Table of Contents
- 1 What is Leadership?
- 2 Definition of Leadership
- 3 Difference Between Leadership and Management
- 4 Types of Power in Leadership
- 5 Importance of Leadership
- 6 Characteristics of Leadership
- 7 Functions of Leaders
- 8 Leadership Traits
- 9 Leadership Styles
-
10 FAQs Section
- 10.1 What is the meaning of Leadership?
- 10.2 What is the simple definition of leadership?
- 10.3 What are the types of power in leadership?
- 10.4 What is the importance of leadership?
- 10.5 What are the characteristics of leadership?
- 10.6 What are the functions of leaders?
- 10.7 What are the different Leadership styles?
What is Leadership?
Leadership is the ability to influence individuals or groups toward the achievement of some particular goal or goal. Leadership, as a process, shapes the goals of a group or organization, motivates behavior toward the achievement of those goals, and helps define group or organizational culture. It is primarily a process of influence.
Leadership is a dynamic force essential for the success of any human group effort. Without leadership, no organization or enterprise can flourish. In fact, it is vital to the survival of a business.
For all the technological changes that name taken place in the business industry, the need for human leadership is no less today. Leadership is an important aspect of managing. It can be said that management works when the manager like his role as leader.
Definition of Leadership
These are the definitions of leadership explain below:
Leadership is the initiation of acts which result in a consistent pattern of group interaction directed towards the solution of a mutual problem.
J.K. Hemphill
Leadership is the ability to get other people to do what they don’t want to do and like it.
Harry Trumann
Leadership is the ability to persuade others to seek defined objectives enthusiastically. It is the human factor which kinds a group together and motivates it towards goals.
Keitlo Davis
Thus, Leadership may be defined as a humanized activity of influencing a group of people to act for the attainment of group goals.
Difference Between Leadership and Management
Although some managers are able to influence followers to work toward the achievement of organizational goals, the conferring of formal authority upon a manager does not necessarily make that individual a leader.
Yes, that individual has authority, but whether or not they are able to influence their subordinates may depend on more than just that authority. The fundamental difference between a manager and a leader:
- A manager administers, but a leader innovates,
- A manager maintains while a leader develops,
- A manager focuses on systems and structures, whereas a leader’s focus is on people,
- A manager relies on control, but a leader inspires trust,
- A manager keeps an eye on the bottom line, while a leader has an eye on the horizon,
- A manager does things right, a leader does the right thing.
These are the points of difference between leadership and management:
| Basis of Difference | Leadership | Management |
| 1. Meaning | Leadership is a process of influencing people to direct their efforts towards the attainment of some particular. | Management is the process of getting things done through others. |
| 2. Power and Authority | Leadership is based on power. The Power may be desired from format authority or from any other source. in superior position. | Management is based on authority which is delegated to a management position by a person. |
| 3. Structures | Leadership structures are more flexible, open, informal, and dynamic than management. | Management is bound by an organized formal structure. |
| 4. Goal | Leaders achieve goals by inspiring others. | Managers achieve goals by directing others. |
| 5. Existence of Position | The existence of Existence a Leaders position depends on the pleasure of his followers. | The existence of a manager’s IXhition is independent of the coil of his subordinates. It depends on the terms and conditions of his service |
Types of Power in Leadership
Let us try to understand each of these types of power in leadership:
Reward Power
Reward power is based on the subordinate’s perception that the leader has the ability to control rewards that the followers are looking for; for example, the leader’s ability to influence the decisions regarding pay, promotion, praise, recognition, increased responsibilities, allocation and arrangement of work, granting of privileges, etc.
Coercive Power
Coercive power is based on fear and the subordinate’s perception that the leader has the ability to punish or to cause an unpleasant experience for those who do not comply with directives.
Examples include withholding pay raises, promotions, or privileges; allocation of undesirable duties or responsibilities; withdrawal of friendship or support; formal reprimands or possibly dismissal. This is in effect the opposite of reward power.
Legitimate Power
Legitimate power is based on the subordinate’s perception that the leader has a right to exercise influence because of holding a particular position in the hierarchy of the organizational structure. Legitimate power is thus based on authority and not on the nature of personal relationships with others.
Referent Power
Referent power is based on the subordinate’s identification with the leader. The leader is able to influence the followers because of interpersonal attraction and his personal charisma. The followers obey the leader because of their respect and esteem towards him.
Expert Power
Expert power is derived from the subordinate’s perception of the leader as someone who has access to information and relevant knowledge.
Importance of Leadership
Without Leadership, an organization would only be a confusion of people and machines. The importance of Leadership is as follows:
- Determines Goals and Guides for It
- Boosts Morale
- Team-Spirit
- Optimum Use of Human Resources
- Facilitates Change
- Other Importance
Determines Goals and Guides for It
A leader plans goals & policies for his group. The trigger is a person’s will to do, show the way and guide group members toward group accomplishment. He created enthusiasm for, performance (best) among his followers.
Boosts Morale
Morale is the internal feeling of a person. A good leader can arouse the will to, cooperate among the employees. He transforms lukewarm desires for achievement into burning passions for successful accomplishments.
Team-Spirit
A leader provides a healthy & satisfying work climate by harmonizing individuals to accomplish group goals. He tries to reconcile conflicts & create team spirit among his group.
Optimum Use of Human Resources
Leadership can leave man’s vision to higher sights, raise man’s standard to higher performance, and build man’s personality beyond his normal limitations. A leader can influence the activities and behavior of his followers to contribute their best.
Facilitates Change
Leaders can induce and introduce change. They are instrumental in conceiving change. They introduce change by convincing their followers about the positive effects of the change.
Other Importance
The other importance of leadership:
- Creates confidence and enthusiasm among his group members.
- Leadership acts as a catalyst that transforms potential into reality.
- Leadership plays a vital role in ensuring the survival and effectiveness of the organization.
- Leadership is necessary in the organization in order to create a work environment that is productive and satisfying for human beings.
- Leadership helps maintain order and discipline in the organization.
- Leaders play a crucial role in resolving conflicts arising in the group.
- A leader is a bridge between group members and top management.
Characteristics of Leadership
The following are the important characteristics of Leadership:
- Leadership is Process of Influence
- Leadership is Function of Motivation
- Leadership is Related to a Situation
- Personal Quality
Leadership is Process of Influence
A leader can be regarded as successful only when he is able to influence the behavior, attitude, and beliefs of his subordinates.
Leadership is Function of Motivation
Leadership is the function of motivating people to attempt willingly to attain organizational objectives. Leaders are considered successful when they are able to encourage and develop self-confidence in their subordinates.
It means leadership styles are different for different circumstances. It is always related to a particular situation, at a given point in time, and under specific circumstances.
Personal Quality
A leader should be courageous, should have willpower, should possess physical and nervous energy, and have enthusiasm, self-confidence, and moral qualities.
Functions of Leaders
The most important functions of Leaders are as follows:
- Goal Setter
- Organization of Different Activities
- Achieving Co-ordination
- Representing
- Motivation of Employees
- Guiding Employers
- Building Employee’s Moral
- Managing Time
Goal Setter
A leader performs the role of goal setter for his subordinates. He also acts as a guide and teacher.
Organization of Different Activities
A leader divides all the activities of the organization among the different subordinates in a systematic manner. It may reduce the chances of conflicts between employees.
Achieving Co-ordination
A leader integrates the individual’s goal with the organizational goal and creates a community of interest. A leader shares all the information, which is related to the organizational goal with the employees, and it may achieve coordination in the organization.
Representing
A leader is a representative of his subordinates. He also tries to fulfill the psychological needs of his subordinates.
Motivation of Employees
Motivation is necessary for accomplishing desired results from the subordinates. A good leader motivates his subordinates for better performance. A leader motivates his subordinates by giving them monetary or non-monetary rewards.
Guiding Employers
A leader guides and directs the subordinates to achieve a unity of purpose. He is always present to solve the problems which his subordinates may face.
Building Employee’s Moral
Good leadership is very important for increasing employee morale. The leader shapes the thinking and attitude of the subordinates according to the objectives of the organization.
Managing Time
One of the important functions of a leader is to ensure the timely completion of activities undertaken by his/her team members.
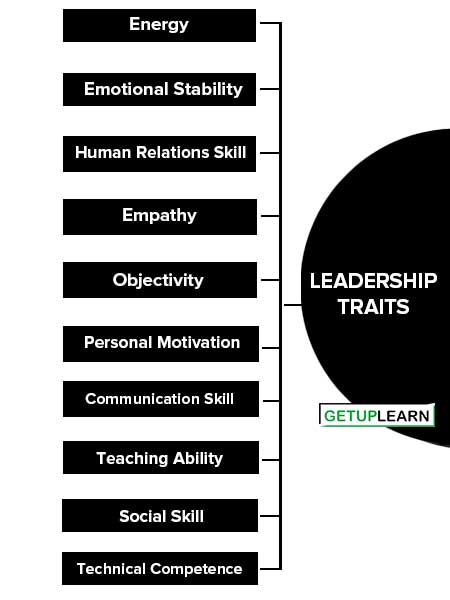
Leadership Traits
The traits/qualities of a successful leader are as follows:
- Energy
- Emotional Stability
- Human Relations Skill
- Empathy
- Objectivity
- Personal Motivation
- Communication Skill
- Teaching Ability
- Social Skill
- Technical Competence
- Administrative Skill
- Intelligence
Energy
A leader should be energetic. The energy both mental and physical are required for a job.
Emotional Stability
It enables a leader to act with confidence. It avoids anger and deals with his subordinates with understanding.
Human Relations Skill
A leader should have human relations skills. It requires an understanding of human behavior.
Empathy
It enables him to look at things objectively and from another’s viewpoint.
Objectivity
It prevents him from getting emotionally involved.
Personal Motivation
A leader is personally motivated and enthusiastic to get the job done.
Communication Skill
The communication skills of a leader should be powerful. It is the ability to talk and write clearly and forcefully.
Teaching Ability
A leader should have the technical ability. It will help him to develop and inspire his subordinates.
It enables him to understand people and know their strengths and weaknesses and presents himself as a friendly and approachable person.
Technical Competence
A leader should be technically competent. It provides him with effective working knowledge and insight into the operations under his guidance.
Administrative Skill
A leader should have administrative skills. It helps to implement plans & policies and to organize and mobilize resources in a pragmatic manner.
Intelligence
A leader should be intelligent. It makes him think scientifically.
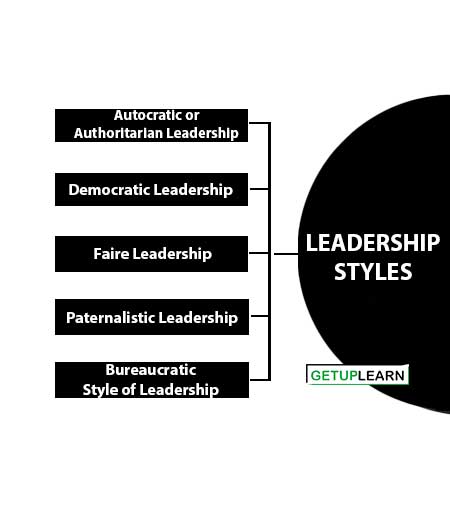
Leadership Styles
Every leader usually develops his own style of leadership style of every leader are differ from the other. There exist different leadership styles. The main leadership styles are:
- Autocratic or Authoritarian Leadership
- Democratic Leadership
- Faire Leadership
- Paternalistic Leadership
- Bureaucratic Style of Leadership
An autocratic leader takes all decisions solely. He centralizes power and tells his group members what to do and expects them to obey his order without any question or remark. This can be further categorized as:
-
Hard Boiled/Negative/Pure Autocrat: Such leaders use heavy negative influence. They superimpose their orders/decisions on subordinates. He uses fear of punishment to carry out his orders.
-
Benevolent Autocrat: Such leaders try to use positive leadership techniques by using praise and pats on the back to secure personal loyalty for achieving acceptance of their own decisions.
- Manipulative Autocrat: Such leaders make the subordinates feel that they are actually participating in the decision-making even though managers have made the decisions themselves.
Democratic Leadership
Democratic leaders decentralize authority and encourage subordinates’ participation in decision-making. He believes in the free flow of two-way communication. He tries to lead through persuasion and example rather than through fear or force.
Faire Leadership
This type of leader prefers to give little or no direction and seeks to lead his group with a very loose rein, allowing his subordinates a great deal of freedom. Free-rein leadership helps subordinates train and develop them independently. This style is suitable where subordinates are duty-conscious and highly competent.
Paternalistic Leadership
This style of leadership adopts the paternal or fatherly attitude as the right one for the relationship between the leader and his group.
Its objective is to help, guide, protect, and keep the followers happily working together as members of a family. It is based on the ground that, “Happy employees work harder” while otherwise stated employees will work harder out of gratitude.
Bureaucratic Style of Leadership
It is also referred to as rules-centered or procedure-centered leadership. It is less dynamic and less proactive. It is noticed in the Indian sector, often criticized for delay and favoritism. This is also a very rigid style.
FAQs Section
What is the meaning of Leadership?
Leadership is the ability to persuade others to seek defined objectives enthusiastically. It is the human factor that kinds a group together and motivates it toward goals.
What is the simple definition of leadership?
Leadership is the initiation of acts that result in a consistent pattern of group interaction directed toward the solution of a mutual problem.
What are the types of power in leadership?
Reward Power, Coercive Power, Legitimate Power, Referent Power, and Expert Power are the types of power in leadership.
What is the importance of leadership?
These are the importance of leadership given below:
1. Determines Goals and Guides for It
2. Boosts Morale
3. Team-Spirit
4. Optimum Use of Human Resources
5. Facilitates Change
6. Other Importance.
What are the characteristics of leadership?
Leadership is a Process of Influence, Leadership is a Function of Motivation, Leadership is Related to a Situation, and Personal Quality are the characteristics of leadership.
What are the functions of leaders?
The most important functions of Leaders are as follows:
1. Energy
2. Emotional Stability
3. Human Relations Skill
4. Empathy
5. Objectivity
6. Personal Motivation
7. Communication Skill
8. Teaching Ability
9. Social Skill
10. Technical Competence.
What are the different Leadership styles?
Autocratic or Authoritarian Leadership, Democratic Leadership, Faire Leadership, Paternalistic Leadership, and Bureaucratic Style of Leadership are Leadership styles.
