Table of Contents
- 1 What is Mass Communication?
- 2 Definitions of Mass Communication
- 3 Functions of Mass Media
-
4 Characteristics of Mass Communication
- 4.1 Specific Objectives
- 4.2 Common Messages
- 4.3 Source of Message
- 4.4 Messages are Sophisticated and Complex
- 4.5 Limited Information
- 4.6 Mass Medium
- 4.7 Impersonality
- 4.8 Portability and Mobility
- 4.9 Universality
- 4.10 Permanency
- 4.11 A large Number of Audiences
- 4.12 Delayed Feedback
- 4.13 Use of Modern Technological Media
- 5 Types of Mass Communication
- 6 Importance of Mass Communication
- 7 Process of Mass Communication
-
8 FAQ Related to Mass Communication
- 8.1 What exactly is mass communication?
- 8.2 What is the best definition of mass communication?
- 8.3 What are the 8 functions of media?
- 8.4 What are the 3 types of mass communication?
- 8.5 What are the characteristics of mass communication?
- 8.6 What is the importance of mass communication?
- 8.7 What is the process of mass communication?
- 8.8 What is the meaning of mass communication?
What is Mass Communication?
Mass communication is the process of transmitting ideas, information, opinions, norms, attitudes, cultures, etc. to a relatively large, heterogeneous, and anonymous audience simultaneously through the use of technological devices.
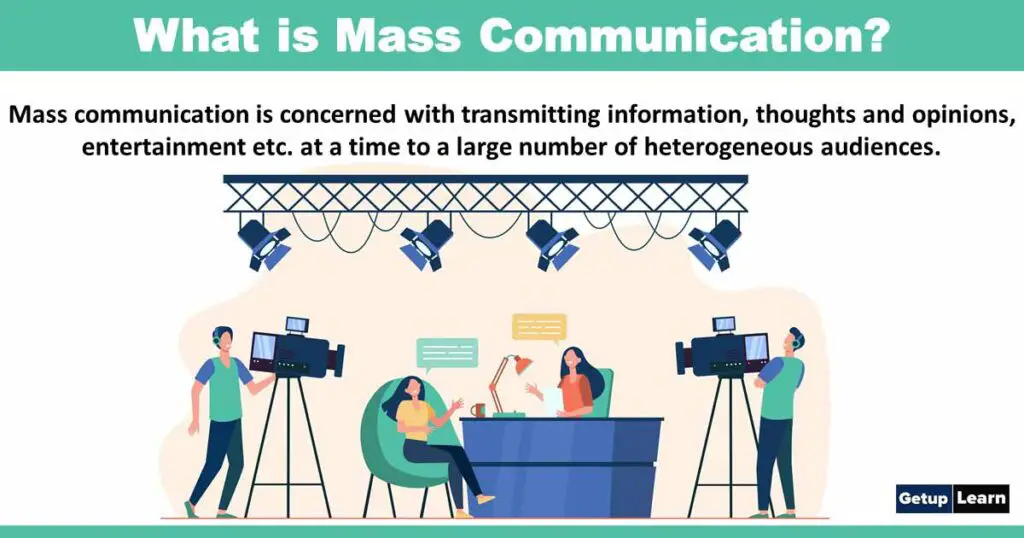
Table of Contents
To put it simply, Mass communication involves communication with the mass audience and hence the name communication. Group communication has now been extended by the tools of mass communication: books, the press, the cinema, television, radio, video, and the internet.
Mass communication is generally identified with these modern mass media, but it must be noted that these media are processes and must not be mistaken for the phenomenon of communication itself.
Definitions of Mass Communication
Here are a few definitions of mass communication:
[su_quote cite=”Metha”]Mass communication is concerned with transmitting information, thoughts, opinions, entertainment, etc. at a time to a large number of heterogeneous audiences.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Emery”]Mass communication is a process of sending a message, though, and attitude through some media at a time to a large number of heterogeneous audiences.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”R. P. Molo”]Mass communication is a process through which an individual, organization, or govt. communicates with the general people.[/su_quote]
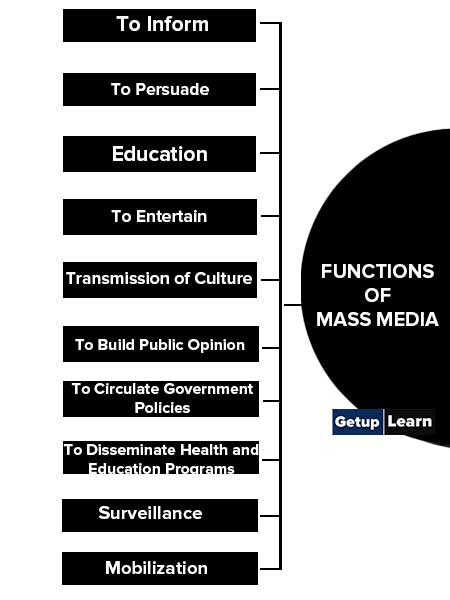
Functions of Mass Media
The following are functions of mass media explained briefly:
- To Inform
- To Persuade
- Education
- To Entertain
- Transmission of Culture
- To Build Public Opinion
- To Circulate Government Policies
- To Disseminate Health and Education Programs
- Surveillance
- Mobilization
To Inform
Dissemination of information is the primary function of the news media. Newspapers, radio, and TV provide us with news from around the world and keep us informed. In describing the events, news media have come to include human interest, analysis, and factorized treatment of the news.
Journalists are not just ‘reporters’ now. They have become news analysis analysts who discuss the implications of important news stories. Also, more ‘soft stories’ are filed these days. In addition to dissemination of information news media provided us with information and also helps us understand the news events, ideas, policy changes, etc.,
To Persuade
Most of the mass media are used as vehicles for promotion and persuasion. Goods, services, ideas, persons, places, and events the range of things that are advertised through mass media is endless. Different media have different features and reach. Advertisers and advertising agencies analyze these features and depending upon the nature of the message and the target audience, choose where and how the message should be placed.
Education
Mass media provides our education on different subjects and topics. It is taken as a good source of education for all levels of people. It provides education directly and indirectly in two ways. “Many distance education programs are direct and many programs provide education regarding health, environment, and moral norms indirectly.
For example, Japan’s NHK has very ambitious educational broadcasting. It provides programs for primary, secondary, and higher education to mentally and physically handicapped, foreign languages, vocational and technical instruction, advice on agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and special programs for children, adolescents, and women.
To Entertain
The most common function of mass communication is entertainment. Radio, television, and films are basically entertainment media. Even newspapers provide entertainment through comics, cartoons, features, crossword puzzles, etc., Entertainment through radio consists of mainly music and also drama, talk shows, comedy, etc.
Television has become primarily an entertainment medium. Even highly specialized channels like news, nature, and wildlife channels also have a lot of humorous and comic content. Among all media, films are perhaps the only medium concentrating on entertainment.
Transmission of Culture
Any communication leaves a direct or indirect impact on an individual. It becomes part of one’s experience, knowledge, and accumulated learning. Through individuals, communication becomes part of the collective experience of groups, audiences of all kinds, and finally the masses. Mass communication plays an important role in the transmission of culture from one generation to another.
To Build Public Opinion
Another important objective of mass communication is to create public opinion on any national or international issue. Mass media attempts to create public opinion by providing their audiences with a realistic picture of the world, activities of the leaders, governmental politics, etc. The mass media also tries to build public opinion through special articles, editorials, and commentaries.
To Circulate Government Policies
Another objective of mass communication is to announce and circulate government programs and policies. Mass media can bring such policies to the public notice very quickly.
To Disseminate Health and Education Programs
The government takes various health and educational programs like vaccination, sanitation, birth control, open education, mass education, etc. these health and education programs are disseminated and implemented through mass media like radio, television, films, newspapers, etc.
Surveillance
The first function of mass communication is to serve as the eyes and ears for those seeking information about the world. The internet, televisions, and newspapers are the main sources for finding out what‘s going around you. Society relies on mass communication for news and information about our daily lives, it reports the weather, current issues, the latest celebrity gossip, and even starts times for games.
Do you remember the Boston Marathon Bombing that happened in 2013? How did you hear about it? Thanks to the internet and smartphones instant access to information is at the user’s fingertips. News apps have made mass communication surveillance accessible by sending notifications to smartphones with the latest news.
Mobilization
Mass communication functions to mobilize people during times of crisis (McQuail, 1994). Think back to the Boston Marathon Bombing. Regardless of your association with the incident, Americans felt the attack as a nation and people followed the news until they found the perpetrators.
With instant access to media and information, we can collectively witness the same events taking place in real-time somewhere else, thus mobilizing a large population of people around a particular event. The online community Reddit.com is a key example of the internet‘s proactivity.
While the FBI was investigating the bombing, the Reddit community was posting witness photos and trying to help identify the culprits. People felt they were making a difference.
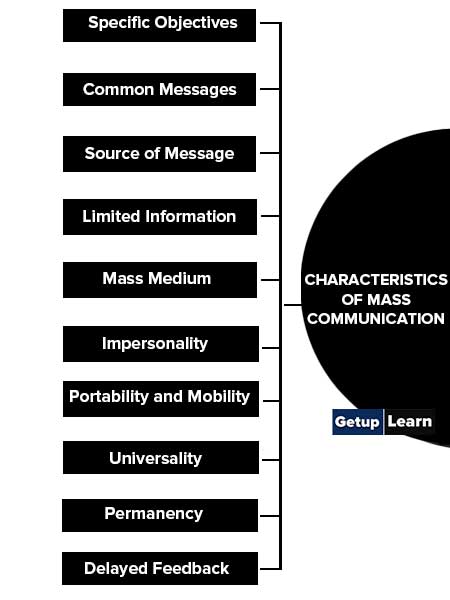
Characteristics of Mass Communication
The main features or characteristics of mass communication are as follows:
- Specific Objectives
- Common Messages
- Source of Message
- Messages are Sophisticated and Complex
- Limited Information
- Mass Medium
- Impersonality
- Portability and Mobility
- Universality
- Permanency
- A large Number of Audiences
- Delayed Feedback
- Use of Modern Technological Media
Specific Objectives
Every communication has a specific objective. Without objectives, no communication is held. Mass communication has also a specific objective that is dependent on the subject matter of communication.
Common Messages
Mass communication transmits or delivers the same simultaneous messages to vast diverse and scattered audiences.
Source of Message
The sources of mass communication messages generally are a person or group operating within an organizational setting. These sources include news reporters, television producers, magazine editors, etc.
Messages are Sophisticated and Complex
In mass communication, messages are sophisticated and complex. Whereas the message in interpersonal communication may be simple words and short sentences, mass media messages are quite elaborate. Examples of mass media messages are news reports, a novel, a movie, television programs, newspaper columns, magazine articles, music videos, and billboard advertisements.
Limited Information
Such audiences are brought together by a single shared interest in the particular message available through the mass medium. Message sources generally have only limited information about their audiences.
Mass Medium
Radio, Television, the Internet, etc are examples of media that are regarded as mass media because they can reach out to a vast audience at a time.
Impersonality
Messages of mass communication have remained impersonal since there is no personal touch of a medium. The impersonality of mass communication is informed by the need to reach large, diverse and scattered audiences almost at the same time.
Portability and Mobility
Portability has to do with the fact that messages of mass communication are handy and that the medium through which the messages are passing could be carried from one place to another at any geographical location.
Universality
This refers to the extensiveness or commonness of a medium and the acceptability of messages. A person does not need to be literate or educated in a particular language before listening to a radio program or a watch television program in that native language.
Permanency
This refers to the period for which a medium can hold its message thereby making the message reviewable. A reader of a book, newspapers, and magazines can read and re-read and store it for a long term.
A large Number of Audiences
In mass communication, information reaches a large and vast number of heterogeneous audiences. The audiences of mass communication exceed millions after millions.
Delayed Feedback
Feedback in mass media is slow and weak message flow typically is one-way, from source to receiver. Traditionally, feedback has been minimal and generally delayed. A newspaper reader could write a letter to the editor but it remains limited and delayed.
Use of Modern Technological Media
Channels of mass media use modern technology. Radio involves tape machines, microphones, and devices that digitize sound waves transmitters that disseminate them, and receiving units that decode the sound waves and render them back into audio form approximating the original.
Types of Mass Communication
These are the following types of mass communication:
Print Media
Johannes Gutenberg’s invention of the moveable metallic type in the fifteenth century paved the way for the proliferation of print media. The printing press using moveable types introduced the method for mass production of texts. Before the invention of the printing press, books were expensive materials affordable only to the aristocrats and royal families.
Printing reduced the cost of books and made them available to the common men also. Rapid duplication of multiple copies of handy texts led to the innovation of modern newspapers.
Print Media Include
- Newspapers
- Magazines
- books
- other textual documents
Electronic Media
The history of electronic mass media starts with the invention of the radio by Marconi. The first radio station was set up in Pittsburg, New York, and Chicago in the 1920s. Following the USA, European countries also started radio stations for broadcasting news and entertainment content.
The colonial powers like Briton and France set up radio stations in Asian and African countries in the early years of the 20th century. The next step in electronic communication media history was the invention of cinema. Following cinema, television broadcasting was initiated in the US on an experimental basis during the 1920s.
But, the dramatic impact of television as a mass medium began in the 1950s. Parallel to these, the recording industry also boomed in western countries. In short, the term electronic media mainly include:
- Radio
- Movies
- Television
- Audio and Video records
New Media
Online and digital means of producing, transmitting, and receiving messages are called new media. The term encompasses computer-mediated communication technology. It implies the use of desktop and portable computers as well as wireless and handheld devices.
Every company in the computer industry is involved with new media in some manner. The forms of communicating in the digital world include
- CD-ROMs
- DVDs
- Internet facilities like World Wide Web, bulleting boarding, email, etc.
Importance of Mass Communication
The importance of mass communication is as follows:
- Contact With Families and Friends
- Universality
- Permanency
- Launching a Business and Introducing New Products
- Wide Cover
- Advertising Product and Services
- Interdepartmental Coordination
- Inform Market Price, Demand and Supply
Contact With Families and Friends
With the help of mass communication, many people can communicate with their families or with their friends. Actually, people travel around the world and for this reason, they need a good way in order to not lose contact with their families in their native country.
The studies reveal that approximately 95% of the population use electronic devices for their communication for example Mobile phones, Telephones, Computers, etc.
Universality
This refers to the extensiveness or commonness of a medium and the acceptability of messages. A person does not need to be literate or educated in a particular language before listening to a radio program or a watch television program in that native language.
Permanency
This refers to the period for which a medium can hold its message thereby making the message reviewable. A reader of a book, newspapers, and magazines can read and re-read and store it for a long term.
Launching a Business and Introducing New Products
Mass communications are used to make the wide circulation of senses regarding forming and launching a business and introducing new products to the organization.
Wide Cover
The audiences of mass communication are spread over a vast or a wide geographic area in a given time. It can spread the product and business news of the organization over a large part of the country and the world.
Advertising Product and Services
Mass communication plays an important role in advertising products and services. Mass media like radio, television, newspaper, and the internet are the main vehicles of advertisement.
Interdepartmental Coordination
Generally, large organizations have various departments like procurement, production, marketing, administration, human resource; accounts, etc. Through the help of mass communication, managers of this department cooperate and coordinate with each other.
Inform Market Price, Demand and Supply
Mass communication helps to inform market price, demand, and supply of products and services for home and abroad.
Process of Mass Communication
These are the following points of how the process of mass communication follows:
Source
Source mostly represents the institution or organization where the idea has been started. In the case of the source and the sender being different, the sender belongs to a media institution or is a professional in media communication. Thus, a scientist or a technologist may use the mass communication media himself for propagating his idea. Or else, they can send the script of the message to the media for delivering a message by an announcer or a reporter.
Message
A message needs reproduction for making it communicable through the media. the message is processed and put into various forms like talk, discussion interviews, documentaries, plays, etc., in the case of radio and TV. In the case of newspapers, the message is processed by means of articles, feature news stories, etc.
Channel
The terms channel and media are used interchangeably in mass communication. Modern mass media like radio, television, and newspapers spread the message with an enormous speed far and wide. The ability of mass communication to encompass by Mc Luhan’s term.
Global Village
The term expresses that the world is smaller than before due to advances in mass communication. More information is coming faster, at cheaper rates per unit, from farther away and from more sources through more channels including multimedia channels with a more varied subject matter. Channels of mass communication can be classified into two broad categories:
-
Print Media: Newspapers, Magazines, Books, Pamphlets, etc.
- Electronic Media: Radio, Cinema, Television, Internet (New Media)
Receiver
Mass communication means communication to the mass, so there remains a mass of individuals at the receiver end of the communication. This mass of receivers is often called a mass audience.
The mass audience can be defined as ‘individuals united by a common focus of interest (to be informed, educated or entertained) engaging in identical behavior towards common ends (listening, viewing or reading)’. Mass communication has an enormous ability to multiply a message and make it available in many places.
Feedback
Mass communication will have indirect feedback. A source having communicated a message regarding family planning through radio, television or print either has to depend on indirect means like a survey of audience reaction, letters and telephone calls from audience members, review of the program by columnists to know the response of the audience to the message. Direct feedback which is possible in interpersonal and to a limited extent in group communication, is almost absent in mass communication.
Gate Keeping
This is again a characteristic unique to mass communication. The enormous scope of mass communication demands some control over the selection and editing of the messages that are constantly transmitted to the mass audience. Both individuals and organizations do gatekeep. Whether done by individuals or organizations, gatekeeping involves setting certain standards and limitations that serve as guidelines for both content development and delivery of a mass communication message.
Noise
It is in mass communication is of two types- channel noises and semantic noise.
Channel Noise is any disturbance within transmission aspects of media. In print media, it may be misspellings, scrambled words, or misprints. Any type of mechanical failure stops the message from reaching the audience in its original form.
Semantic Noise will include language barriers, differences in education level, socio-economic status, occupation, age, experience, and interests between the source and the audience members.
Read More Related Articles
[su_spoiler title=”What is Communication? | Mass Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
What is Communication?
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Types of Communication | Principles of Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
-
Types of Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Visual Communication
- Feedback Communication
- Mass Communication
- Group Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Nonverbal Communication | Verbal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Written Communication | Oral Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
Written Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Business Communication | Organizational Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Formal Communication | Informal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Interpersonal Communication | Informal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Downward Communication | Upward Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Barriers to Communication | Horizontal or Lateral Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Self Development | Effective Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Difference Between Oral and Written Communication | Theories of Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
What exactly is mass communication?
Mass communication is the process of transmitting ideas, information, opinions, norms, attitudes, cultures, etc. to a relatively large, heterogeneous, and anonymous audience simultaneously through the use of technological devices.
What is the best definition of mass communication?
Mass communication is concerned with transmitting information, thoughts, opinions, entertainment, etc. at a time to a large number of heterogeneous audiences.
What are the 8 functions of media?
The following are functions of mass media explained briefly:
1. To Inform
2. To Persuade
3. Education
4. To Entertain
5. Transmission of Culture
6. To Build Public Opinion
7. To Circulate Government Policies
8. To Disseminate Health and Education Programs
9. Surveillance
10. Mobilization etc.
What are the 3 types of mass communication?
These are the following types of mass communication: Print Media, Electronic Media, and New Media.
What are the characteristics of mass communication?
Following are the characteristics of mass communication:
1. Specific Objectives
2. Common Messages
3. Source of Message
4. Messages are Sophisticated and Complex
5. Limited Information
6. Mass Medium
7. Impersonality
8. Portability and Mobility
9. Universality
10. Permanency.
What is the importance of mass communication?
These are the importance of mass communication given below:
1. Contact With Families and Friends
2. Universality
3. Permanency
4. Launching a Business and Introducing New Products
5. Wide Cover
6. Advertising Product and Services
7. Interdepartmental Coordination
8. Inform Market Price, Demand, and Supply.
What is the process of mass communication?
Following are the steps of the process of mass communication:
1. Source
2. Message
3. Channel
4. Global Village
5. Receiver
6. Feedback
7. Gate Keeping
8. Noise.
What is the meaning of mass communication?
Mass communication is communicating with the masses. It is distinguished from other forms of communication as it caters to a large number of heterogeneous receivers separated from each other both physically and emotionally. Mass communication uses technological systems to produce the message and disseminate it to a multitude of receivers. Mass communication thus overcomes the barrier of time and space.