Download National Income Accounting Class 12 Notes PDF, Question papers, MCQ PDF, NCERT Books, and Syllabus free of cost in just minutes. We provide complete study material of national income accounting Class 12 Notes.
This study material includes national income accounting Class 12 Notes, previous year question paper class 12, Mcq Pdf, NCERT books, Latest syllabus by CBSE 2022-2023.

Table of Contents
You can download national income accounting Notes PDF Class 12 from the below article.
Table of Contents
- 1 Download National Income Accounting Class 12 Notes PDF
- 2 National Income Accounting Class 12 Notes Pdf
- 3 National Income Accounting Class 12 MCQ Questions PDF
- 4 National Income Accounting Class 12 MCQ Questions and Answers PDF
- 5 National Income Accounting Class 12 Questions and Answers PDF
- 6 National Income Accounting Class 12 Important Questions PDF
- 7 More About National Income Accounting Class 12 Notes
- 8 National Income Accounting
- 9 Concept of National Income
- 10 FAQ Related to National Income Accounting class 12 Notes
Download National Income Accounting Class 12 Notes PDF
This is a downloading table for download national income accounting class 12 notes pdf:
| National Income Accounting Class 12 | (HOW TO DOWNLOAD) |
| ????National Income Accounting Class 12 Notes PDF | ????Download |
| ????National Income Accounting Class 12 MCQ Questions PDF | ????Download |
| ????National Income Accounting Class 12 MCQ Questions and Answers PDF | ????Download |
| ????National Income Accounting Class 12 Questions and Answers PDF | ????Download |
| ????National Income Accounting Class 12 Important Questions PDF | ????Download |
National Income Accounting Class 12 Notes Pdf
CBSE Class 12 Macroeconomics chapter 2 national income accounting Notes PDF are made by research of last ten years NCERT question paper. Further, they are all designed with the latest CBSE guidelines 2022-2023, and only important topics are covered because of the high chances to appear in exams.
NCERT Class 12 Macroeconomics chapter 2 national income accounting Class 12 Notes is very useful for students because it is necessary to understand all important questions and answer them in an efficient manner.
[su_button url=”https://drive.google.com/file/d/1c3pCI8asawp6crR1h_YG5Q1fKHDO8j89/view” target=”blank” style=”flat” wide=”yes” center=”yes” radius=”10″ text_shadow=”0px 0px 0px #ffffff” download=”https://drive.google.com/file/d/1c3pCI8asawp6crR1h_YG5Q1fKHDO8j89/view” id=”download”]Download PDF[/su_button]

Download All: ????Macroeconomics Class 12 Notes PDF????
Download Class 12th Notes PDF
[su_spoiler title=”Macroeconomics Class 12 | Indian Economy Class 12” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
Macroeconomics Class 12
Indian Economy Class 12
- Indian Economy on the Eve of Independence
- Indian Economy 1950 to 1990
- Economic Reforms Since 1991
- Liberalisation Privatisation and Globalisation
- Poverty
- Human Capital Formation in India
- Rural Development
- Employment and Unemployment
- Infrastructure
- Environment and Sustainable Development
- Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
[/su_spoiler]
With these national income accounting notes pdf sample papers, students will have no problem making revision notes before exams and they don’t have to waste time making CBSE revision notes. You guys can download macroeconomics notes class 12 in just minutes. National Income Accounting Notes Pdf notes are well structured and prepared based on CBSE latest syllabus class 12 2022-2023.
These NCERT macroeconomics notes chapter 2 national income accounting Notes PDF for class 12 are well-defined and easy-to-understand concepts and include some practical questions for practice purposes.
We provided CBSE notes in pdf format for Students and they can use sample papers for preparing for the CBSE board exam 2022-202. CBSE Class 12 macroeconomics chapter 2 national income accounting Notes is very important for exam perspectives because it is a practical question chapter, not theory-based chapter. And for exam perspective this important chapter because it has higher marks weightage in macroeconomics.
With the help of CBSE revision notes students can revise for the exam. Class 12 macroeconomics Chapter 2 national income accounting Notes are the best finest notes because these are prepared by very experienced teachers. Class 12 macroeconomics chapter 2 national income accounting notes is made in very easy language which helps the students understand easily.
National Income Accounting Class 12 MCQ Questions PDF
Below that you can download the national income accounting class 12 MCQ questions pdf. We have covered all related MCQ’s national income accounting class 12 MCQ questions in this pdf. You can practice all of them by these national income accounting MCQ questions PDF.
National Income Accounting Class 12 MCQ Questions and Answers PDF
Here are some of the national income accounting class 12 mcq questions and answers pdf mentioned below. You can download national income accounting class 12 MCQ pdf form. These are the most relevant MCQ questions and have a higher chance of appearing on exam papers.
National Income Accounting Class 12 Questions and Answers PDF
Here we are providing national income accounting class 12 questions and answers pdf and in this notes we have covered all Important Questions and Answers from Chapter 2 national income accounting. National Income Accounting notes of Economics Class 12 Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in class 12 board exams.
National Income Accounting Class 12 Important Questions PDF
This is the national income accounting class 12 important questions pdf which we are providing for you. We have selected all those important questions from previous years’ question papers. If you learn the following national income accounting class 12 important questions you don’t have to open your textbook again and by these questions, you score high in exams.
More About National Income Accounting Class 12 Notes
CBSE is an educational board in India and is based on the NCERT syllabus for CBSE schools and other schools affiliated with the CBSE Board of India. Also, we are providing Study material for Class 12 macroeconomics for students so they can get rid of stress.
Getuplearn provides chapter-wise macroeconomics revision notes and short keynotes for the CBSE board exam. You can download national income accounting class 12 notes pdf Keynotes is easy to understand and also free downloadable PDF format so students can practice it for their exams and get good marks in their board examinations.
Getuplearn provides class 12 notes for subjects like Accounts, Economics, Hindi, Business Studies, English, and Physical Education. You can download free study material in pdf format for all streams science, commerce, arts, etc. Also, class 6 notes, class 7 notes, class 8 notes, class 9 notes, class 10 notes, class 11 notes, and class 12 notes.
National Income Accounting
What is National Income Accounting?
A variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region. National Income Accounting is a branch of macroeconomics that captures the total flows of income as well as of goods and services within a certain period.
In the economy, we receive different types of incomes. We receive wages and salaries from our employers. We receive interest on capital for lending money. We also receive gifts and donations from others without giving anything in return. All these incomes can be grouped into two types of incomes.
Factor Incomes
A Factor Incomes is an income accruing to a factor of production in return for the services rendered to the production unit. We know that production is the result of the joint efforts of the four factors of production. These four factors of production are Factor incomes, Labour, Land, Capital, Entrepreneurship.
Non Factor Incomes
There are certain money receipts that do not involve any sacrifice on the part of their recipients, the examples are gifts, donation charities, taxes, fines etc. No production activity is involved in getting these incomes. These incomes are called transfer incomes because such income merely represents a transfer of money without any good or service being provided in return for the receipts. These incomes are not included in national income.
National Income: Components, Importance, Methods, Limitation
Basic Economic Activities
Production consumption and investment are three basic economic activities that take place in every economy:
Production
Production is the addition of value to an existing commodity. During the production process, already existing commodities are made more useful by combined efforts of factors of production which increase their value. This increase in value is known as production. Suppose, a carpenter purchase wood worth 1000/- and makes furniture from it sells it for 2000/- In this production process he has added value of 1000/- ( 2000-1000).
Consumption Goods
Those final goods satisfy human want directly. E.g.: ice cream and milk used by the households. Using up of produced goods and services for the direct satisfaction of individual and collective wants of the people is called consumption. It includes all goods and services purchased by households like food items, clothes shoes etc. and by the government for collective consumption like roads, bridges, parks, schools etc.
Investment
Investment is that part of production which is left after consumption and used for creating physical assets like machines, equipment, material etc. It is that part of production which is used for further production. It increases the future production capacity of the economy.
Stock and Flow
The distinction between stock and flows is very significant for national income estimates:
Stock
A stock is a quantity that is measured at a point of time i.e. at 4 p.m. on 31st March etc. wealth, population, money supply etc. are stock concepts. It has no time dimension.
Flow
A flow is a quantity that is measured over a period of time i.e. days, months, years etc. It has a time dimension. National income, population growth is flow concepts.
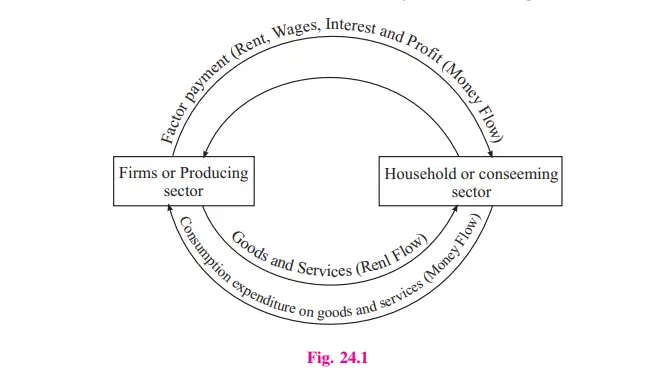
Circular Flow of Income
Production, consumption and investment are important economic activities of an economy. In carrying out these economic activities, people make transactions between different sectors of the economy. Because of these transactions, income and expenditure move in circular form. This is called the circular flow of income. It is based on two principles.
- The expenditure of the buyer because the income of the sellers.
- Good and services flow in one direction from sellers the buyers while money payment for these goods, and services flow in opposite direction i.e. from buyers to sellers
In this way, the flow of goods and services (real flow) and the flow of money payments (money flow) together make a circular flow.
Real flow
Households render factor services as owners of land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship to firms. The firms produce goods, and services to meet the demand of the households. Such flow of factor services from households to firms and flow of goods and services from firms to households is known as real flow.
Money Flow
In modern economies, goods and services and factor services are valued in terms of money. Households receive rent for land, wages for labour, interest for capital and profit for entrepreneurship- from firms and make payment for goods and services supplied by firms.
This flow of money between firms and households is called money flow: Circular flow can be shown with the help of a diagram given below: Circular flow of income in a two-sector economy without savings.
Concept of National Income
To understand the meaning of national income it is essential to understand some basic concepts related to national income and its related aggregates. These concepts are:
Domestic Territory
In common language, the domestic territory of a country is understood to mean political territory of a nation. But, in economics, it refers to ‘economic territory’ which is a much wider concept than political territory. According to United Nations, “Economic territory is the geographical territory administered by a government within which persons, goods and capital circulate freely.”
Normal Resident
A normal resident is a person who ordinarily resides in a country and whose centre of economic interest also lies in that particular country. Normal residents include both nationals (such as Indians living in India) and foreigners (non-nationals living in India).
Intermediate Goods and Final Goods
To understand the concept of national income and its related aggregates it is necessary to understand the meaning and difference between intermediate goods and final goods:
Intermediate Goods
Intermediate goods are those goods that are meant either for reprocessing or for resale. Goods used in the production process during an accounting year are known as intermediate goods. These are non-durable goods and services used by the producers such as raw materials, oil, electricity, coal, fuel etc. and services of hired engineers and technicians etc.
Goods that are purchased for resale are also treated as intermediate goods. For example, Rice, Wheat, sugar etc. purchased by a retailer/wholesaler.
Final Goods
Goods that are used either for final consumption by the consumers or for investment by the producers are known as final goods. These goods do not pass through the production process and are not used for resale. For example, bread, butter, biscuits etc. used by the consumer.
Which is an example of national income accounting?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Net National Product (NNP), Gross National Product (GNP) It, personal income, and disposable income are the important metrics determined by national income accounting.
What are the four components of national income accounts?
The four components of national income account are Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Gross National Product (GNP), Net National Product (NNP), Net National Product at Factor Cost (NNPfc), Net Domestic Product At Market Prices (NDPMP), Income From Domestic Product Accruing To Private Sector, Private Income, Personal Income, Personal Disposable Income.
What are the 5 measures of national income?
Methods of Measuring National Income are Census of Product Method, Census of Income Method, Census of Expenditure Method, Value Added Method.
What is national income accounting definition?
A national income estimate measures the volume of commodities and services turned out during a given period counted without duplication. In other words, Is defined as the total market value of all the final goods and services produced in an economy in a given period of time.