In a small business unit like mom & a pop shop, a single person may be able to manage all the activities of the unit, but as the scale of operations increases, one may find it difficult to manage various functions then requires some suitable persons to employ.
It is quite possible that you may start It is quite possible that you may start your own business and face such a situation and employ people to assist you in running the business unit or shop, on the other hand, you yourself may be a job seeker.
In both situations, you may find it useful if you know how employees are recruited, selected and trained for the various positions in an organisation. The need for Staffing arises with the events such as performance appraisal of employees, transfers or promotions.
These events create a gap in the organisational structure when an employee has been moved upward in the job responsibilities or been shifted to some other department or maybe a place of work. Below that we will be looking at the staffing process.
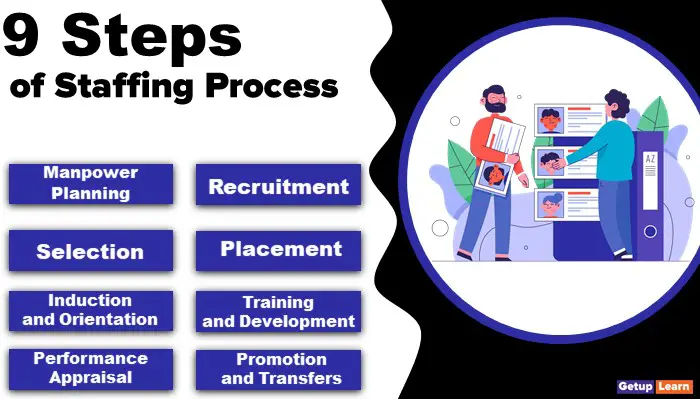
Staffing Process
The staffing function is performed by all managers at all levels. However, its scope is different in small and large organizations. In a large organization, there is a separate department called Human Resources Department (HRD), with specialists to manage the people.
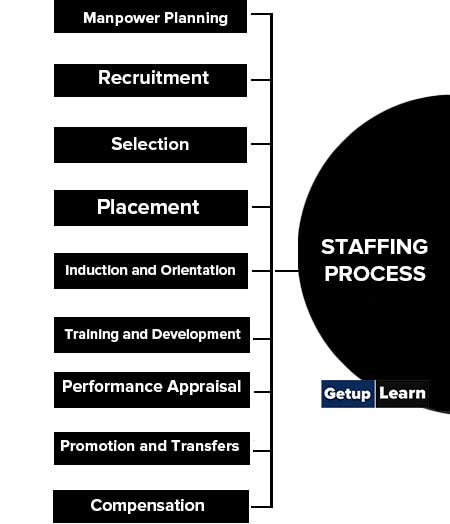
Staffing is an inherent part of Human Resources Management as it is the practice of finding evaluating and establishing a working relationship with people. The following are the steps involved in the staffing process:
- Manpower Planning
- Recruitment
- Selection
- Placement
- Induction and Orientation
- Training and Development
- Performance Appraisal
- Promotion and Transfers
- Compensation
Manpower Planning
Estimation of manpower requirements in the future is the first stage in the staffing process. It is known as manpower or human resources planning. Its purpose is to make the right kind of personnel available so that there is no surplus or shortage of people in any department.
To determine the qualifications needed to meet the requirements of jobs, the organization, first of all, has to analyze the jobs, write the job description and prepare job specifications.
Recruitment
Once the requirement for manpower is known, the process of recruitment starts. It is the process of identifying the sources for prospective candidates and stimulating them to apply for the jobs. It is a positive process as it attracts suitable candidates to apply for available jobs.
The process of recruitment and the cost involved in it depends on the size of the undertaking and the type of persons to be recruited. The sources of recruitment can be a) Internal sources (recruitment from within the enterprise) and b) External Sources (recruitment from outside).
Selection
The process of selection leads to the employment of persons who possess the ability and qualifications to perform the jobs which have fallen vacant in the organization. Selection is frequently described as a negative process as it eliminates all the candidates who do not match up to the requirements of the job offered.
As the employees are placed in the jobs for which they are best suited, they derive maximum job satisfaction reducing labour turnover and increasing the overall efficiency of the organization. The candidates have to go through the whole selection process of an organization i.e. interviews, tests, medical examinations etc.
Placement
The candidate selected for appointment are to be offered specific jobs. Personnel should be placed on a position where there is full use of their strength and capabilities. Proper placement reduces absenteeism and turnover.
Induction and Orientation
Induction is the process of familiarizing a new employee with the new workplace, surroundings, company rules and regulations. The induction programme is generally informal in the case of small organizations.
But in large organizations, the orientation or induction is carried on formally so that the new employee develops a favourable attitude towards the company.
Training and Development
Training is an organized activity for increasing the knowledge and skills of people for a definite purpose. Its purpose is to achieve a change in the behaviour of the employees and to enable them to do their jobs better.
The initiative for training usually comes from the management. Development emphasizes the growth of an individual. It’s a continuous process Development helps in the overall growth of the employee.
Performance Appraisal
It refers to all the formal procedures used in an organization to evaluate the employees and their contributions. It also reveals how efficiently the subordinate is performing his job and knows his aptitudes and other qualities necessary for performing the job assigned to him.
Promotion and Transfers
Promotion refers to being placed in a higher job position with more salary, job satisfaction and responsibility.
On the basis of feedback reports of employees’ performance, they are given promotions and other opportunities Transfer means shifting an employee from one job to another or one department to another. The transfer may take place due to changes in the organization structure or changes in the volume of work.
Compensation
Compensation of employees for their services is an important responsibility of any organization. Every organization must offer good wages, pay, salary and other rewards to attract and retain talented employees.
Compensation to workers will vary depending upon the nature of jobs, skills required, the risk involved, the nature of work etc.
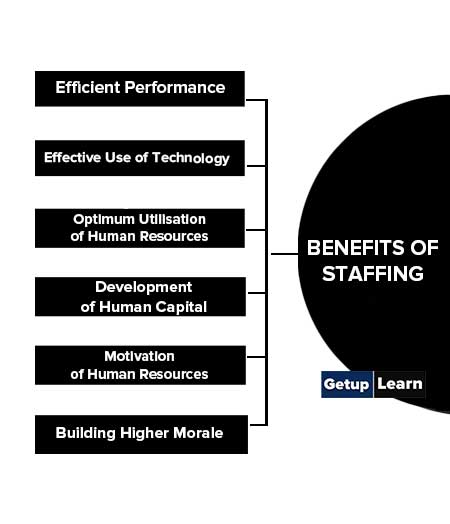
Benefits of Staffing
These are the benefits of staffing for an organisation:
- Efficient Performance
- Effective Use of Technology
- Optimum Utilisation of Human Resources
- Development of Human Capital
- Motivation of Human Resources
- Building Higher Morale
Efficient Performance
For the efficient performance of other functions of management, staffing is key. Since, if an organisation does not have competent personnel, then it cannot perform the functions of management like planning, organising and controlling functions properly.
Effective Use of Technology
It is the human factor that is instrumental in the effective utilization of the latest technology, capital, material, etc. the management can ensure the right kinds of personnel by performing the staffing function.
Optimum Utilisation of Human Resources
The wage bill of big concern is quite high. Also, a huge amount is spent on recruitment, selection, training, and development of employees. To get the optimum output, the staffing function should be performed in an efficient manner.
Development of Human Capital
Another function of staffing is concerned with human capital requirements. Since the management is required to determine in advance the manpower requirements. Therefore, it has also to train and develop the existing personnel for career advancement. This will meet the requirements of the company in the future.
Motivation of Human Resources
In an organisation, the behaviour of individuals is influenced by various factors which are involved such as education level, needs, socio-cultural factors, etc.
Therefore, the human aspects of the organisation have become very important so that the workers can also be motivated by financial and non-financial incentives in order to perform their functions properly in achieving the objectives.
Building Higher Morale
The right type of climate should be created for the workers to contribute to the achievement of the organizational objectives. Therefore, by performing the staffing function effectively and efficiently, the management is able to describe the significance and importance that it attaches to the personnel working in the enterprise.
How many steps are there in staffing process?
There are nine steps in the staffing process:
1. Manpower Planning
2. Recruitment
3. Selection
4. Placement
5. Induction and Orientation
6. Training and Development
7. Performance Appraisal
8. Promotion and Transfers
9. Compensation.
What are the benefits of staffing?
The following are the benefits of staffing:
1. Efficient Performance
2. Effective Use of Technology
3. Optimum Utilisation of Human Resources
4. Development of Human Capital
5. Motivation of Human Resources
6. Building Higher Morale.