Table of Contents
What is Project Management?
Project management is the art of directing and coordinating human and material resources throughout the project by using modern management techniques. The main purpose of project management is to achieve the predetermined objectives of scope, cost, time, quality, and the satisfaction of the participant.
Project management includes developing and implementing a plan for the project while considering the available resources such as manpower, material, and cost in the organization. Project management involves the following activities:
- Planning and analyzing the objectives of the project.
- Measuring and controlling the risk involved in the project.
- Estimating the organizational resources required in the project.
- Assigning tasks to the employees related to the project.
- Directing and motivating employees to improve their performance.
-
Organizing project activities.
- Formulating the project.
- Forecasting trends in the project.
- Completing the project on time.
- Keeping up the quality of the project.
Project Management Approaches
There are generally two main approaches to carrying out a project: Traditional project management and agile project management or modern project management approaches.
The traditional project management approach is mostly followed in cases where there is little or no possibility of a change of the scope and where the project has a proper sequence of activities, for example, construction projects.
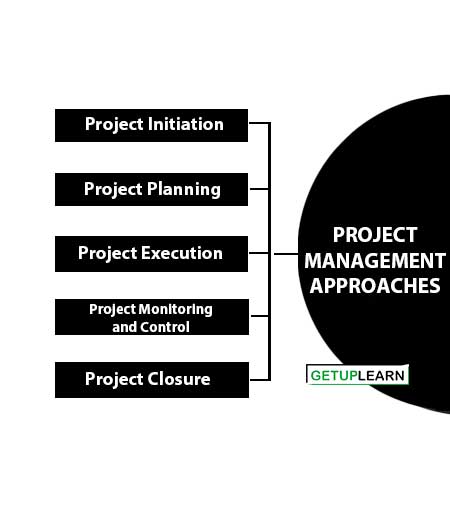
Projects having scope that can change are managed better using the agile approach, for example, IT projects. The five phases of the traditional approach to project management are explained as follows:
- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Execution
- Project Monitoring and Control
- Project Closure
Project Initiation
In this phase of traditional project management, the project is defined at a broad level and the feasibility of the project is established. If all the stakeholders of the project are satisfied with the feasibility of the project, the project is taken up. At this stage, a project charter is created.
Project Planning
In this phase, the project team chalks out a project management plan keeping in mind the cost that can be incurred, the required quality level, and available resources. This plan acts as a roadmap that must be followed by all project members.
In this phase, the first activity is to define the project goals. The plan contains details regarding various activities and when they should be completed. In addition, the project plan also defines the roles and responsibilities of each member of the project team. At this stage, documents like Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) and communication plan are developed.
Project Execution
In this phase, the actual work starts, and teams are developed. In addition, resources are assigned to the project team. This is the ‘Doing’ phase of the project.
Project Monitoring and Control
The project execution and the project monitoring and controlling phases run in parallel. However, the monitoring and controlling phase is listed after the project execution phase in the project management process because until an activity is started in the execution phase, it cannot be monitored or controlled.
In this phase, all the work that is done in the execution phase is monitored to assess whether the work is being done as planned. If any deviations from the planned activities are identified, appropriate control measures are taken.
Project Closure
This phase of the project is initiated once all the project activities have been finished and the required project goals have been achieved. The project manager announces whether the project goals have been or not been achieved and the project is closed.
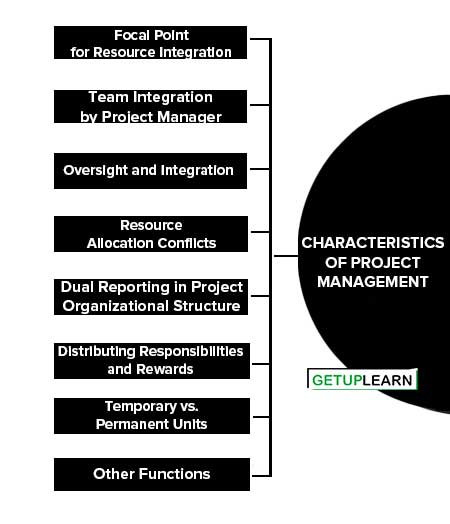
Characteristics of Project Management
Project management requires attention to goal-oriented systems, the environment, sub-systems, and their relationships. This is what makes project management a ‘systems approach’ to management.
The application of principles and practices from the classical and behavioral and systems viewpoints to the unique requirements of projects has led to a new set of concepts which may be called the ‘project viewpoint’. Cleland and Kind have identified the following characteristics of project management:
- Focal Point for Resource Integration
- Team Integration by Project Manager
- Oversight and Integration
- Resource Allocation Conflicts
- Dual Reporting in Project Organizational Structure
- Distributing Responsibilities and Rewards
- Temporary vs. Permanent Units
- Other Functions
Focal Point for Resource Integration
The project manager is the single focal point for bringing together all the necessary resources for achieving the project objectives. He/she formally heads the project organization and operates independently from the normal chain of command. The project organization reflects the cross-functional, goal-oriented nature of the project.
Team Integration by Project Manager
Since each project requires a variety of skills and resources, many functional areas may perform the work in a combined form. The project manager is responsible for integrating people from different functional disciplines working on the project.
Oversight and Integration
The project manager will negotiate directly with the functional managers for support. The functional managers are responsible for the activities of the individuals and for the personnel coming under the scope of their functional groups.
However, the project manager has to concentrate on integrating all the project activities and overseeing the activities from beginning to end.
Resource Allocation Conflicts
Resource Allocation Conflicts: Project vs. Functional Managers: The project manager focuses on delivering a particular product or service at a certain point in time and cost to the satisfaction of the technical requirements.
In contrast, the functional units must maintain an ongoing pool of resources to reach the ultimate organizational goals instead of the limited project goals. Thus, conflicts may often arise between the project and functional managers over the optimum allocation of resources to a project.
Dual Reporting in Project Organizational Structure
A project in an organizational structure has two chains of command. One is the vertical, functional reporting relationship and the other is the horizontal, project reporting mechanism.
Distributing Responsibilities and Rewards
For rewarding incentives and distributing responsibilities, the decision-making, accountability, outcomes, and rewards should be shared among all the members of the project team and the supporting functional units.
Temporary vs. Permanent Units
Temporary Project Organization and Permanent Functional Units: Though the project organization is temporary, the functional units from which it is formed are permanent. Thus, when a project ends, the project team is scattered and the project personnel either return to their functional units or are reassigned to new projects.
Projects may originate from different areas of the organization. Product development and related projects tend to emerge from marketing whereas technological applications originate in Research and Development (R&D).
Other Functions
Project management sets into motion numerous other support functions such as personnel evaluation, accounting, and information systems.
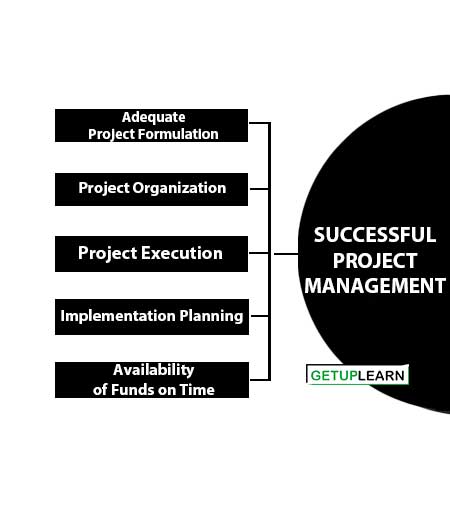
Successful Project Management
In order to reduce the cost of constructing a project, organizations should consider various factors such as cost and time for successful competition among projects. The following are the key factors essential for successful project management:
- Adequate Project Formulation
- Project Organization
- Implementation Planning
- Availability of Funds on Time
- Effective Monitoring
Adequate Project Formulation
Project formulation is the process of converting project ideas into project proposals in a structured manner. Generally, project formulation suffers from the following shortcomings:
- Use of informal methods for estimating the costs and benefits, such as maintaining paper records instead of using computers.
- Deliberate overestimation of benefits and underestimation of the cost of constructing a project.
- Faulty judgments due to a lack of experienced managers and employees.
It is essential for an organization to avoid these shortcomings in order to have adequate and meaningful project formulation.
Project Organization
A sound organization possesses the following characteristics:
- The proper working environment for employees.
- Well-defined working methods and systems.
- Proper rewards and penalties to employees for their performances and faults.
Implementation Planning
After taking investment-related decisions, it is necessary for an organization to do proper implementation planning before commencing the actual implementation. Proper implementation planning includes the following steps:
- Developing a plan for various activities such as land acquisition, tender evaluation, recruitment of staff, construction of buildings, and creation of an industrial plant.
- Estimation of the resource requirements such as manpower, materials, and money in the project.
Availability of Funds on Time
It is important to have funds on time for taking advanced actions in the project activities. Timely availability of funds facilitates the organization to negotiate the cost of the project with suppliers and contractors.
Effective Monitoring
In order to have a successful management of the project, a project monitoring system must be established in the organization. This is because effective monitoring helps in analyzing emerging problems and taking corrective actions for the project activities.
The following are the factors that should be kept in mind while developing an effective system of monitoring:
- It should emphasize on the critical aspects such as the finance of the project management.
- It should be simple and not overcomplicated as it may result in a lot of documentation and a waste of resources.
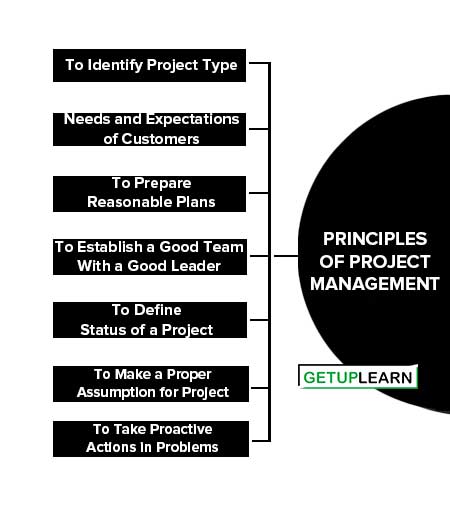
Principles of Project Management
Successful project management can be achieved by the proper application of principles instead of implementing different kinds of techniques. The following are the seven principles of project management:
- To Identify Project Type
- Needs and Expectations of Customers
- To Prepare Reasonable Plans
- To Establish a Good Team With a Good Leader
- To Define Status of a Project
- To Make a Proper Assumption for Project
- To Take Proactive Actions in Problems
To Identify Project Type
To identify the project type that is suitable for the business. One needs to select projects that are good for business.
Needs and Expectations of Customers
To understand the needs and expectations of the customers.
To Prepare Reasonable Plans
To prepare reasonable plans which define the scope, cost, and approach of the project. This helps in reducing unplanned areas in the project.
To Establish a Good Team With a Good Leader
To establish a good team with a good leader. This principle conveys that there should be a proper working environment and communication flow between the project managers and team members.
To Define Status of a Project
To define the status of the project. This helps to improve the project quality and to recognize the various problems in it.
To Make a Proper Assumption for Project
To make a proper assumption for the project. This principle focuses on the verification of the critical items used in the project in order to reduce the risk.
To Take Proactive Actions in Problems
To take proactive actions in the problems of the project. This is because the problem usually gets worse over time which in turn increases the chances of risk.
Importance of Project Management
The scope of a project is determined by using product scope and project scope. Product scope explains all the functions and features that are to be included in a product or service of the project. On the other hand, project scope deals with the deeds to be done for delivering the needed product.
The tools and techniques to manage the product scope change with the nature of the project. The project manager uses various tools and techniques such as product and cost-benefit analysis for developing the scope of a project.
Once the project has been selected, the project manager and the client jointly prepare the scope of the project and deliverables. Organizations have to manage their projects effectively in order to create and maintain their reputation in the market. Many organizations fail to manage their projects properly due to the following reasons:
- The project is completed late or without fulfilling the demands of the client
- Project is not giving any valuable information
- The project lacks proper planning and organization of the activities
- The techniques and standards used are not advanced.
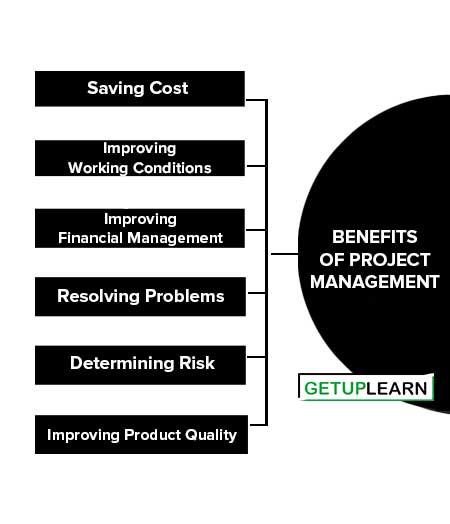
Benefits of Project Management
Good project management offers various techniques and guidelines to manage employees and workloads. Benefits of Project management involve the following benefits in an organization:
- Saving Cost
- Improving Working Conditions
- Improving Financial Management
- Resolving Problems
- Determining Risk
- Improving Product Quality
Saving Cost
Project management offers a common methodology for managing the project, i.e., if the processes and procedures are planned once, then they can be used in all future projects again. Consequently, it helps save the cost and time required in completing the project.
Improving Working Conditions
If the projects are successful, the client will be more involved in the projects. This helps in improving the working environment of the organization, which in turn encourages the morale and confidence of the project team.
Improving Financial Management
Better estimation of the actual costs involved in the project helps in managing the budget of the organization. This results in better financial predictability and cost control.
Resolving Problems
Team members in a project spend a lot of time and energy dealing with project problems. This is because the project team members do not know how to resolve the project problems. If the project is properly managed and planned, then the process of project management helps in solving the project problems quickly.
Determining Risk
The process of project management helps in identifying and managing risks in the near future.
Improving Product Quality
The process of project management helps team members understand the needs of customers. Once customer needs are recognized, team members can implement quality control and assurance techniques to fulfill customer demands.
FAQs About the Project Management
What are the project management approaches?
There are generally two main approaches to carrying out a project: Traditional project management and agile project management or modern project management approaches. These are the five phases of project management approaches: Project Initiation 2. Project Planning 3. Project Execution 4. Project Monitoring and Control 5. Project Closure.
What are the characteristics of project management?
The following are the characteristics of project management:
1. Focal Point for Resource Integration
2. Team Integration by Project Manager
3. Oversight and Integration
4. Resource Allocation Conflicts
5. Dual Reporting in Project Organizational Structure
6. Distributing Responsibilities and Rewards
7. Temporary vs. Permanent Units
8. Other Functions.
What are the tips for successful project management?
The tips for successful project management are 1. Adequate Project Formulation 2. Project Organization 3. Implementation Planning 4. Availability of Funds on Time 5. Effective Monitoring.
What are the principles of project management?
The principles of project management are:
1. To Identify the Project Type
2. Needs and Expectations of Customers
3. To Prepare Reasonable Plans
4. To Establish a Good Team With a Good Leader
5. To Define the Status of a Project
6. To Make a Proper Assumption for the Project
7. To Take Proactive Actions in Problems.
What are the benefits of project management?
The following are the benefits of project management:
1. Saving Cost
2. Improving Working Conditions
3. Improving Financial Management
4. Resolving Problems
5. Determining Risk
6. Improving Product Quality.