Table of Contents
- 1 What is Business Communication?
- 2 Definition of Business Communication
- 3 Types of Communication in Business
- 4 Importance of Communication in Business
- 5 7 Cs of Communication in Business
- 6 4 P’s of Business Communication
- 7 Purpose of Business Communications
- 8 Barriers to Business Communications
- 9 FAQ Related to Business Communications
What is Business Communication?
Business communication defines as the flow of information, perception and idea, etc. either within a business organization or outside the organization among different parties.
It is also a means of relying on a supply chain, for example, the consumer and manufacturer. At its most basic level, the purpose of communication in the workplace is to provide employees with the information they need to do their jobs.
To put it simply, Business includes those organizations, which are engaged in the production and distribution of goods and services to earn profit. Therefore Business communication means, the “Flow of information, perception, etc. either within a business organization or outside the organization among different parties”.
Definition of Business Communication
Following are the definitions of business communication:
[su_quote cite=””]Business communication defines as the flow of information, perception, and idea, etc. either within a business organization or outside the organization among different parties.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=” William G. Scott”]Business Communication as “Administrative communication is a process which involves the transmission and accurate replication of ideas ensured by feedback for the purpose of eliciting actions which will accomplish organizational goals.”[/su_quote]
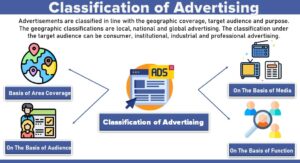
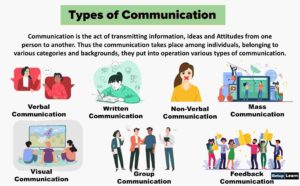
Types of Communication in Business
These are the following types of communication in business on basis of:
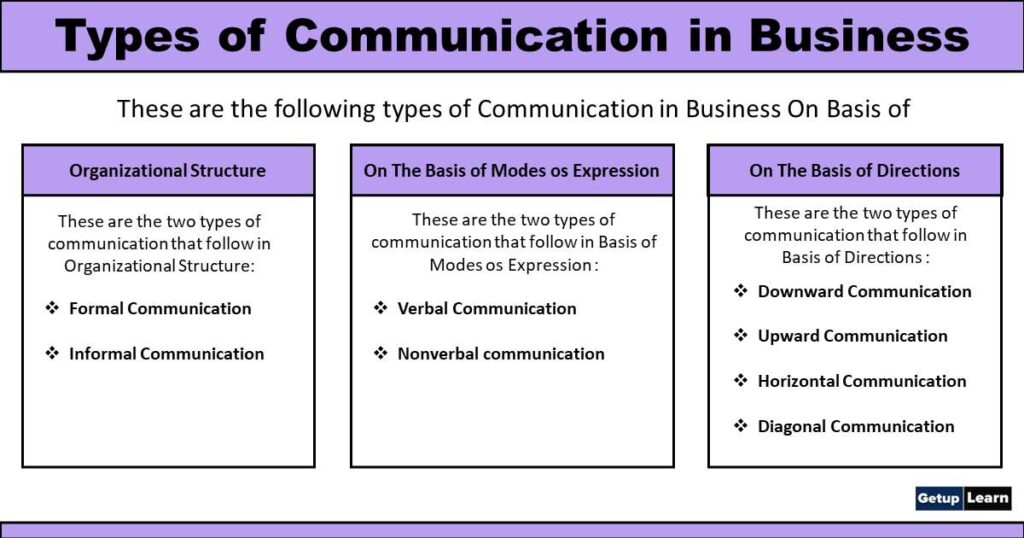
Organisational Structure
These are the two types of communication that follow in Organisational Structure:
Formal Communication
Formal communication of communication in an organisation is based on the organisational philosophy, policies and structure. The formal channels can be upward, downward, horizontal and diagonal. This is the way a piece of communication moves in an organisation. But it is not all, since communication is not always one to one. It can be in a group, or its movement can be at various levels.
For example, a sales representative reporting to the District Manager and Sales Manager at the same time can be considered as upward communication but this description is not complete in itself.
Informal Communication
Informal communication is also called the grapevine. It is characterized by proximity between persons, perception of members as reliable or knowledgeable, friendship and trust between one another, getting to know each other outside the workplace, and seeing each other at times when an informal communication network is needed.
It is unsanctioned communication and usually releases stress while persons are at work. It is important because it gives an opportunity to build relationships among the employees.
On the Basis of Modes os Expression
Verbal Communication
Verbal communication consists of words. It is not only oral but also written. Generally, people consider oral communication synonymous with verbal communication. Well, it is because one of the meanings of “verbal” is “oral” in the dictionary. Verbal communication can be broadly categorized into speech and writing.
Verbal communication includes:
- Face-to-face conversation
- Talking over the phone
- In public
- And meetings
Nonverbal communication
Nonverbal communication basically unveils an individual’s behaviour. It reflects the personality and temperament of a person. Therefore, managers are expected to understand the meaning of nonverbal cues- singular and clusters. Nonverbal cues consist of kinesics, proxemics, paralanguage, sign language, time language, object language, action, silence, and demonstration.
On the Basis of Directions
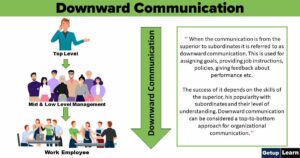
Downward Communication
Downward communication that flows from a higher level in an organization to a lower level is a downward communication. In other words, communication from superiors to subordinates in a chain of command is downward communication.
Downward communication is used by the managers for the following purpose:
- Providing feedback on employees’ performance.
- Giving job instructions.
- Providing a complete understanding of the employees’ job as well as to communicate them how their job is related to other jobs in the organization.
- Communicating the organizations mission and vision to the employees.
- Highlighting the areas of attention.
Upward Communication
Communication that flows to a higher level in an organization is called upward communication. It provides feedback on how well the organization is functioning. The subordinates use upward communication to convey their problems and performances to their superiors.
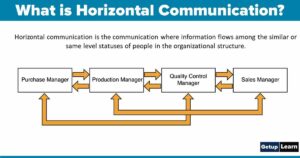
Horizontal Communication
Communication that takes place at the same levels of hierarchy in an organization is called horizontal communication,
For example
- Communication between peers
- Between managers at same levels
- Between any horizontally equivalent organizational member
Diagonal Communication
Communication that takes place between a manager and employees of other workgroups is called diagonal communication. It generally does not appear on the organizational chart. For instance – To design a training module a training manager interacts with Operations personnel to enquire about the way they perform their task.
The Accounts people of an organization visiting different employees in various departments for their IT calculation, bonus for workers etc. fall under diagonal communication.
Importance of Communication in Business
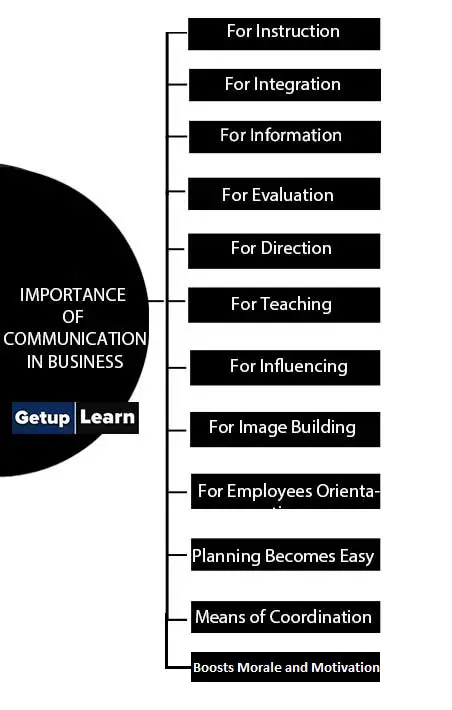
These are the following points of importance of communication in business:
- For Instruction
- For Integration
- For Information
- For Evaluation
- For Direction
- For Teaching
- For Influencing
- For Image Building
- For Employees Orientation
- Planning Becomes Easy
- Means of Coordination
- Boosts Morale and Motivation
For Instruction
The instructive function is unvarying and importantly deals with the commanding nature. It is more or less of a directive nature. Under this, the communicator transmits with necessary directives and guidance to the next level, so as to enable them to accomplish his particular tasks. In this, instructions basically flow from the top to the lower level.
For Integration
It is a consolidated function under which the integration of activities endeavours. The integration function of communication mainly involves bringing about inter-relationship among the various functions of the business organization. It helps in the unification of different management functions.
For Information
The purpose or function of communication in an organization is to inform the individual or group about the particular task or company policies and procedures. Top management informs policies to the lower level through the middle level. In turn, the lower level informs the top level of the reaction through the middle level. Information can flow vertically, horizontally and diagonally across the organization. Becoming informed or informing others is the main purpose of communication.
For Evaluation
Examination of activities to form an idea or judgement of the worth of the task is achieved through communication. Communication is a tool to appraise the individual or team, their contribution to the organization. Evaluating one’s own inputs or other outputs or some ideological scheme demands an adequate and effective communication process.
For Direction
Communication is necessary to issue directions by the top management or manager to the lower level. An employee can perform better when he is directed by his senior. Directing others may be communicated either orally or in writing. An order may be common order, request order or implied order.
For Teaching
The importance of personal safety on the job has been greatly recognized. A complete communication process is required to teach and educate workers about personal safety on the jobs. This communication helps the workers to avert accidents, risks etc. and avoid costs, procedures etc.
For Influencing
A complete communication process is necessary for influencing others or being influenced. The individual having the potential to influence others can easily persuade others. It implies the provision of feedback which tells the effect of communication.
For Image Building
A business enterprise cannot isolate from the rest of society. There is an interrelationship and interdependence between the society and an enterprise operating in the society. Goodwill and confidence are necessarily created among the public. It can be done by communication with the different media, which has to project the image of the firm in the society. Through an effective external communication system, an enterprise has to inform society about its goals, activities, progress and social responsibility.
For Employees Orientation
When a new employee enters the organization at that time he or she will be unknown to the organization programs, policies, culture etc. Communication helps to make people acquainted with the co-employees, superior and with the policies, objectives, rules and regulations of the organization.
Planning Becomes Easy
Communication facilitates planning. Planning is made easy by communication. Any type of information regarding the human resource requirement of each department of the organization with their qualifications, the type and kinds of job etc. can be collected through communication which helps in human resource planning.
Policies and programs for their acquisition can be prepared and implemented. In the entire process, communication plays a vital role, it also facilitates managerial planning of the organisation.
Means of Coordination
Communication is an important tool for coordinating the efforts of various people at work in the organisation.
Boosts Morale and Motivation
An effective communication system would be confidence among subordinates and workers ensuring change in their attitude and behaviour. The main cause of conflict and dissatisfaction is a misunderstanding which can be removed through communication skills.
The removal of misunderstanding makes the manager and his subordinates understand each other and create good industrial relations. This boosts up the morale of the people and motivates them to work harder.
7 Cs of Communication in Business
These are the following 7 Cs of communication in business:
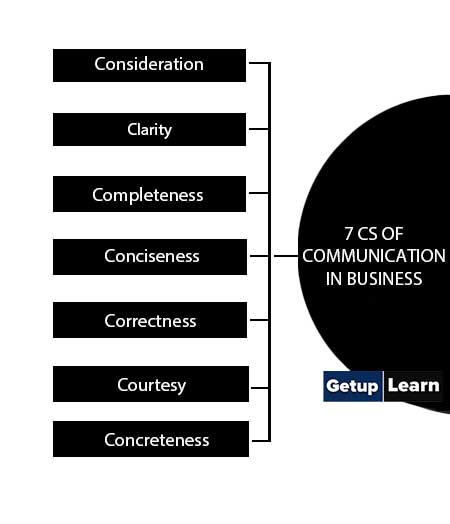
Consideration
consideration states that every message should be prepared to keep in mind the person who will be the receiver of the message
Clarity
Clarity is the most important characteristic of communication especially in the case of oral Communication/Presentation. The clarity in words, the language of expression is very important to ensure the proper presentation of ideas, message one wants to communicate during the conversation.
Completeness
A complete message is very important to communicate the main idea or information behind the message.
Conciseness
Conciseness is the essential requirement of oral communication. Concise message saves time on expense for both sender on receiver concise means brief, short on informative message which is able to explain the idea of the message with minimum words.
Correctness
In oral communication grammatical errors should be avoided. The right level of language should be used both in formal & informal communication.
Courtesy
A proper decorum of speaking should be maintained while making oral communication/ presentation. One should say things with the force of assertiveness without being rude. The polite or humble language shall be used which should not be insulting, against the religious, social as personal values of the listener.
Concreteness
it means specific, definite on valid use of information than vague or general. Concrete facts on figures should be used to make the receivers know exactly what is required or desired.
4 P’s of Business Communication
These are 4 p’s of business communication disscused below:
Public Versus Private
Think not only about what you want to communicate but how you are going to do it. For instance, I once overheard a man’s cellphone conversation while on a train. The person he was talking to apparently kept trying to discuss the qualifications of a candidate for a job. To his credit, the person on the train refused to discuss the issue: “I can’t talk about it right now, I’m on the train.”
Proof Read
Excusing your errors by putting a note at the end of a text saying “Please excuse typos; this was written on my phone” does not remove the impression that you are careless, it just reinforces it. Be particularly careful in today’s digital world because auto-correct can make you look foolish, and spell-check is no guarantee that everything is correct.
Pronunciation
Mispronouncing words can make you look like you don’t know what you are talking about. Mispronouncing a person’s name can be a fatal error, especially in a job interview or meeting a new client. Find out how to pronounce a person’s name ahead of time. Doing so will ensure your meeting will start off on a positive, professional note.
Patience
Take your time when communicating, especially when replying. If you’re feeling a little frustrated, wait five minutes before returning a call so the frustration you feel subsides and isn’t heard in your tone of voice. When using digital communications, try the “send later” or “draft” button. Wait a few minutes and then reread your message. Ask a colleague to read it to be sure of its tone.
Purpose of Business Communications
These are the following purpose of business communications:
- Information
- Counselling
- Influencing
- Motivation
- Healthy Organizational Environment
- Trade Unions: Labour Problems
Information
Passing or receiving information about a particular fact or circumstance is one of the most important purposes of communication. It can be done either through spoken or written language or by using any other system of signs or signals. Managers need complete, accurate and precise information to plan and organize; employees need it to translate planning into reality.
Information on the following aspects is very essential for the existence and welfare of any organization:
- Consumer response to its products in comparison with competing products with reference to quality as well as price.
- Whether they are being produced in conformity with the latest trends?
- What kind of effect, the rules and regulations of the government and the changing political scene can have on the product policy of the organization?
Counselling
Counselling is very similar to giving advice. Only, counsel is objective and impersonal. A counsellor is a man of greater skill or knowledge on some specific subject and he offers his counsel without any personal interest or involvement. Advice has a personal touch about it; counsel is almost professional. Advice is often unsought and is unwelcome; counsel is eagerly sought.
A number of large business houses now have their counselling departments, which offer the employees advice on domestic or personal problems.
Influencing
A complete communication process is necessary for influencing others or being influenced. The individual has the potential to influence others can easily persuade others. It implies the provision of feedback which tells the effect of communication.
Motivation
Motivation energises and activates a person and channelises his behaviour towards the attainment of desired goals. Motivation and behaviour are intimately related to each other. In order and persuasion, the communicator enjoys an upper hand. But in motivation, he keeps himself in the background.
Healthy Organizational Environment
Organizations are social systems formed on the basis of mutual interest. The mutual interests are safeguarded by various activities of planning by the management. They must skillfully apply the communication systems to keep a healthy organizational environment.
It must be remembered that the activities of the management and the employees in any business organization are governed by social as well as psychological laws. If the management has to keep the healthy organizational environment and healthy relations with the individuals from outside, other business houses, government authorities, etc.
Trade Unions: Labour Problems
The businessmen are mostly after productivity gains and other economic and technical benefits. Sometimes, this tendency of the businessmen comes in conflict with the problems, which are primarily human. The employees are now more conscious of their rights than before. They are organized into trade unions, which continuously demand rights of the employees, better working conditions and dignity of the labour. The progressive employers are convinced that there ought to be some ways of effective communication between the management and the workers to develop better employees satisfaction and a sense of security.
Barriers to Business Communications
The barriers in communication may be broadly classified into external, organisational factors.
- Noise
- External Barriers
- Semantic Barriers
- Badly expressed message
- Organisational Rules and Regulations
- Status Relationship
- Information Overload
- Poor Timing
Noise
For example, if an office is too noisy because it lacks soundproofing or a group is too large so they cannot hear what is being said in a presentation.
External Barriers
External barriers may affect communication in any context. Such external barriers may be in the following forms.
Semantic Barriers
Semantic barriers are caused in the process of receiving or understanding of the message during the process of encoding and decoding the ideas and words. These barriers arise from the linguistic capacity of the parties involved. The following are some of the semantic barriers.
Badly expressed message
Lack of clarity in a message makes it badly expressed. Poorly chosen and empty words and phrases, careless omission, bad organisation of ideas and failure to clarify implications are some faults found in this case.
Organisational Rules and Regulations
Organisational rules may restrict the flow of certain messages and may leave out many important ones. The communication through proper channels in a specified way prescribed by these rules delay it and works against the willingness of persons to convey the message.
Status Relationship
The placing of people in superior-subordinate capacity in the formal organisation structure blocks the flow of communication. When there is a great difference between various positions in terms of their status, greater would be the possibility of communication breakdown.
Information Overload
For example, during a meeting a manager might try to give his audience a long list of facts and figures in a short period of time; this would mean that most of his message would not be communicated successfully.
Poor Timing
For example, telephoning at lunchtimes and on Friday afternoons may make it difficult to get through because the person you need to contact is unavailable; or if you are talking to someone in an appraisal interview telling them how long-term planning in the firm might affect their role, they are unlikely to be listening if they know that the next topic concerns their annual pay rise!
What do you mean by business communications?
Business communication defines as the flow of information, perception and idea etc. either within a business organization or outside the organization among different parties.