Table of Contents
Barriers of Communication
No fixed classification of the barriers to communication is possible. However, for the purpose of easy understanding of their nature, we may classify barriers of communication into four categories:
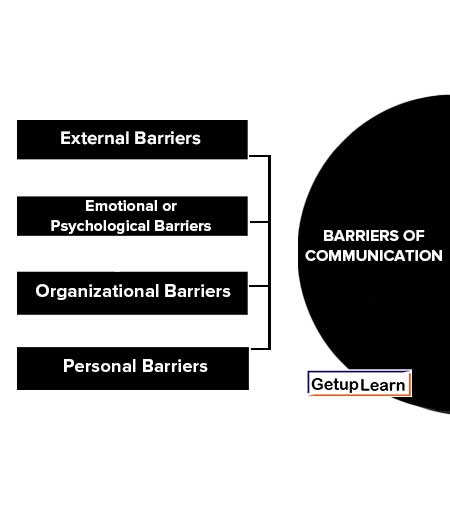
External Barriers
External barriers to communication are factors that exist outside of the communication parties. These include language, poor expression, faulty translations, and unclear assumptions. In organizations, language barriers are common due to differences in academic backgrounds and intellectual faculties among individuals.
Even simple language may result in semantic problems, as words can have different meanings to different people. Technical groups may use specialist language that is difficult for non-technical people to understand.
Poorly translated messages may result in the receiver misunderstanding the intended message, leading to impaired efficiency and high costs. Additionally, unclear assumptions can also act as a communication barrier. Communication is successful when the sender and receiver share a common language and understanding.
Emotional or Psychological Barriers
Emotional and psychological factors can impede interpersonal communication. In addition to the message itself, there is also a “meta-message” that is conveyed through the decoding of the message. Differences in mental wavelengths between communicators and receivers can affect how the meta-message is interpreted.
Psychological barriers in the minds of receivers can filter some communications while blocking others. Distrust of a communicator who modifies their original message can also create a barrier to communication. Preoccupation, inattention, poor retention, and loss of transmission can all contribute to psychological barriers to communication.
Written communications that only convey what needs to be done without explaining why it should be done can also create barriers to cooperation and confidence. Face-to-face communication should precede written communication to ensure employees respond spontaneously. Laziness or procrastination on the part of managers in transmitting messages can also act as a barrier between management and employees.
Organizational Barriers
An organization is nothing but an inter-relationship between functions and staff. It is designed for the achievement of certain stated objectives through well-defined policies, rules, regulations, and procedures. There are also norms of behavior as well as systems of rewards and punishments.
Accordingly, the types of organizational barriers include the following:
- Organizational Policy
- Organizational Rules and Regulations
- Organizational Facilities
- Status Difference
- Complexity in Organisation Structure
Organizational Policy
Unless the organizational policy is supportive of the smooth flow of communication in different directions, the policy itself will act as a barrier to the smooth and adequate flow of communication. The organizational policy regarding communication should act as a guideline to everyone in the organization as to what is expected of them.
Organizational Rules and Regulations
The organizational rules and regulations such as the requirement of routing communications through proper channels may act as barriers and restrict the flow of information. Rigid rules and regulations often make employees reluctant or unwilling to communicate. In most cases, this is a strong barrier.
Organizational Facilities
Unless adequate organizational facilities such as meetings, group discussions, conferences, suggestions, complaints boxes, etc., are provided to the employees by the organization, they will fail to communicate effectively.
Status Difference
The flow of communication will also be affected due to status differences among hierarchical positions in the organization. The superior-subordinate relationship in the formal organization structure often blocks the flow of communication. This is particularly true in the case of upward communication.
Complexity in Organisation Structure
Where there are a number of managerial levels in an organization, communications not only get distorted but also heavily filtered. People will tend to be non-committal in their communication in the upward direction.
Personal Barriers
Personal behavior and attitudes toward the communication between supervisors and subordinates can also act as barriers to communication. Negative views, opinions, and attitudes can harden over time and block communication.
Managers may have a narrow attitude towards communication, viewing it as a one-way process and failing to listen to employees or engage in face-to-face dialogue. They may lack communication skills, fear losing authority, lack confidence in subordinates, or lack awareness and time to talk to them.
These shortcomings can all hinder effective communication. Similarly, employees may be unwilling to communicate or lack proper incentives to do so. They may omit unfavorable information or avoid revealing their shortcomings.
To overcome or minimize these barriers, managers should provide incentives, encourage open communication, and create an atmosphere of trust and cooperation.
FAQs About
What are the barriers of communication?
The following are the barriers of communication:
1. External Barriers
2. Emotional or Psychological Barriers
3. Organizational Barriers
4. Personal Barriers.