Table of Contents
- 1 What is Oral Communication?
- 2 Definitions of Oral Communication
- 3 Importance of Oral Communication
- 4 Types of Oral Communication
- 5 Methods to Improve Oral Communication Skills
- 6 Advantages and Disadvantages of Oral Communication
- 7 Advantages of Oral Communication
- 8 Disadvantages of Oral Communication
- 9 Oral Mode is Used Where
-
10 FAQ Related to Oral Communication
- 10.1 What is oral communication in one word?
- 10.2 What is oral communication according to different authors?
- 10.3 What is the importance of an oral communication essay?
- 10.4 What are the methods of oral communication?
- 10.5 What is oral communication according to the authors?
- 10.6 What is the importance of oral communication?
- 10.7 What are the six types of oral communication?
- 10.8 What are the advantages of communication?
- 10.9 What are the disadvantages of communication?
What is Oral Communication?
Oral communication implies communication through the mouth. It includes individuals conversing with each other, be it direct conversation or telephonic conversation. Speeches, presentations, and discussions are all forms of oral communication.
Oral communication is generally recommended when the communication matter is of a temporary kind or where a direct interaction is required. Face-to-face communication (meetings, lectures, conferences, interviews, etc.) is significant so as to build rapport and trust.

Table of Contents
In other words, Oral communication is the process of expressing information or ideas by talking. It is predominantly referred to as speech communication.
Definitions of Oral Communication
These are the following definitions of oral communication:
[su_quote cite=” Ricky W. Griffin”]Oral communication takes place in face-to-face conversations, group discussions, telephone calls and other circumstances in which spoken word is used to express meaning.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=” Bovee”]Oral communication expresses ideas through the spoken word.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=” S. K. Kapur”]Oral communication takes place when spoken words are used to transfer information and understanding from one person to another.[/su_quote]
Importance of Oral Communication
The following are the importance of oral communication:
- Clear Pronunciation
- Brevity
- Precision
- Conviction
- Logical Sequence
- Appropriate Word Choice
- Use natural voice
- Communicate With Right Person
- Do Not Get Guided by Assumptions
- Look for Feedback
- Allow to Ask Questions
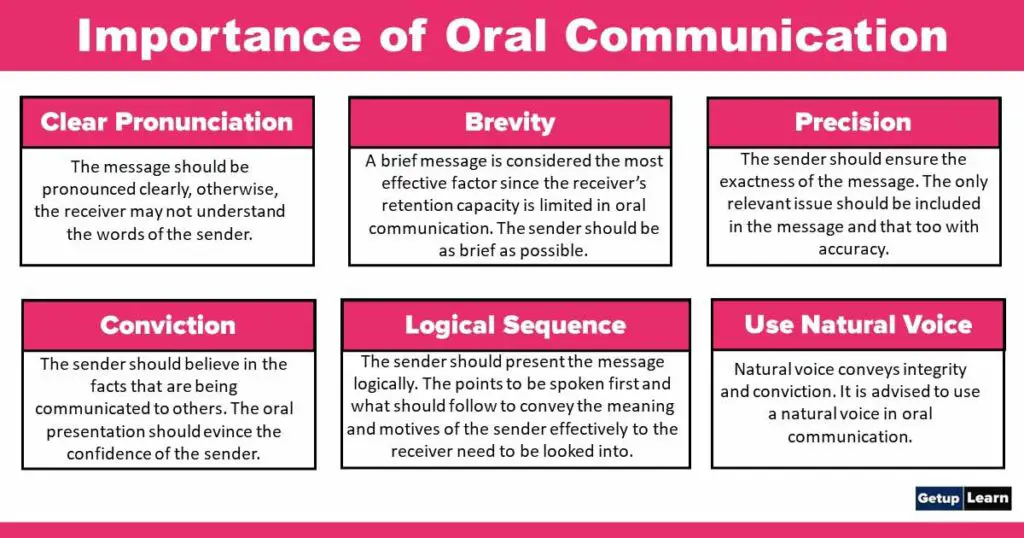
Clear Pronunciation
The message should be pronounced clearly, otherwise, the receiver may not understand the words of the sender.
Brevity
A brief message is considered the most effective factor since the receiver’s retention capacity is limited in oral communication. The sender should be as brief as possible.
Precision
The sender should ensure the exactness of the message. The only relevant issue should be included in the message and that too with accuracy.
Conviction
The sender should believe in the facts that are being communicated to others. The oral presentation should evince the confidence of the sender.
Logical Sequence
The sender should present the message logically. The points to be spoken first and what should follow to convey the meaning and motives of the sender effectively to the receiver need to be looked into.
Appropriate Word Choice
Words are symbols. They have no fixed or universal meanings. The meanings of words at that moment are in the mind of the sender. Therefore, the sender should select the words which are suitable and understandable to the other party and those which convey exactly the same meanings as the sender wanted.
Use natural voice
A natural voice conveys integrity and conviction. It is advised to use a natural voice in oral communication.
Communicate With Right Person
It is essential to know with whom to communicate. If you communicate the right message to the wrong person, it may lead to a lot of problems. Be sure in recognizing the right person to communicate with.
Do Not Get Guided by Assumptions
Never assume that your listener has knowledge already of the subject matter. You may be wrong many times in such assumptions. You can be good only when you are confident in your message without any omission.
Look for Feedback
When communicating, if you are smart enough in collecting feedback verbally or non-verbally, you can quickly alter the message, if necessary.
Allow to Ask Questions
It is important to give freedom to the receiver to rise questions whenever he feels ambiguity or confusion. In a way, the communicator should encourage the receiver to ask questions. Such questions are opportunities to clarify doubts.
Types of Oral Communication
These are the types of oral communication discussed below in detail:
Face-to-Face Conversation
Oral communication is best when it is face-to-face. A face-to-face setting is possible between two individuals or among a small group of people in an interview or in a small meeting; communication can flow both ways in these situations. There is always immediate feedback, which makes clarification possible.
Telephone
Telephone talk depends entirely on the voice. It does not have the advantage of physical presence. Clarity of speech and skillful use of voice is important. There can be confusion between similar sounding words like pale and bale or between light and like.
Names and addresses communicated on the telephone are sometimes wrongly received. It is therefore customary to clarify spellings by saying C for Cuttack, B for Bal sore, and so on.
Presentation
A presentation has a face-to-face setting. It is a formal and well-prepared talk on a specific topic, delivered to a knowledgeable and interested audience. Visual aids are used to enhance a presentation. The person who makes the presentation is expected to answer questions at the end.
It is the responsibility of the presenter to ensure that there is a clear understanding of all aspects of the topic among the audience.
Public Speech
A public speech or lecture, with or without microphones, has a face-to-face setting, but the distance between the speaker and audience is great; this distance increases as the audience gets larger, as in an open-air public meeting.
The purpose of a public speech may be to entertain, encourage and inspire. Much depends on the speaker’s skill in using gestures and using the microphone. Feedback is very little as the speaker can hardly see the facial expressions of people in the audience. A public speech is followed by applause rather than by questions from the audience.
Interview
An interview is a meeting in which a person or a panel of persons, who are the interviewers, ask questions from the interviewee. The purpose is, usually, to assess and judge whether it would be worthwhile to enter into a business relationship with the other.
Each side makes an assessment of the other. An interview is structured and is characterized by the question and answer type of communication.
Meeting
Usually, a meeting involves many persons; there is a chairman or a leader who leads and guides the communication and maintains proper order. There is a fixed agenda, i.e., a list of issues to be discussed at the meeting.
Meetings are of many types, from the small committee meeting consisting of three or four persons to the large conference or the shareholders’ meeting. This type of oral communication is backed up by note-taking and writing up minutes.
Methods to Improve Oral Communication Skills
These are some methods to improve oral communication skills:
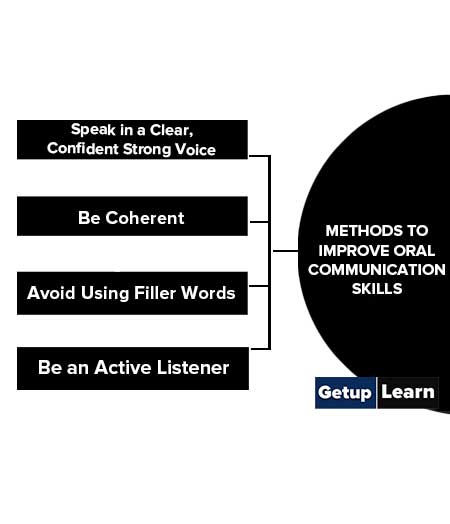
Speak in a Clear, Confident Strong Voice
one should speak in a confident, clear, and strong voice so that it is audible to everyone in the audience. Keep the pace of your speaking average, not very slow not very fast. While speaking, face the audience.
Be Coherent
One should speak coherently with a concentration on your subject only. Try not to be distracted from your subject, try to prevent other thoughts at that time.
Avoid Using Filler Words
It is better to pause for a second rather than using filler words, such as “Yeah”, “So”, “Um”, and “Like” frequent use of filler words disturbs coherence and distracts the audience.
Be an Active Listener
Verbal communication is a two-way process; you should, therefore, be an active listener too. Try to understand a question/query quickly, because it looks odd to ask to repeat the question.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Oral Communication
These are the following advantages and disadvantages of oral communication:
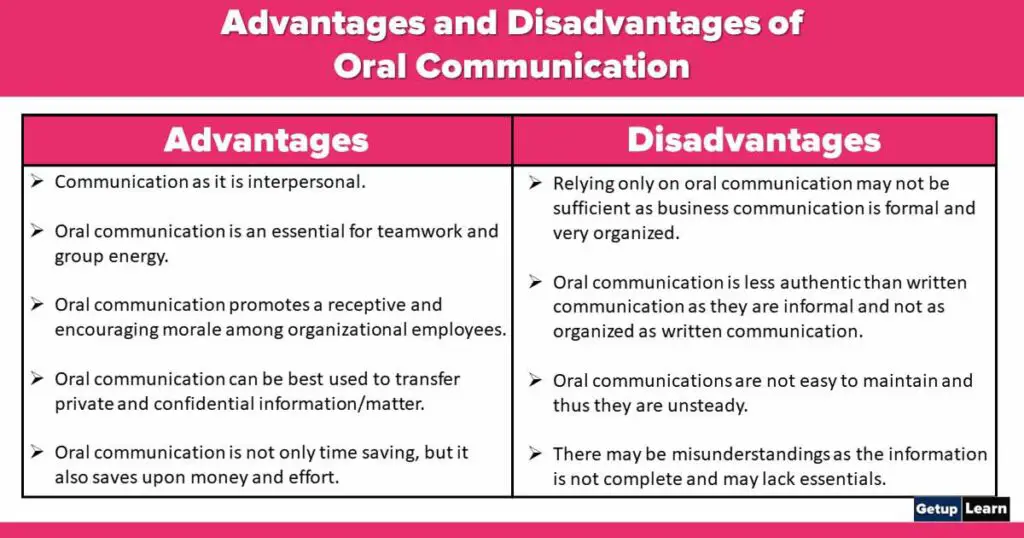
Advantages of Oral Communication
Following are the advantages of oral communication:
- Quickness in Exchange of Ideas
- Immediate Feedback
- Flexibility
- Economic Sources
- Personal Touch
- Effective Source
- Saves Time and Increases Efficiency
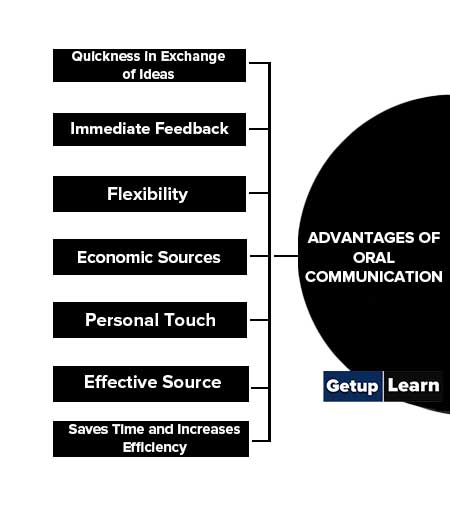
Quickness in Exchange of Ideas
Quickness in Exchange of Ideas: The ideas can be conveyed to distant places quickly because this medium does not require the message to be written.
Immediate Feedback
Immediate Feedback: Oral communication helps in understanding the extent to which the receiver has understood the message through his feelings during the course of the conversation.
Flexibility
Flexibility: Oral communication has an element of flexibility inherent in it. Flexibility means changing ideas according to the situation or changing ideas according to the interest of the receiver.
Economic Sources
Economic Sources: It is an economic source of communication because the message is communicated only orally.
Personal Touch
Personal Touch: Oral communication has a personal touch. Both sides can understand each other’s feelings, being face to face. The conversation takes place in a clean environment, which increases mutual confidence..
Effective Source
Effective Source: Oral Communication leaves much impression on the receiver. It is said that sometimes a thing can be communicated more effectively with the help of some sign. The use of signs or gesticulation can only be made in oral communication.
Saves Time and Increases Efficiency
Saves Time and Increases Efficiency: This communication consumes less time and the superiors can utilize the time saved for some other more important work. As a result of this the efficiency of the sender increases.
Disadvantages of Oral Communication
Let’s discuss some disadvantages of oral communication:
- Unfit for Lengthy Message
- Unfit for Policy Matters
- Lack of Written Proof
- Expensive Method
- Lack of Clarity
- Misuse of Time
- Presence of Both the Parties Necessary
Unfit for Lengthy Message
Unfit for Lengthy Message: Oral communication is profitable in having a brief exchange of ideas only. It is not possible for the receiver to remember a long message.
Unfit for Policy Matters
Unfit for Policy Matters: Where policies, rules, or other important messages are to be communicated, oral communication has no importance.
Lack of Written Proof
Lack of Written Proof: In the case of oral communication no written proof is left for future reference. Therefore, sometimes difficulty has to be faced.
Expensive Method
Expensive Method: When less important information is sent to distant places through telephone, etc. oral communication proves costly.
Lack of Clarity
Lack of Clarity: This is possible when there is little time for conversation. Sometimes wrong can be uttered in a hurry, which can lead to adverse results.
Misuse of Time
Misuse of Time: Oral communication is considered a misuse of time when during meetings the conversation is lengthened unnecessarily. Parties involved in the communication waste their time in useless talks.
Presence of Both the Parties Necessary
Presence of Both the Parties Necessary: In oral communication, it is essential for the sender and the receiver to be present face to face, it does not mean in the physical sense. But in written communication, one party is required.
Oral Mode is Used Where
These are the following points where we used oral mode:
- Personal authentication is needed. e.g., between an officer and her personal secretary; a journalist and her source (“I heard it from a reliable source”)
- Social or gregarious needs must be met. e.g.,’ speaking with a visiting delegation
- Warmth and personal qualities are called for. e.g., group or team interaction
- Exactitude and precision are not vitally important. e.g., brainstorming for ideas I
- Situations demand maximum understanding. e.g., sorting out problems or differences between individuals, or between two groups such as administration and students.
- An atmosphere of openness is desired. e.g., talks between management and. workers
- Added impact is needed to get the receiver’s focus. e.g., a chairperson of an organization addressing the staff; a presidential or royal address to a nation
- Decisions or information have to be communicated quickly. e.g., officers issuing officers during natural disasters such as floods or an earthquake
- Confidential matters are to be discussed. e.g., exchange of positive or negative information about an organization or an individual. In the process of appointments or promotion or selection of individuals, a period of open discussion may precede the final decision that is recorded in writing.
Read More Related Articles
[su_spoiler title=”What is Communication? | Mass Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
What is Communication?
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Types of Communication | Principles of Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
-
Types of Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Visual Communication
- Feedback Communication
- Mass Communication
- Group Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Nonverbal Communication | Verbal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Written Communication | Oral Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
Written Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Business Communication | Organizational Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Formal Communication | Informal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Interpersonal Communication | Informal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Downward Communication | Upward Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Barriers to Communication | Horizontal or Lateral Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Self Development | Effective Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Difference Between Oral and Written Communication | Theories of Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
What is oral communication in one word?
Oral communication expresses ideas through the spoken word.
Oral communication takes place when spoken words are used to transfer information and understanding from one person to another. BY S. K. Kapur
What is the importance of an oral communication essay?
The following are the importance of oral communication: Clear Pronunciation, Brevity, Precision, Conviction, Logical Sequence, Appropriate Word Choice, Use of natural voice, etc.
What are the methods of oral communication?
Following are some methods to improve oral communication skills: Speak in a Clear, Confident Strong Voice, Be Coherent, Avoid Using Filler Words, Be an Active Listener, etc.
Oral communication expresses ideas through the spoken word. By Bovee
What is the importance of oral communication?
Following are the importance of oral communication:
1. Clear Pronunciation
2. Brevity
3. Precision
4. Conviction
5. Logical Sequence
6. Appropriate Word Choice
7. Use a natural voice
8. Communicate With Right Person
9. Do Not Get Guided by Assumptions
10. Look for Feedback
11. Allow to Ask Questions.
What are the six types of oral communication?
These are the six types of oral communication:
1. Face-to-Face Conversation
2. Telephone
3. Presentation
4. Public Speech
5. Interview
6. Meeting.
What are the advantages of communication?
Advantages of Communication given below:
1. Quickness in Exchange of Ideas
2. Immediate Feedback
3. Flexibility
4. Economic Sources
5. Personal Touch
6. Effective Source
7. Saves Time and Increases Efficiency.
What are the disadvantages of communication?
Disadvantages of Communication:
1. Unfit for Lengthy Message
2. Unfit for Policy Matters
3. Lack of Written Proof
4. Expensive Method
5. Lack of Clarity
6. Misuse of Time
7. Presence of Both the Parties Necessary.