Table of Contents
- 1 What is Organizational Culture?
- 2 Definition of Organizational Culture
- 3 Elements of Organizational Culture
- 4 Characteristics of Organizational Culture
- 5 Types of Organizational Culture
-
6 FAQs About the Organizational Culture
- 6.1 What is the meaning of organizational culture?
- 6.2 How to Create Culture in an Organisation?
- 6.3 What is the simple definition of organizational culture?
- 6.4 What are the elements of organizational culture?
- 6.5 What are the characteristics of organizational culture?
- 6.6 What are the types of organizational culture?
What is Organizational Culture?
Organizational culture is a system of shared assumptions, values, and beliefs, which governs how people behave in organizations. These shared values have a strong influence on the people in the organization and dictate how they dress, act, and perform their jobs.
Every organization develops and maintains a unique culture, which provides guidelines and boundaries for the behavior of the members of the organization.
Let’s explore what elements make up an organization’s culture. Organizational culture is composed of seven characteristics that range in priority from high to low. Every organization has a distinct value for each of these characteristics, which, when combined, defines the organization’s unique culture.
Members of organizations make judgments on the value their organization places on these characteristics and then adjust their behavior to match this perceived set of values. Let’s examine each of these seven characteristics.
Definition of Organizational Culture
After knowing the meaning of culture, we may attempt to define organizational culture. There are many different definitions of organizational culture, although almost all of the most widely accepted ones are similar and cover many of the same aspects. Here are some of the many meanings or definitions of organizational culture:
Culture is the social glue that helps hold an organization together by providing appropriate standards for what employees should say or do.
He has described organizational culture as “The set of the set of beliefs, values, and norms, together with symbols like dramatized events and personalities, which represents the unique character of an organization, and provides the context for action in it and by it.”
Gareth Morgan
“Organizational culture can be defined as a pattern of basic assumptions invented, discovered or developed by a given group as it learns to cope with its problems of external adaptation and internal integration – that has worked well enough to be considered valuable and therefore, to be taught to new members as the correct way to perceive, think and feel in relation to those problems.“
Edgar Schein
“The culture of an organization refers to the unique configuration of norms, values, beliefs and ways of behaving that characteristics the manner in which groups and individuals combine to get things done.”
Elderdge and Crombien
The other aspect of organizational culture that is often true is that it becomes very deeply rooted. It is the identity of a company, in some ways, it becomes the identity of those who work there. This is always important to remember, as culture becomes like a circular argument. The people end up affecting the culture as much as the culture is affecting them.
Because culture is so deeply rooted in an organizational history of success or failure, and because of its collective experience, any organization that needs to work to change it will be facing an uphill battle and a huge investment in time, resources, and work.
Therefore, while there are many definitions of organizational culture, all of them focus on the same points: collective experience, routine, beliefs, values, goals, and systems. These are learned and re-learned, passed on to new employees, and continue as part of a company’s core identity.
Elements of Organizational Culture
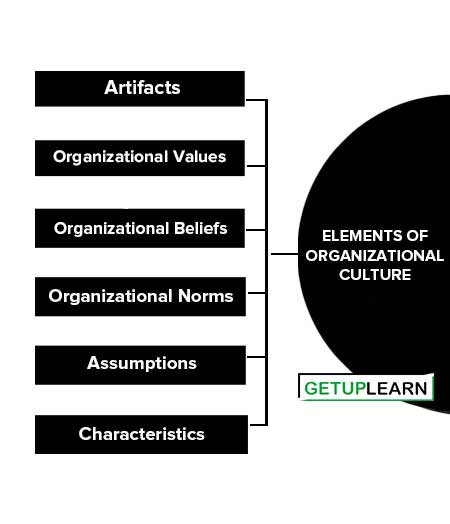
Culture works like a social adhesive or glue that helps in holding the organization together. It is essential to know about the elements of organizational culture, these are as follows:
- Artifacts
- Organizational Values
- Organizational Beliefs
- Organizational Norms
- Assumptions
- Characteristics
Artifacts
Organizational artifacts can consist of visible items that symbolize culture. An artifact may be as formal as an employee handbook or a company logo, or as informal as flowers in the front lobby. However, artifacts may also be less tangible. Keyton describes artifacts as anything that you can “see, hear, or feel” in the organizational experience.
Organizational Values
Values reflect what we feel is important. Organizations may have core values that reflect what is important in the organization. These values may be guiding principles of behavior for all members of the organization.
For example, an organization could state that its core values are creativity, humor, integrity, dedication, mutual respect, kindness, and contribution to society.
Organizational Beliefs
Beliefs that are part of an organization’s culture may include beliefs about the best ways to achieve certain goals such as increasing productivity and job motivation. For example, an organization may convey the belief that the expression of humor in the workplace is an effective way to increase productivity and job motivation.
Organizational Norms
Norms reflect the typical and accepted behaviors in an organization. They may reflect the values and beliefs of the organization. They may reflect how certain tasks are generally expected to be accomplished, the attributes of the work environment, the typical ways that people communicate in the organization, and the typical leadership styles in the organization.
For example, the work environment of a company may be described as relaxed, cheerful, and pleasant. Moreover, the organization may have a participative decision-making process in which many people in the organization are able to express their views concerning important decisions. Also, an organization must have many meetings to discuss ideas.
Assumptions
Assumptions are beliefs that are so ingrained that organizational members do not even discuss them, yet they guide behavior by directing how organizational members should think, feel, and act. For instance, an assumption may be to do whatever is necessary to make a customer happy, regardless of cost or time.
Because assumptions are not formal or documented and do not usually surface in conversation, they pose an extra challenge to new employees striving to learn acceptable practices within their new workplace.
Characteristics
Organizational culture may play out in many ways. To get a feel for an organization’s culture, observe how employees interact with each other formally or informally. Note the dress code and whether the organization has casual days.
Also take into account work hours, whether options such as flex time and telecommuting are available, and the organization’s position about maintaining a work-life balance.
Consider how conflict is addressed within the organization. Moreover, assesses the organizational structure, how often senior managers interact with other organizational members, and the degree of transparency by which the organization shares information.
Characteristics of Organizational Culture
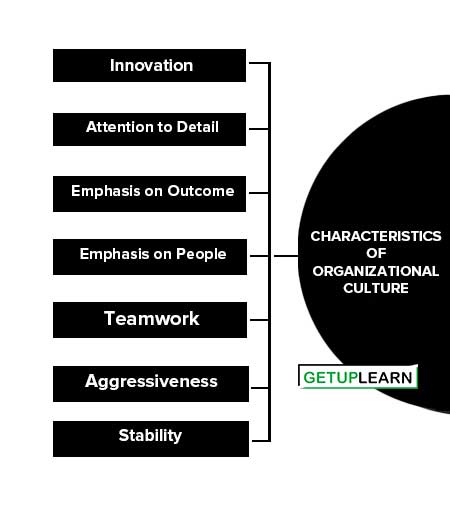
The seven characteristics of organizational culture are:
- Innovation
- Attention to Detail
- Emphasis on Outcome
- Emphasis on People
- Teamwork
- Aggressiveness
- Stability
Innovation
Innovation (Risk Orientation): Companies with cultures that place a high value on innovation encourage their employees to take risks and innovate in the performance of their jobs.
Attention to Detail
Attention to Detail (Precision Orientation): A culture that places a high value on attention to detail expects its employees to perform their work with precision. A culture that places a low value on this characteristic does not.
Emphasis on Outcome
Emphasis on Outcome (Achievement Orientation): Companies that focus on results, but not on how the results are achieved, place a high emphasis on this value of organizational culture. A company that instructs its sales force to do whatever it takes to get sales orders has a culture that places a high-value emphasis on outcome characteristics.
Emphasis on People
Emphasis on People (Fairness Orientation): Companies that place a high value on this characteristic of organizational culture place a great deal of importance on how their decisions will affect the people in their organizations. For these companies, it is important to treat their employees with respect and dignity.
Teamwork
Teamwork (Collaboration Orientation): Companies that organize work activities around teams instead of individuals place a high value on this characteristic of organizational culture. People who work for these types of companies tend to have a positive relationship with their co-workers and managers.
Aggressiveness
Aggressiveness (Competitive Orientation): This characteristic of organizational culture dictates whether group members are expected to be assertive or easygoing when dealing with companies they compete with within the marketplace. Companies with an aggressive culture place a high value on competitiveness and outperforming the competition at all costs.
Stability
Stability (Rule Orientation): A company whose culture places a high value on stability is rule-oriented, predictable, and bureaucratic in nature. These types of companies typically provide consistent and predictable levels of output and operate best in non-changing market conditions.
Types of Organizational Culture
The practices, principles, policies, and values of an organization form its culture. The culture of an organization decides the way employees behave amongst themselves as well as the people outside the organization. Let us understand the various types of organizational culture:
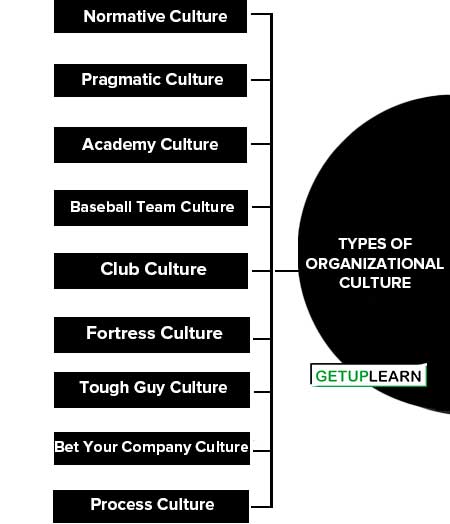
- Normative Culture
- Pragmatic Culture
- Academy Culture
- Baseball Team Culture
- Club Culture
- Fortress Culture
- Tough Guy Culture
- Bet Your Company Culture
- Process Culture
Normative Culture
In such a culture, the norms and procedures of the organization are predefined and the rules and regulations are set as per the existing guidelines. The employees behave in an ideal way and strictly adhere to the policies of the organization. No employee dares to break the rules and sticks to the already laid policies.
Pragmatic Culture
In a pragmatic culture, more emphasis is placed on the clients and the external parties. Customer satisfaction is the main motive of the employees in a pragmatic culture. Such organizations treat their clients as Gods and do not follow any set rules. Every employee strives hard to satisfy his clients to expect maximum business from their side.
Academy Culture
Organizations following academy culture hire skilled individuals. The roles and responsibilities are delegated according to the background, educational qualification, and work experience of the employees. Organizations following academy culture are very particular about training the existing employees.
They ensure that various training programs are being conducted at the workplace to hone the skills of the employees. The management makes sincere efforts to upgrade the knowledge of the employees to improve their professional competence.
The employees in an academy culture stick to the organization for a longer duration and also grow within it. Educational institutions, universities, and hospitals practice such a culture.
Baseball Team Culture
A baseball team culture considers the employees as the most treasured possession of the organization. The employees are the true assets of the organization and have a major role in its successful functioning.
In such a culture, the individuals always have an upper edge and they do not bother much about their organization. Advertising agencies, event management companies, and financial institutions follow such a culture.
Club Culture
Organizations following a club culture are very particular about the employees they recruit. The individuals are hired as per their specialization, educational qualification, and interests. Each one does what he is best at. The high-potential employees are promoted suitably and appraisals are a regular feature of such a culture.
Fortress Culture
There are certain organizations where the employees are not very sure about their careers and longevity. Such organizations follow a fortress culture. The employees are terminated if the organization is not performing well. Individuals suffer the most when the organization is at a loss. Stockbroking industries follow such a culture.
Tough Guy Culture
In a tough-guy culture, feedbacks are essential. The performance of the employees is reviewed from time to time and their work is thoroughly monitored. Team managers are appointed to discuss queries with the team members and guide them whenever required. The employees are under constant watch in such a culture.
Bet Your Company Culture
Organizations that follow bet your company culture take decisions that involve a huge amount of risk and the consequences are also unforeseen. The principles and policies of such an organization are formulated to address sensitive issues and it takes time to get the results.
Process Culture
As the name suggests the employees in such a culture adhere to the processes and procedures of the organization. Feedback and performance reviews do not matter much in such organizations. The employees abide by the rules and regulations and work according to the ideologies of the workplace.
FAQs About the Organizational Culture
What is the meaning of organizational culture?
Organizational culture is a system of shared assumptions, values, and beliefs, which governs how people behave in organizations. These shared values have a strong influence on the people in the organization and dictate how they dress, act, and perform their jobs.
How to Create Culture in an Organisation?
Organizational Behaviour is so important matter for an organization to operate its business. We know every organization their ultimate target is to maximize profit by satisfying customers’ need, want and demand successfully. If any organization wants to do business for a long time it must have to organize its business organization and create a good culture to compete in a highly competitive global market.
What is the simple definition of organizational culture?
“Organizational culture can be defined as a pattern of basic assumptions invented, discovered, or developed by a given group as it learns to cope with its problems of external adaptation and internal integration – that has worked well enough to be considered valuable and therefore, to be taught to new members as the correct way to perceive, think and feel in relation to those problems.“ By Edgar Schein
What are the elements of organizational culture?
Some of the elements of organizational culture are 1. Artifacts 2. Organizational Values 3. Organizational Beliefs 4. Organizational Norms 5. Assumptions 6. Characteristics.
What are the characteristics of organizational culture?
Innovation, Attention to Detail, Emphasis on Outcome, Emphasis on People, Teamwork, Aggressiveness, and Stability are the characteristics of organizational culture.
What are the types of organizational culture?
The following are the 9 types of organizational culture: Normative Culture, Pragmatic Culture, Academy Culture, Baseball Team Culture, Club Culture, Fortress Culture, Tough Guy Culture, Bet Your Company Culture, and Process Culture.
