Table of Contents
What is Financial Environment?
The financial environment is an important part of an economy, where the major participants are the business firms, investors, and the market. An important ingredient of the financial environment is the financial market.

The financial environment in a country highlights the condition of the financial markets as well as the economy of the country. Understanding the monetary and fiscal policies helps us in understanding the financial system. The financial market in the country is divided into two broad categories
- Capital Markets
- Money Markets
What is Financial Market?
Financial markets can be defined as those markets where buyers and sellers trade or buy and sell various long terms and short terms securities such as equities, bonds, currencies, and derivatives. Financial markets have their own rules and regulations for transactions.
The Indian financial market comprises mainly of the following.
- Credit market
- Money market
- Capital market
- Foreign exchange market
- Debt market
- Derivatives market
All these are important in the financial environment of an economy. All these markets are not yet as developed and regulated as the credit/foreign exchange/money/capital market etc. Banks have been allowed to undertake insurance business. The bank assurance market is also emerging.
Types of Financial Markets
Financial markets can broadly be divided into two categories we have here discussed the types of financial markets:
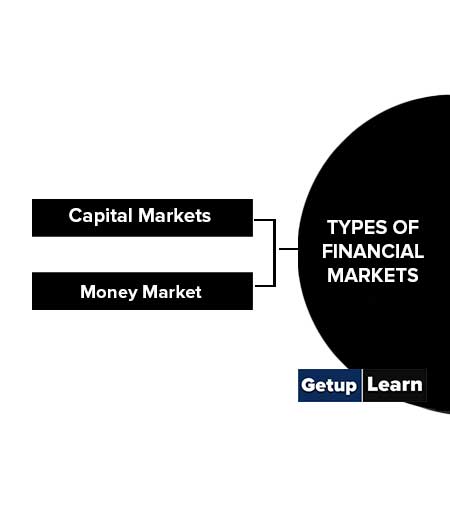
Capital Markets
The capital market is generally understood as the market for long-term funds. However, sometimes the term is used in a very broad sense to include the market for short-term funds also. Capital markets are one in which individuals and institutions, generally buy and sell long-term equities and securities.
Here individuals and institutions purchase and sell securities to raise funds. Capital market deals in ordinary securities such as shares and debentures, bonds, and government securities.
The funds which flow into the capital market come from individuals, merchant banks, commercial banks, and non-bank financial intermediaries, such as insurance companies, finance houses, unit trusts, investment trusts, venture capital firms, leasing finance, and mutual funds, building societies, etc. Capital markets are of two types:
Primary Market
Primary markets are ones in which new securities and issues are bought and sold. The types of issues in the primary market are listed below.
- Initial public offer (IPO) (in case of an unlisted company),
- Follow-on public offer (FPO),
- Rights offer such that securities are offered to existing shareholders,
- Preferential issue/ bonus issue
- The composite issue, that is, a mixture of rights and public offers, or offers for sale (offer of securities by existing shareholders to the public for subscription).
Secondary Market
A secondary market is one in which securities are bought and sold after being initially offered to the public in the primary market and/or listed on the stock exchange.
Money Market
The money market is the market for short-term funds as distinct from Capital Market which deals in long-term funds. In simple words, the money market is that segment of the financial market that deals in short-term financial instruments having high liquidity.
The participants of the money market purchase and sell financial securities of very short-term maturity and the period varies from a few days to not more than a year.
Money Market is a center for dealings, mainly of short-term monetary assets. It meets the short-term requirements of the borrowers and provides liquidity or cash to the lenders.
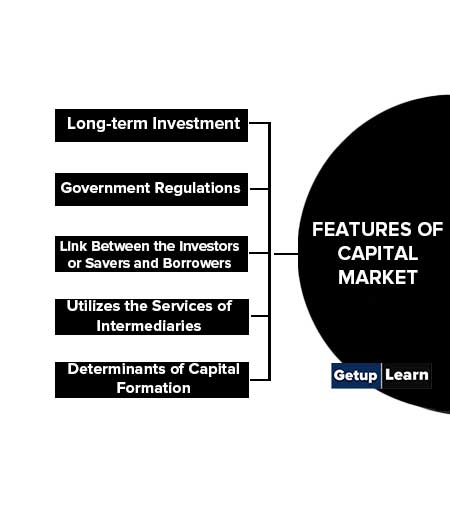
Features of Capital Market
Features of the capital market are given below:
- Long-term Investment
- Government Regulations
- The Link Between the Investors or Savers and Borrowers
- Utilizes the Services of Intermediaries
- Determinants of Capital Formation
Long-term Investment
Capital markets deal in securities that are of medium or long-term duration. This means that organizations, institutions, and individuals invest their funds in the capital market for the long term.
Government Regulations
Capital Markets in India have to work under the regulations formed by the Government of India. For example, the stock exchanges in India are regulated by the SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) which is a government body.
The Link Between the Investors or Savers and Borrowers
The capital market is an important connecting link between the investors and the borrowers. Those who are interested in earning some extra income from their savings can invest or utilize their money in purchasing shares, debentures, and other securities.
Utilizes the Services of Intermediaries
Intermediaries such as brokers, underwriters, depositories, etc. play an important role in the capital markets by providing the role of facilitators. In addition to the intermediaries, there are some promotional bodies like the training Institute of National Stock Exchange, Bombay Stock Exchange, Stock Holding Corporation, etc. They inform, help and guide the investors on where to invest, when to invest, how to invest, etc.
Determinants of Capital Formation
A capital market is a platform, which offers investors the opportunities to invest their surplus funds in the market. The activities of the capital market are an important indication of the rate of capital formation in the country. In developed countries, the capital markets are well developed.
The pace of economic development is conditioned, among other things, by the rate of long-term investment and capital formation.
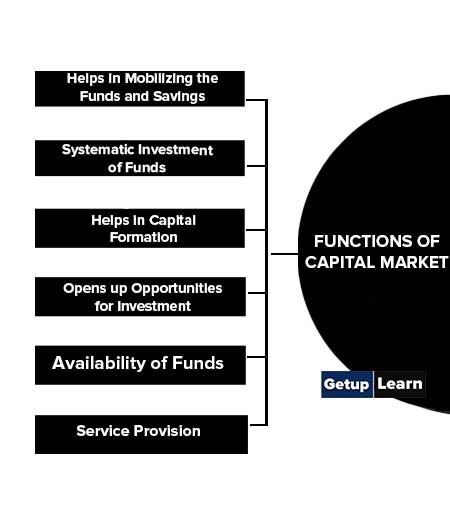
Functions of Capital Market
The functions of the capital market can be understood with the help of the following points:
- Helps in Mobilizing the Funds and Savings
- Systematic Investment of Funds
- Helps in Capital Formation
- Opens up Opportunities for Investment
- Availability of Funds
- Service Provision
Helps in Mobilizing the Funds and Savings
The capital market helps in mobilizing the surplus funds and savings of the people through channels of investment in a systematic manner. In the absence of this, the investors and the common people would not have got the opportunity to channel their funds to earn handsome returns and dividends.
Systematic Investment of Funds
The capital market provides opportunities for investors to utilize their funds in a systematic manner so that they can be properly utilized in various avenues available in the market. Investors can make investments in the shares of IT companies or steel companies. Each sector has different opportunities and challenges.
Helps in Capital Formation
An important function of the capital market is that it helps in capital formation in the country. The capital market helps in mobilizing the idle funds of the investors which are used in funding the various crucial sectors of the economy such as agriculture, industry, etc. For the investments to yield high returns, it requires sound project proposals and execution by enterprising firms.
Opens up Opportunities for Investment
The capital market opens up various investment opportunities to investors. Capital markets provide many investment opportunities such as mutual funds, insurance, shares, debentures, bonds, government securities, etc. Each of these instruments has different advantages and challenges. Some of them are risky. Some of them provide stable returns, but at a low rate. The investors have to look into various aspects and decide on the best possible mix.
Availability of Funds
The capital market helps in ensuring the continuous availability of funds to both the buyers and the sellers. An investor gets easy liquid funds whenever they require it and similarly a seller can also raise funds from the market whenever a need arises in the business.
Service Provision
As an important financial set-up, the capital market provides various types of services. It includes underwriting services, consultancy services, export finance, etc. These services help the enterprising firms to generate resources and the investors avail the facilities provided by the institutions in the capital market.
What are the types of financial markets?
These are the types of financial markets:
1. Capital Markets
2. Money Market.
What are the features of capital market?
Following are the features of capital market:
1. Long-term Investment
2. Government Regulations
3. The Link Between the Investors or Savers and Borrowers
4. Utilizes the Services of Intermediaries
5. Determinants of Capital Formation.
What are the functions of capital market?
Functions of Capital Market:
1. Helps in Mobilizing the Funds and Savings
2. Systematic Investment of Funds
3. Helps in Capital Formation
4. Opens up Opportunities for Investment
5. Availability of Funds
6. Service Provision.