Table of Contents
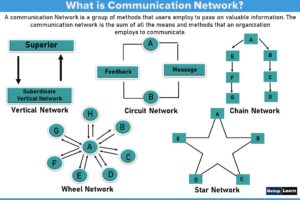
What is Theories of Communication?
Communication has existed since the beginning of human beings, but it was not until the 20th century that people began to study the process. As communication technologies developed, so did the serious study of communication. When World War I ended, the interest in studying communication intensified. The social science study was fully recognized as a legitimate discipline after World War II.

Before becoming simply communication studies, the discipline was formed from three other major studies: psychology, sociology and anthropology. Psychology is the study of human behaviour; Sociology is the study of society and social process and Anthropology is the study of communication as a factor that develops, maintain and change the culture.
Communication studies focus on communication as central to the human experience, which involves understanding how people behave in creating, exchanging, and interpreting messages. Communication theory has one universal law posited by S.F. Scudder (1980). Theories of Communication.
The Universal Communication Law states that “All living entities, beings and creature communicates”. All of the living communicates through movements, sounds, reactions, physical changes, gestures, languages, breath etc. Communication is means of survival. Examples – the cry of a child (communication that he is hungry, hurt, cold etc.), the cry of an animal (communicating that it is injured, hungry or angry etc.).
Every living communicates in its quest for survival. Communication theories can be best understood if we are able to know about the atmosphere, limitations and assumptions, under which a message is sent. In other words, a communication that establishes certain values under certain assumptions and limitations for the whole society at large can be termed as communication theories.
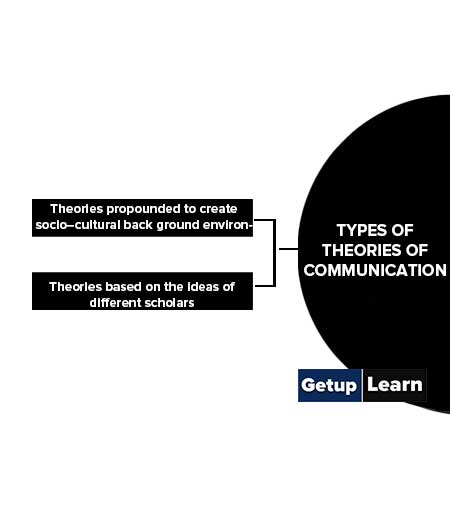
Types of Theories of Communication
Types of theories of communication are divided into two categories:
- Theories propounded to create socio–cultural back ground environments.
- Theories based on the ideas of different scholars.
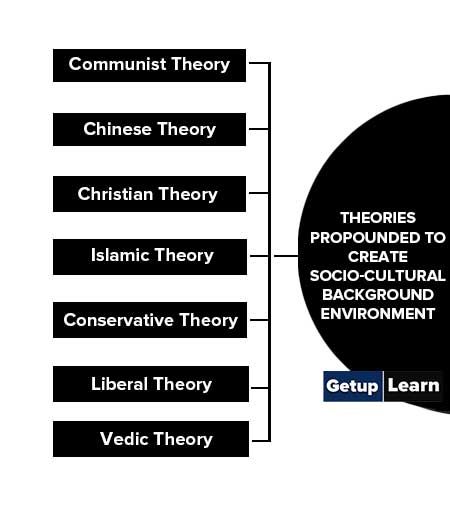
Theories Propounded to Create Socio-cultural Background Environment
This includes communications that aim at creating and saving ideal value for a universal community within certain limits. These theories areas:
- Communist Theory of Communication
- Chinese Theory of Communication
- Christian Theory of Communication
- Islamic Theory of Communication
- Conservative Theory of Communication
- Liberal Theory of Communication
- Vedic Theory of Communication
Communist Theory of Communication
This theory is based on the principles of communism. After the success of the revolutionary process in 1917, in the erstwhile USSR, this theory was put to use. This theory is based on the undermentioned principles of communism:
- The voice of labourers will be heard prominently, who were raising the voice against injustice and crimes against them.
- Voice will be raised against the exploitation of man by man.
- Role of public will be supreme in the construction of a strong nation.
- Interest of the nation will remain supreme.
The effect of this theory was widely felt. Lenin’s principles were followed not only in Soviet land but in China and other countries as well. This was a sufficiently strong theory. However, this theory could not achieve popularity because of the narrow and impractical ideas of communism. Division of the Soviet Union was one of the reasons due to which this theory could not become popular universally.
Chinese Theory of Communication
Communism prevails in China too, but its philosophy is quite different. Therefore, its communication policy is also different and is known as the Chinese Communication policy. In this policy, instead of revolution, peace is the main theme of the whole communication policy.
The ideas hidden in this theory are respect, dedication and faithfulness towards the nation. The communication policy of China is based on India’s principles of ‘Panchsheel’.
Christian Theory of Communication
In this communication theory, emphasis is placed on free-thinking, personal freedom and dedication toward almighty God. This theory is based on human sensitivity and service quality in a man. The theory serves as the foundation of a communication system in European countries.
The theory is popular among the masses because it does not believe in obstacles. Moreover, any new thing conducive to human welfare is communicated to the people. England ruled over many countries and so this theory travelled to those countries too, wherever England had its rule. India too had adopted this theory. But due to peculiar socio-cultural background in India, this theory could not flourish.
Islamic Theory of Communication
This theory is divided into two parts. As one being the pure theory of Islam, which has the deep insight into human rationale, scientific and love. And the other part is the interpretation of some religious leaders and preachers is rigid and narrow-minded. This theory is practised mostly in Muslim Countries.
Conservative Theory of Communication
The name “Conservative” is attached to this theory because one way of communication is resorted to on the pretext of religion and caste and restrictions are imposed on the Vedic Theory of Communicationpublic. People cannot breathe freely as was the case in Afghanistan quite recently under Laden sponsored government. The restriction is imposed on people’s movements, their education and their way of living. When this theory fails, Liberal Theory sets in better-informed countries like Nepal and Thailand.
Liberal Theory of Communication
This is considered to be the best theory. Under this theory, full freedom is given to communicate messages and ideas against government and society. There exists no check, control or regulation on messages being communicated.
Vedic Theory of Communication
This theory is in practice since the Vedic era and this is why it is known to be the oldest theory. This communication system is based on the Guru-Shisyha Disciple form of the education system. There was a verbal communication system in our country in early times. The theory considers Indian culture and traditions as the base of traditional values. These traditional values were crushed mercilessly under British rule in India.
Theories based on Ideas of Different Scholars
The ideas of different scholars on the communication process have been put forward in the form of communication theories, some of which are explained below:
- Aristotle’s Theory of Communication
- Lasswell’s Theory of Communication
- Shammon and Weaver’s Theory of Communication
- Schramm Theory of Communication
- Katz-Lazarsfeld Theory of Communication
- Berlo’s Theory of Communication
- Modern Theory of Communication

Aristotle’s Theory of Communication
This theory was propounded by Aristotle. According to Aristotle if persuasive techniques are used, the thinking process of the receiver can be changed. Under this theory, there are three components of communication-sender, message and receiver. But of these three, the sender is the most important. He can change the thinking of the receiver. In other words, communication is one-sided if persuasive techniques are employed by the sender.
Lasswell’s Theory of Communication
This theory was presented by Lasswell and is considered a one-sided theory. Alike, Aristotle, the sender is important in this theory too. Lasswell laid emphasis on the channel of communication. According to this theory, the sender will bring a change in the thinking process of the receiver by using appropriate channel of communication. Thus, according to Lasswell, channel of communication is more important as compared to sender of the message.
Shammon and Weaver’s Theory of Communication
According to Shammon and Weaver, after receiving the message it must be encoded and then transmitted so that receiver is in a position to understand the message, and can transmit his feedback well in time. The idea behind encoding the message was to avoid the effect of noise. Thus, the message is transmitted in full and pure form.
Schramm Theory of Communication
Schramm presented a wide and reformed form of the theory as was given by Shammon and Weaver. Schramm prescribed three models of his theory.
- Model 1: First model was more or less same as was presented by Shammon and Weaver. The difference with that theory was that message does not contain the element of noise and the message too is not wrong and is not distorted.
- Model 2: In this model Schramm suggested that sender should select a channel to transmit the message in a way that receiver understands the message. Thus, he laid emphasis
- Model 3: In this model, Schramm considered the reaction of receiver, as an important aspect. Thus according to him, the components of communication are:
- Sender
- Encoding process
- Decoding process
- Destination
- Response
Katz-Lazarsfeld Theory of Communication
The theory was mainly propounded for mass communication and therefore one can call it mass communication theory also. In this theory, after encoding the message, sender transmits the message by some appropriate channel to an opinion leader. This leader relays it to the public. The theory has three components-message, sender and the group leader.
Berlo’s Theory of Communication
This theory lays stress on perception. This theory says that the sender encodes the message (employing his skills and knowledge) and transmits the same using some suitable channel. How the receiver receives the message, it depends upon his knowledge and perception of the receiver.
Modern Theory of Communication
The communication process is being presented in the form of a circle in modern theory of communication. According to this communication cycle, message is dispatched to the receiver. The receiver expresses his response after receiving the message which is in a real sense is the feedback.
The different stages of this process are:
- Input: It means those ideas and information which the sender wants to dispatch.
- Message: The actual message which is transmitted.
- Channel: This means medium i.e. letter, report, telephone, fax, conference, e-mail etc.
- Output: That message which receiver gets.
- Feed back: Receiver’s response after receiving the messages which may be positive or negative.
- Communication loss: The message which was to be sent or already sent and received by the receiver may be wrong in some way or the other. This is called communication loss. The obstacles in communication process cause communication loss. These obstacles create problems in understanding the message.
What are the two theories of communication?
Communism prevails in China too, but its philosophy is quite different. Therefore, its communication policy is also different and is known as the Chinese Communication policy. In this policy, instead of revolution, peace is the main theme of the whole communication policy.
What are the four theories of communication?
Types of theories of communication are divided into two categories:
Theories propounded to create socio–cultural back ground environments.
Theories based on the ideas of different scholars.