Table of Contents
- 1 What is Human Resource Accounting?
- 2 Definition of Human Resource Accounting
- 3 Objectives of Human Resource Accounting
- 4 Methods of Human Resource Accounting
- 5 Cost-Based Methods
- 6 Value-Based Methods
- 7 Advantages of Human Resource Accounting
- 8 Limitations of Human Resource Accounting
- 9 FAQ Related to Human Resource Accounting
What is Human Resource Accounting?
Human Resource Accounting is the process of identifying and reporting the Investments made in the Human Resources of an Organisation that are presently not accounted for in the conventional accounting practices. In simple terms, it is an extension of the Accounting Principles of matching the costs and revenues and of organizing data to communicate relevant information in financial terms.
The primary aim of Human Resource accounting is to assist the management in planning and controlling human resources in an effective manner. Through Human Resource accounting, the cost and value of the workforce can be estimated. Human Resource accounting quantifies the value of human resources just like assessing the value of physical assets. This helps the organization to understand the actual worth of the human resource.
It also helps the organization determine the contribution of the human resource. In the present times, human resources are emerging as an important resource of the organization and due to this, Human resource accounting is gaining more importance. Due to this, Human resource accounting is becoming a strategic tool to manage and control human resources effectively.
Employees also benefit from this activity as the organization would be able to recognize the skills, talents, and knowledge of the employees and treat them in an appropriate manner. Human Resource accounting helps the management to utilize Human Resources in an effective manner as it optimizes the ability of human resources.
By estimating the value of human resources and ensuring that they are utilized in an effective manner, Human Resources accounting enables the organization to recognize the skills of employees and utilize them in a manner that helps them to achieve the goals of the organization in an effective and efficient manner.
Definition of Human Resource Accounting
The Following are some simple definitions of human resource accounting:
[su_quote cite=”American Accounting Association”]Human Resource Accounting is the process of identifying and measuring data about human resources and communicating this information to interested parties[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”R.L. Woodruff Jr.”]Human Resource accounting is an attempt to identify and report investments made in human resources of an organization that is presently not accounted for in conventional accounting practices.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Flamholtz”]Human Resource Accounting is the measurement and reporting of the cost and value of people in organizational resources.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Prof. Davidson”]Human Resource Accounting is the term used to describe a variety of proposals that seek to report and emphasize the importance of human resource knowledgeable, trained, and loyal employees in a company earning process and total assets.[/su_quote]
Objectives of Human Resource Accounting
Human Resource accounting supports the decisions taken by the management in many ways by facilitating proper allocation and scheduling of various activities of the organization. The general aim of Human Resource accounting is to facilitate managers in planning, supervising, and controlling human resources in the most effective manner.
The following are the various objectives of Human Resource accounting:
- It provides quantitative information about the cost and value of human resources in an organization.
- It also creates a base for decisions concerning the human resources of the organization.
- A human cost or budget for performing human resource functions such as acquisition, development, and compensation of employees can be prepared.
- Methods and standards for evaluating the worth of people to the organization can be devised.
- The quality of the human resource can be monitored in an effective manner for optimum utilization of labor.
- Planned and measured changes in the value of human resources can be undertaken.
- It gives adequate warning to the management regarding any changes that might occur in the value of the human resources.
- It helps the management to reward the employees in an appropriate manner according to their performance.
- It facilitates the determination of the true value of human resources by all stakeholders.
- It also helps in developing various principles for understanding the financial impact of various practices.
Read full details about the: Examlabs
Methods of Human Resource Accounting
The traditional accounting practices tend to ignore the value of human resources and prefer to treat them as an expense. This attitude works against the interest of the employees. Though Human Resource accounting is still in its developing stages, many experts have tried to develop various techniques to study and account for the human resources in the organization even though they have failed to get universal acceptance.
The following are the various methods of human resource accounting:
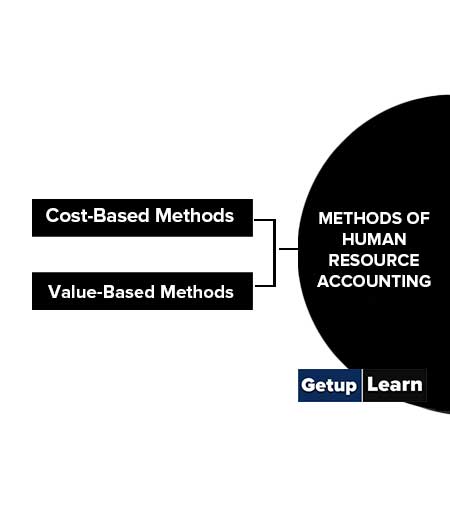
Cost-Based Methods
The various techniques of cost-based methods operate like a traditional financial accounting system. The following are the various techniques of cost-based methods:
Historical Cost Method
It was developed by Lee Brummet, Eric Flamholtz, and William Pyle. According to this approach, the cost incurred for retirement, training, and development of employees should be considered a capital expenditure and it should be written over the estimated useful life of human resources.
In case an employee leaves the organization prematurely, the entire balance amount which has not been deducted is treated as an expense and written off completely. This method is systematic and objective as it records each and every cost associated with the procurement and development of human resources.
The major advantage of this method is that it is simple and easy to understand as well as easy to operate. But it is subjective and involves tough estimates. Further, it ignores the basic characteristics of a human asset that its value appreciates as time passes. Further, the inflammatory costs are not taken into consideration and due to that, the accounting of human resources which is undertaken might have little relevance.
Replacement Cost Method
Another approach was propounded by Rensis Likert and Eric Flamholtz. They suggested an accounting approach that was more realistic in nature. In order to determine the value of human resources, the cost of recruiting, training, and developing new people as suitable replacements is considered.
It has two approaches namely personnel replacement and positional replacement. When the cost of replacing a job holder in any specific position in an organization is considered then it is known as personnel replacement while when the skills and knowledge required for job performance are considered, then it is known as a positional replacement.
One of the major advantages of this method is that it is more practical and logical than the historical cost approach. But it is not so easy to find a replacement for a person or position. Moreover, the assessment of the value of human resources cannot be objectively determined. As a result, it is very difficult to adopt this method in real life.
Opportunity Cost Method
This approach was introduced by Hekman and Jones. According to them, opportunity cost exists for all human resources that are short in supply. In order to value the cost of human resources, the sacrifices made for choosing one decision over another are considered.
It should be kept in mind that where alternatives are not available for any particular decision, there would be no opportunity cost. In Human Resource accounting, opportunity cost arises for employees when their services are required or bidden for by many heads. So, on the basis of those bids, the value of the human resources is assessed.
One of the major advantages of this method is that it provides a quantitative approach to the concept of Human Resource Management and also ensures that scarce human resources are allotted in an efficient manner. But such an approach is suitable only to value Human Resources at the middle management level. Similarly, there is no guarantee that the services rendered by the employee in one department would be similar to what he would do in other departments.
Standard Costing Method
This approach was given by David Watson. Under this, the human resources data is used to set standard costs for various human resource years. The employees are classified into different groups or grades based on their position in the organization.
Then the standard cost for each grade of employees would be fixed which would be taken as standard for undertaking various human resource-related activities. It might be possible that such costs may be revised depending upon the conditions that prevail. After that, an aggregate standard cost for the entire workforce would be calculated which would be considered as the cost of human resources in the organization.
This approach is simple and easy to operate as well as easy to understand. But it lacks objectivity with regard to the estimation of standards regarding human resources. Further, it might be time-consuming to determine the cost for each grade in the organization.
Value-Based Methods
Under the various methods which are considered to be value-based, the primary criteria on which the value of human resources depends is the ability of the human resources to generate revenues. These methods focus more on the future earning capacity of the human resource. The following are the various Human Resources valuation models which are classified as value-based methods:
- Present Value of Future Earnings Model
- Certainty Equivalent Model
- Stochastic Reward Valuation Model (SRVM)
- Human Asset Multiplier Model
Present Value of Future Earnings Model
It was developed by Brauch Lew and Aba Schwartz. Here the value of human resources depends on the present value of future earnings to be made from a person’s employment. It basically depends on the economic concept of human capital. The years of service remaining of the employee in the organization determines the value of an employee.
It estimates the present value of future income of an employee from the remaining services after adjusting for the possibility of premature death or permanent disability.
One of the limitations of this method is that the role of authority in deciding how an employee should be used in it is ignored and the concept that an employee might leave the organization is ignored. Further, the impact of job changes such as promotions and transfers is also not taken into consideration.
Certainty Equivalent Model
It was given by Pekin Ogan. It considers the net benefit and certainty factor for determining the net present value of the human resource. The net benefit is the difference between the total investment made by the organization in acquiring, training, developing, integrating, and maintaining the employees and the total benefits received out of the skills, ability, and knowledge of those employees.
It views compensation policies, promotion policies, industry averages, labor market conditions, and skills requirements as a major determinants of the cost of human resources. Further, factors such as age and remaining years of service are also taken into consideration.
One of the major highlights of this approach is the concept of certainty equivalent which includes the probability of an employee continuing in the organization and the probability of his survival. Using all these, the value of human resources can be determined.
Stochastic Reward Valuation Model (SRVM)
It was originally propounded by Eric Flamholz. Under this, the value of employees depends on the variability of that person from four perspectives and potentialities namely productivity, promotability, transferability, and retain ability.
Through this model, the organization can decide the employee’s estimated tenure in the organization, the mutually exclusive positions that he may occupy the value of each position occupied by him, and the probability that an employee might occupy a certain position in the organization in the future. Like all other approaches, this approach also has certain limitations which are as under:
- The organization might find it hard to get specific and reliable data about the value derived by the organization when the employee occupies a specific position in a very uncertain future period.
- It might also be possible that the individual performance of an employee might be different from the way in which he performs in a group which is not considered in this model.
Human Asset Multiplier Model
It was developed by W.J. Giles and D.F. Robinson, The valuation of human resources per this model is normally made according to the going concern concept. Giles and Robinson developed a human asset multiplier which is then applied to the gross remuneration of employees which is obtained from a financial formula based on the market value of the organization.
Then these multipliers are weighted for different grades of employees. The age, experience, qualifications, expertise, commitment, performance and promotion capabilities, replacement scarcity, and remaining period of services are taken into account and used as weights. By totaling all individual values, which are calculated separately, the gross value of human resources can be determined.
Advantages of Human Resource Accounting
Human Resource accounting provides a base to assess the efficacy of Human Resource Management and helps in assigning quantitative value to human resources. This helps the organization to ascertain the value of its human resources. The following are the advantages of human resource accounting in the field of Human Resource Management:
- It helps the organization to identify the changes that occur in Human Resources over a period of time and ascertain their impact on the value of those on human resources.
- It helps the management to maintain a record of investments made on human resource and their likely cost of replacement in the future.
- It provides information to management for activities such as Human Resource Planning, recruitment, training and development, and career and succession planning.
- It allows the organization to evaluate returns earned from individuals on investments made to them.
- It enables the organization to understand problems related to Human Resource Management in a better manner.
- It allows optimum utilization of available human resources.
- It helps in identifying high-value employees by offering them better facilities.
- It assesses the worth of money spent on human resource functions and helps in deciding whether to continue such activities in the future or not.
-
Human Resource accounting helps the organization to proclaim the value of Human Resources confidently. When the Human Resources accounts indicate a high value of the human resources, it helps the organization to earn goodwill in the organization.
- It improves employee motivation and morale by inculcating a feeling of self-worth among the employees. Further, when the management is aware of the contribution of employees, they give them due respect.
- It also helps the other stakeholders to decide how efficient the human resource of the organization is.
Limitations of Human Resource Accounting
Even though Human Resource accounting helps the management to assess the actual worth of human resources of the organization, there are certain limitations of human resource accounting that it faces which as:
- Not Universally Acceptable System
- Lack of Real Ownership
- Lack of Principles, Concepts, Conventions and Regulating Body
- Non Recognition by Tax Authorities
- Opposition from Employee Union
- Lack of Awareness and Research
Not Universally Acceptable System
Even though many efforts have been made to develop a universally acceptable human resource accounting system, there has been no success so far. It might be possible that such a system was not generated due to the non-recognition of human capital in the financial books according to the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
The GAAP does not recognize human resources as an asset as it violates the conservatism concept and the future benefits obtained are also uncertain.
Lack of Real Ownership
Even though employees work for the organization and are considered an asset, the organization does not have ownership of these employees. As a result, they cannot be referred to as assets in the practical sense.
Lack of Principles, Concepts, Conventions and Regulating Body
Human Resource accounting is not regulated by any authority and it does not have any principles, conventions, or concepts which are related to it. Due to this, a universally accepted human resource accounting model cannot be developed as it would be lacking the required objectivity, validity, and reliability. so, a uniform method of evaluating human resources cannot be developed.
Human Resource accounting has not been recognized by any tax authority for tax concessions and rebates and is only viewed as an expense for calculating the expenses on human resources. So many organizations do not undertake it and consider it an unnecessary expense.
Opposition from Employee Union
As Human Resource accounting assesses the contribution of employees towards the organization, on the basis of the value determined by the organization, there is a possibility that the lower-level employees may be exploited by offering them a low salary. As result, Human Resource accounting may strongly oppose the activity of Human Resource accounting.
Lack of Awareness and Research
As Human Resource Accounting has no immediate necessity as well as organization to regulate it, adequate attention is not given to its development into a fully-fledged and viable concept. Moreover, the organizations are not much concerned regarding human resource data and due to this, they also take very less initiatives regarding the disclosure of human resource-related data to the various stakeholders.
What are human resource accounting and its benefits?
Human Resource Accounting is the measurement and reporting of the cost and value of people in organizational resources. It helps in identifying and reporting the Investments made in the Human Resources of an Organisation.
What is human resource accounting explain its purpose and objective?
Human Resource Accounting is the process of identifying and measuring data about human resources and communicating this information to interested parties.
What are the methods of human resource accounting?
The following are the various methods of human resource accounting:
1. Historical Cost Method
2. Replacement Cost Method
3. Opportunity Cost Method
4. Standard Costing Method
5. Present Value of Future Earnings Model
6. Certainty Equivalent Model
7. Stochastic Reward Valuation Model (SRVM)
8. Human Asset Multiplier Model etc.
What are the limitations of HR accounting?
There are certain limitations of human resource accounting faces which are as:
1. Not Universally Acceptable System
2. Lack of Real Ownership
3. Lack of Principles, Concepts, Conventions, and Regulating Body
4. Non Recognition by Tax Authorities
5. Opposition from Employee Union
6. Lack of Awareness and Research etc.