Table of Contents
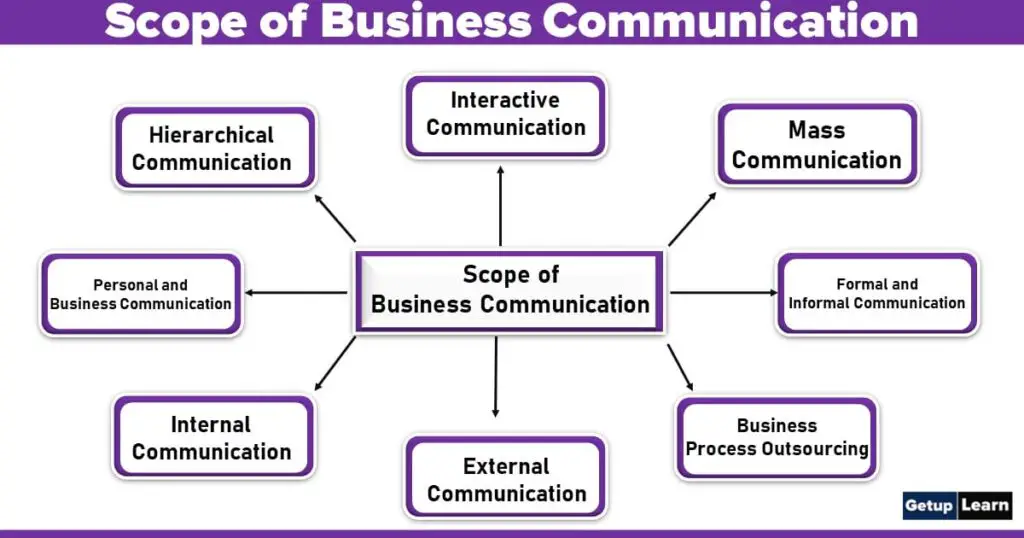
Scope of Business Communication
Apart from different forms and types of communication (non-verbal, verbal, written, audio-visual) one can also look at the scope of business communication. In modern business, the quantum nature of communication is changing. Business communication is utility oriented.
Today business is being influenced and influencing various segments, such as its clientele, society, and other interest groups. On the other hand, communication is also needed at the individual and intra-organizational levels. Some of the prominent areas describing the scope of business communication are as follows:
- Hierarchical Communication
- Personal and Business Communication
- Internal Communication
- External Communication
- Formal and Informal Communication
- Interactive Communication
- Mass Communication
- Business Process Outsourcing
Hierarchical Communication
Every organization has a built-in hierarchical system that can be compared to a pyramid. This normally flows from upper levels to downwards. However, the direction may not always be so. In practice, within a business entity communication is multidimensional and multidirectional. Following may be the directions:
Downstream
Traditionally hierarchical communication was downwards. Usually, in a conventional system, authority holders communicate to the people working under them. The communicators must ensure that their directions/instructions are being understood by subordinates. This requires a system of feedback. Downward communication strengthens the authority structure.
Upstream
In a participative organization, subordinates are given enough opportunity to interact with their supervisors in terms of information, grievances, suggestions, etc. Modern managers having a professional base are encouraging this communication resulting in the democratization of the work environment.
Lateral
This communication is needed to coordinate between people with similar statuses. Interaction amongst equals is very much essential for the smooth working of a system. Functional managers occupying similar positions in the organization, through their mutual intercourse present a good example of lateral communication. For the development of team spirit, peer group communication proves very useful.
Crosswise
When people at various levels interact beyond the boundaries of their reporting relationship is treated to be crosswise or diagonal communication. For example, when Assistant Manager Finance Division is making contact with Deputy Manager-Production Division is a case of this form of communication.
Personal and Business Communication
When communication takes place between any two individuals belonging to a family, group, community, or organization is personal communication. This is a one-to-one communication that is being entered into a personal capacity with an informality character.
This may be in the form of face-to-face meetings, on the telephone, personal letters, e-mails, conversations, and a meeting. However, business communication aims to accomplish business goals. This is found amongst business units, marketplaces, employers and employees, vendors and customers, service providers and beneficiaries, liaison officers, and various agencies supporting business.
Through this communication, businesses get support and favor from various stakeholders. By making intelligent use of this communication, business interests may be promoted and protected. On the other hand, in case of business communication is improper, the organization faces a survival crisis.
Internal Communication
This communication is taking place between the people working within an organization or members of a common group. It may be in a verbal, written, audio-visual, informal, or formal form. It may serve varied purposes such as educating, informing, directing, stimulating, provoking, inspiring, instructing, ordering, caution, and control. This communication is being used to share understanding and skills.
External Communication
Under this communication people belonging to a particular organization interact with people beyond the organization, such as suppliers, government agencies, competitors, commercial organizations, media, prospective buyers, and the community at large. This channel enables the organization to know the expectations of the outside groups and also to communicate to respond to organizational efforts.
External communication may take shape in various ways, like face-to-face meetings, written messages, brochures, audio-visual effects, telephone calls, the internet, visual presentations, press conferences, advertisements, road shows, etc. Through this communication, the organization makes liaisons with outside groups and creates a favorable public image.
Formal and Informal Communication
Formal communication is used by management to dictate who should talk to whom to get a job done. Upstream, downstream, and parallel communication may take place under formal communication.
The formal Communication network is deliberately established to control the flows of communication so as to avoid any confusion and make it more useful, well in time and systematic. Contrary to it, an informal network of communication is not deliberately formed.
This supplements formal communication and fulfills the need for added interaction. People always tend to make personal and social relationships. Informal communication assists them in developing intimate relationships.
The Grapevine channel is associated with this form. This communication permit employees to fill the gaps caused due to formal channels. This communication is free from the rigidly woven hierarchical layers and commonly entered through conversations, body language, informal chats, etc.
Interactive Communication
This communication provides enough opportunity for both the parties (communicator and communicatee) to discuss at length and in an in-depth fashion. It takes place through meetings and conferences, telephonic talk, teleconferencing, or small group presentations.
In the case of a large number of communicators, someone may be given the role of the moderator of facilitating a smooth flow of ideas and information.
Mass Communication
Mass communication is a broad-based communication addressed to a large number of individuals. Now a days this communication is developed as a distinct skill. Mass communication is meant for people at large placed at distinct places, vast in number and with varied temperaments.
For main stream media, the government too has a separate department. Under this communication public relations, journalism, television, radio, advertising, and publicity are the prominent streams. Newsletters, research studies, press releases, and promotional strategies are used to reach a large, varied, well-spread-out audience mix.
Business Process Outsourcing
This is a form of communication that makes beneficial use of advancements in technology. Under this computer and modern messaging systems are being used to provide value-added services to the customers. The time lag that exists between the user and provider country proves to be a beneficial factor in enlarging the scope of this service.
Developed countries, particularly European countries and the USA outsource varied services to countries like India and China. Without waste of time almost real-time services are given to the clients. Knowledge of English, French, and German with appropriate accents is a basic necessity for providing required services.
The manpower involved must have technical, soft, and teleselling skills with accent neutralization, telephone etiquette, culture orientation, and knowledge of customer relationship management.
Read More Related Articles
[su_spoiler title=”What is Communication? | Mass Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
What is Communication?
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Types of Communication | Principles of Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
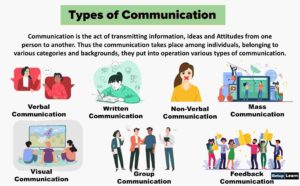
Types of Communication
-
Types of Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Visual Communication
- Feedback Communication
- Mass Communication
- Group Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Nonverbal Communication | Verbal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Written Communication | Oral Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
Written Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Business Communication | Organizational Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
Business Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Formal Communication | Informal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
Formal Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Interpersonal Communication | Informal Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Downward Communication | Upward Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
Downward Communication
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Barriers to Communication | Horizontal or Lateral Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Self Development | Effective Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
[su_spoiler title=”Difference Between Oral and Written Communication | Theories of Communication” style=”fancy” icon=”plus-circle”]
[/su_spoiler]
What is the scope of business communication?
Scope of Business Communication:
1. Hierarchical Communication
2. Personal and Business Communication
3. Internal Communication
4. External Communication
5. Formal and Informal Communication
6. Interactive Communication
7. Mass Communication
8. Business Process Outsourcing.