the authors:
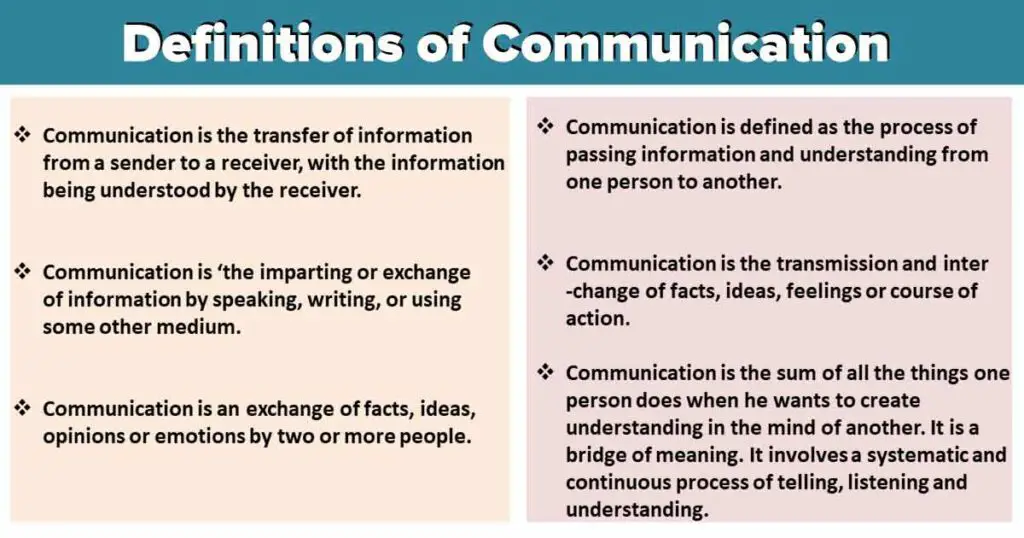
[su_quote cite=” Koontz and Weihrich”]Communication is the transfer of information from a sender to a receiver, with the information being understood by the receiver.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Oxford Dictionary”]communication is ‘the imparting or exchange of information by speaking, writing, or using some other medium.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=” Newman and Summer”]Communication is an exchange of facts, ideas, opinions or emotions by two or more people.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=” Keith Davis”]Communication is defined as the process of passing information and understanding from one person to another.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=” Leland Brown”]Communication is the transmission and interchange of facts, ideas, feelings or course of action.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=” Louis Allen”]Communication is the sum of all the things one person does when he wants to create understanding in the mind of another. It is a bridge of meaning. It involves a systematic and continuous process of telling, listening, and understanding.[/su_quote]
Functions of Communication
These are the following functions of communication
- Informing
- Persuading
- Integrating
- Creating Relationships
- Help in Making Selections between Alternatives
- Improving Connections
- Reducing Misunderstandings
- Solving Problems
- Evaluating
- Making Decisions
Information Function
Informing messages to others is regarded as the principal function of communication. It is done verbally or non-verbally. Verbal messages can be oral or written. Whereas, non-verbal messages are conveyed through the use of body language, gestures, postures, and so forth.
Persuading
Persuading is referred to making someone do or believe something, by giving them a valid and genuine reason to do it. Persuading can be encouraged through effective communication. It is implemented among individuals within homes, educational institutions, and employment settings.
Integrating
It is comprehensively understood that individuals cannot work in seclusion. In order to carry out one’s job duties in a well-organized manner and achieve the desired goals and objectives, individuals need to work in integration with each other. When they work in integration, they are able to benefit in a number of ways.
Creating Relationships
Creating relationships is regarded as the key that would facilitate the achievement of desired goals and objectives. Effective communication is regarded as the foundation for the creation of relationships. When the individuals will communicate with each other in a respectful and polite manner, they will be able to render a significant contribution to creating relationships.
Help in Making Selections between Alternatives
In some cases, the individuals have more than one alternative available and they need to make a selection of one. When the alternatives are selected, it needs to be ensured that they prove to be beneficial to the individuals. When individuals need help in making selections between alternatives, they usually are required to obtain help from others.
Improving Connections
Through communication, individuals contribute to improving connections with others. Improving connections is vital not only with family members but also with other individuals, within educational institutions, employment settings, and the community.
Reducing Misunderstandings
In some cases, misunderstandings take place among individuals, and they are required to solve them. These are regarded as major impediments within the course of the formation of sociable relationships. Effective communication is regarded as one of the indispensable aspects that are used to cause a reduction in misunderstandings.
Solving Problems
Problems are regarded as an integral part of the lives of individuals, irrespective of their occupations, status, categories, and backgrounds. In some cases, they are minor, which one is able to solve on their own.
Evaluating
Evaluating is referred to the implementation of measures and strategies, which are necessary to assess the performance of the individuals. In educational institutions as well as within employment settings, the teachers, instructors, and supervisors put into operation the methods to evaluate the performance of the students and employees.
Making Decisions
The individuals, who are in leadership positions are vested with the authority to make decisions. When they need to make decisions, which prove to be meaningful and advantageous to organizations, on the whole, they need to seek ideas and suggestions from others as well.
Importance of Communication
The following points highlight the importance of communication:
- Basis of Decision-Making and Planning
- Smooth and Efficient Working
- Motivation to Work
- Job Satisfaction
- Commitment to Organisational Objectives
- Coordination
- Adaptability to External Environment
- Internal Functioning of an Enterprise
- Healthy Industrial Relations
- Helps in Performing Managerial Roles
- Facilitates Leadership
- Facilitates control
- Training and Development
- Substance to Organisational Existence

Basis of Decision-Making and Planning
Communication is essential for decision-making and planning. It enables the management to secure information without which it may be possible to take any decision. The quality of managerial decisions depends upon the quality of communication. Further, the decisions and plans of the management need to be communicated to the subordinates.
Without effective communication, it may not be possible to issue instructions and orders. Effective communication helps in the proper implementation of plans and policies of the management.
Smooth and Efficient Working
Communication makes possible the smooth and efficient working of an enterprise. It is only through communication that the management changes and regulates the actions of the subordinates in the desired direction.
Motivation to Work
Employees are motivated to work if their needs are satisfied. Communication helps managers know the needs of their employees so that they can adopt suitable motivators and inspire them to develop a positive attitude towards the work environment.
Job Satisfaction
The exchange of information develops trust, confidence, and faith amongst managers and subordinates. They understand their job positions better and, thus, perform better. People are committed to organizational objectives which promote job satisfaction.
Commitment to Organizational Objectives
Managers who follow an effective system of communication understand employees’ needs, adopt suitable motivators to satisfy them, appraise their performance, and provide them regular feedback. The employees also work with a commitment toward organizational objectives.
Coordination
Communication coordinates organizational resources (human and non-human), individual goals with organizational goals, and the internal environment with the external environment. Coordination is the key to organizational success and communication is an active contributor to coordination.
Adaptability to External Environment
In order to survive in the changing, dynamic environment, managers continuously interact with external parties like government, suppliers, customers, etc. This requires an effective communication system in the organization.
Internal Functioning of an Enterprise
Managers interact with parties internal to business enterprises. They constantly obtain and provide information to them. The more effective the communication system, the more accurate will be the information.
Healthy Industrial Relations
Satisfied workers contribute to healthy organizations. Communication brings managers and trade unions closer, develops mutual understanding, and promotes industrial peace and harmony. This increases industrial production.
Helps in Performing Managerial Roles
According to Henry Mintzberg, managers perform three major roles – interpersonal, informational, and decisional. Communication helps managers in performing these roles effectively.
In interpersonal roles, managers interact with superiors, peers, and subordinates; in informational roles, they receive and give information to people inside and outside the organization and in decisional roles, they take important decisions and communicate them to organizational members for their effective implementation.
Facilitates Leadership
Effective leaders interact with followers and guide and inspire them to perform their individual and organizational goals. Effective communication process facilitates leaders to carry out their leadership functions.
Facilitates control
Planning is effective if accompanied by an effective control system. Control is possible when managers assess subordinates’ performance, correct and prevent deviations and provide them regular feedback on performance. Control function largely depends upon the communication system of the organization.
How effectively managers control organizational activities depends upon how effective is the communication system.
Training and Development
Imparting training and development facilities to employees depends upon how well their superiors communicate with them. Trainers with good communication skills are better than those who have poor communication skills.
Substance to Organizational Existence
The substance of Organizational Obtaining information to make plans, making members aware of the authority-responsibility structure, position in the organizational hierarchy, and coordinating their activities.
Principles of Communication
The 7 Cs provide a checklist for making sure that your meetings, emails, conference calls, reports, and presentations are well constructed and clear – so your audience gets your message.
These are the principles of communication and according to the 7 Cs, communication needs to be
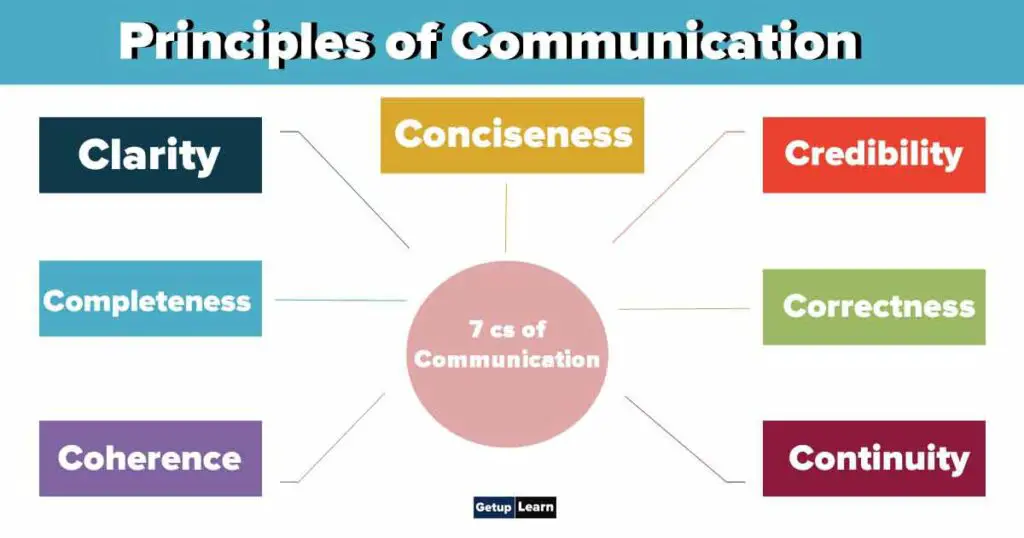
Clarity
The writing should be correctly planned and expressed in a logical way, and the writer should make sure that the ideas flow smoothly from beginning to end. The message must be so clear that even the dullest man in the world should readily understand it.
Completeness
Completeness is an essential factor for effective communication. A message must be organized appropriately in the sense that it must include all the important ideas and their details. The contents of the message must be checked in order to verify that there is no omission of the relevant details. An incomplete message can do little to convey the information and persuade the receiver.
Coherence
Coherency is equally essential for good written communication. Clear communication in simple sentences helps the reader to understand. Facts and figures must be stated plainly and in an intelligent manner. Relation and clarity are the two important aspects of coherence. Coherence means, tying together several ideas, under one main topic in any paragraph.
Conciseness
Conciseness is an important factor in effective communication. It means saying all that needs to be said and no more. The aimless verbiage, unnecessary details, and heavy paragraphs make our communication ridiculous and ineffective. We must omit those words and sentences from our message, which are not likely to bring about results.
Credibility
Good writing is always forceful and direct and has the power and capacity to produce a reaction or desired effect. The clarity in writing brings about credibility because it ensures that others understand the message easily and quickly.
Correctness
Without correctness, readers may refuse your write-up. Communication must be correct in tone and style of expression, spelling, grammar, format, contents, statistical information; stress-unstressed, etc. there should not be any inaccurate statements in the message.
Continuity
As far as possible the writer should avoid jargon. Jargon is a language that is special to science, commerce, technology, trade, and profession. In writing, the jargon should not be incorporated as this could make the writing confusing and unclear. Brevity or the use of fewer words brings about continuity and grace in your writing
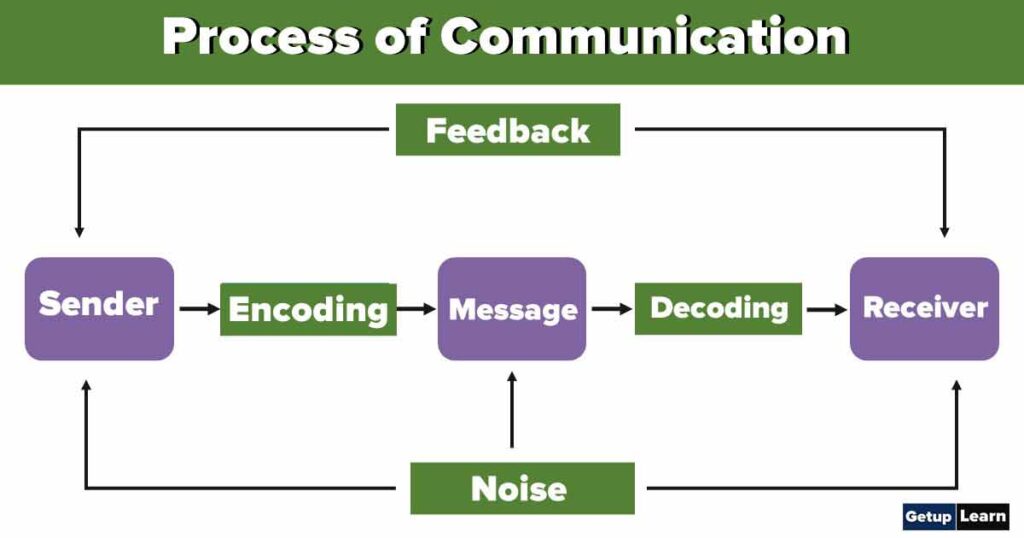
Process of Communication
Communication consists of the following eight components which are interrelated to the process of communication
Idea
Every message, whether oral or written, has its origin in an idea that germinates in the mind of the sender of the message. Every idea refers to some context. Thus the idea or information that the sender wants to convey to the receiver is the source of the message in the communication process.
Sender or Encoder
The person who initiates the communication process is referred to as the encoder. The process of communication begins with the sender who identifies the need to communicate. The sender must have a clear picture in his mind about what he wants to communicate and should accordingly select symbols, words, images, etc.
The sender must identify his audience and formulate the message in such a way that the receiver understands fully what he intends to convey and interprets it within the same context.
Encoding
Encoding takes place when the sender formulates his idea into a message to be transmitted to the receiver, using a series of symbols- verbal/ or non-verbal, written or oral. The sender should encode the message keeping in mind the purpose of communication and should select words or symbols that help the receiver understand the communication correctly and achieve the expected feedback.
Encoding is the process of creating a message for transmission by an addresser to an addressee. A way that an individual puts his thought together with the way he is going to communicate. Eg: using a speech by thinking of another language and the way he is going to put it in a sentence and also if he is going to use sign language.
The sender, as well as the receiver, should attach the same meaning to the symbols or words, otherwise, communication will fail. Thus proper encoding is essential for successful communication.
Message
A message is an idea transformed into words. It can be expressed in different ways depending upon the subject matter, purpose, audience personal style, and cultural background of the sender.
Channel and medium
An appropriate medium chosen to send the message is known as a channel. It is the vehicle that facilitates the sender to convey the message to the receiver. Channel is a system used to transmit a message, whereas medium is one of the forms/ types used under that system. For example, oral communication is a channel and telephone conversation is a medium. There are three broad channels of communication and there are several media under each.
Receiver or Decoder
The person who receives the encoded message is referred to as the receiver. The receiver may be an individual or a group of individuals. As communication is a two-way process, the receiver is as important as the sender of the message. A receiver may be a listener or a reader or a viewer of the message.
He not only receives the message but also tries to understand, interpret and perceive the total meaning of the message.
Decoding
Decoding is a process by which the receiver interprets the message and translates it into meaningful information. The meaning of the message is the sum total of the meanings of the words ( symbols) together with the tone and the attitude of the sender as reflected by his choice of words and the structure of the message.
Feedback
Feedback is the response given by the receiver of the message to the sender of the message. When the encoder receives feedback, he gets to know that communication has been accomplished. Feedback can be immediate, later, and can be positive or negative. It can be verbal or non-verbal.
In communication, feedback plays an important role. It ensures that the receiver has received the message and understood it just as it was intended by the sender. Feedback is the most important component of communication. Without feedback, the communication process is incomplete.
Types of Communication
These are types of Communication.
- Verbal Communication
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Visual Communication
- Feedback Communication
- Public Communication
- Mass Communication
- Group Communication
Verbal Communication
Verbal communication can be done with the use of language to transfer information with help of sign language or speaking. It is considered the most common type. It is used during presentations, video conferences, meetings, one-on-one conversations as well as a phone calls. Verbal communication is important because it is an efficient way of communication.
It can be helpful to support both non-verbal and written communication. Steps include in verbal communication are the use of a strong, confident speaking voice, using the active listing, and avoiding filler words.
There are four types of communication: 1. Intrapersonal Communication, 2. Interpersonal Communication, 3. Oral Communication, 4. Public Communication
Non-Verbal Communication
Non-Verbal communication includes the use of body language, facial expression, and gestures to convey information to others. It can be used both unintentionally and intentionally, you might smile unintentionally when you are pleasing or enjoying a piece of information or idea. Non-Verbal communication is useful for understanding the thoughts and feelings of others.
Written Communication
Written communication includes acts of writing, typing, and printing symbols like numbers and letters to convey information. It is helpful; because this communication provides a record of information for future reference. Writing is generally used to share information through pamphlets, books, letters, blocks, memos, etc. Emails and chats are common forms of written communication at the workplace.
Visual Communication
This is the act of using photographs, sketches, drawings, arts, graphs, and charts to convey information. Visuals are often used as an aid during presentations to provide helpful context along with written and/or verbal communication. Because people may have different learning styles, visual communication might be considered more helpful for some to consume information and idea.
Feedback Communication
When the individuals, who are in leadership positions in educational institutions and in various forms of organizations, such as instructors, supervisors, heads, directors, employers, and so forth, put into operation various types of assessment methods to evaluate the performance of the individuals. After evaluating the performance, they provide their feedback in terms of their performance.
Public Communication
Public communication occurs when a group becomes too large for all members to contribute. One characteristic of public communication is an unequal amount of speaking.
Mass Communication
Mass Communication is the process of delivering information, ideas, and attitudes to a sizeable and diversified audience. This is done through the use of media developed for that purpose namely newspapers, magazines, radio, television, websites, and social media networks.
Group Communication
Communication by many persons in a face-to-face situation is described as group communication. Here, as the group grows in size communication tends to become more and more of a monologue reducing participation.
Elements of Communication
Let us analyze Joseph A Devito’s definition that ‘communication refers to the act by one or more persons, of sending and receiving messages distorted by noise, within a context, with some effect and with some opportunity for feedback’ to find out the essential elements of communication.
According to his definition, communication has the following elements
-
Sender or Decoder: A person who sends a message or a signal is the source of communication. Communication by definition demands that someone send signals and someone receive them.
-
Message: Message is anything that is sent and received. Generally, we think of communication messages as being verbal (oral or written). We can also communicate nonverbally.
- channel: It is the route or vehicle along which the message is transmitted from a sender to a receiver. When you talk to a friend, the sound waves that carry your words constitute the channel. When you write something, the piece of paper becomes the channel. Newspapers, magazines, radio, television, and the internet become the channels of mass communication.
- Receiver or Decoder A person who receives the message or signal is the receiver in a communication process.
- Noise: Noise in communication refers to anything that distorts or interferes with the message. The screeching of a passing car, sunglasses a person wears, prejudices, bias, poor grammar etc. interfere with the effective and efficient transmission of messages from the sender to the receiver.
- Feedback: The information that is fed back to the source is known as feedback. Feedback, in general, refers to any process by which the communicator obtains information as to whether and how his/her intended receiver has received the message.
- Context: Communication always takes place within a context. It can either restrict or stimulate the communication process. Communication in a funeral home, a public park, a cricket stadium, and a church will be entirely different.
- Effect: The consequences of communication are referred to as effects. Communication has always some effect on one or more persons. The effect could be on the source or on the receiver or on both of them.
Read Detailed Article Here:
[su_spoiler title=”Elements of Communication ( Elements Universals of Communication)” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
What is Communication?
Communication is the process of exchange of information, ideas feeling, and understanding among human beings. It is a systematic process of conveying, listening, and understanding something between two or more people through words, figures, symbols, pictures, body language, etc.
What are the 3 definitions of communication?
1st: Communication is any behavior that results in an exchange of meaning. 2nd: Communication is an interchange of thoughts, opinions, or information through speech, writing, or signs. 3rd: Communication is the transfer of information from one person to another person. It is a way of reaching others by transmitting ideas, facts, thoughts, feelings, and values.
What is the 5 importance of communication?
Increase employees’ job performance and effectiveness by updating their knowledge. ii) Promote employees’ sense of belonging and commitment. iii) Effect changes smoothly iv) Motivate and create a sense of identification with the organization and its goals. v) Inform and convince employees about decisions and the reasons behind those decisions. vi) Develop employees’ clear understanding of future growth opportunities in the organization, and vii) Empower employees with information on development and relevant activities.
Read More Related Articles
[su_spoiler title=”What is Communication? | Mass Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
What is Communication?
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Types of Communication | Principles of Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
-
Types of Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Visual Communication
- Feedback Communication
- Mass Communication
- Group Communication
Principles of Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Nonverbal Communication | Verbal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Written Communication | Oral Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
Written Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Business Communication | Organizational Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Formal Communication | Informal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Interpersonal Communication | Informal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Downward Communication | Upward Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Barriers to Communication | Horizontal or Lateral Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Self Development | Effective Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Difference Between Oral and Written Communication | Theories of Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]