Table of Contents
- 1 What is Planning Process?
- 2 Planning Process
- 3 8 Types of Plans
-
4 Objectives of Planning
- 4.1 Achievement of Organizational Objectives
- 4.2 Fulfillment of Organizational Commitments
- 4.3 It Facilitates Decision Making
- 4.4 It Provides Stability to Organizations
- 4.5 Overall View of Organization or Coordination
- 4.6 Development of Managers
- 4.7 Promotes Innovation or Creativity
- 4.8 Basis for Control
- 4.9 Reduction of Risk
- 4.10 Morale Boost Up
- 4.11 Facilitates Delegation
- 5 Need for Planning
- 6 Limitations of Planning
- 7 FAQ Related to Planning Process
What is Planning Process?
Planning is a process that embraces a number of steps to be taken. Planning is an intellectual exercise and a conscious determination of courses of action. Therefore, it requires courses of action.
The planning process is valid for one organization and for one plan, but may not be valid for other organizations or for all types of plans, because various factors that go into the planning process may differ from organization to organization or from plan to plan.
For example, the planning process for a large organization may not be the same for a small organization.
Planning Process
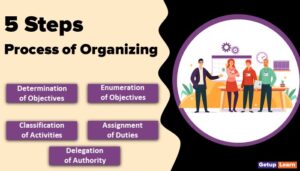
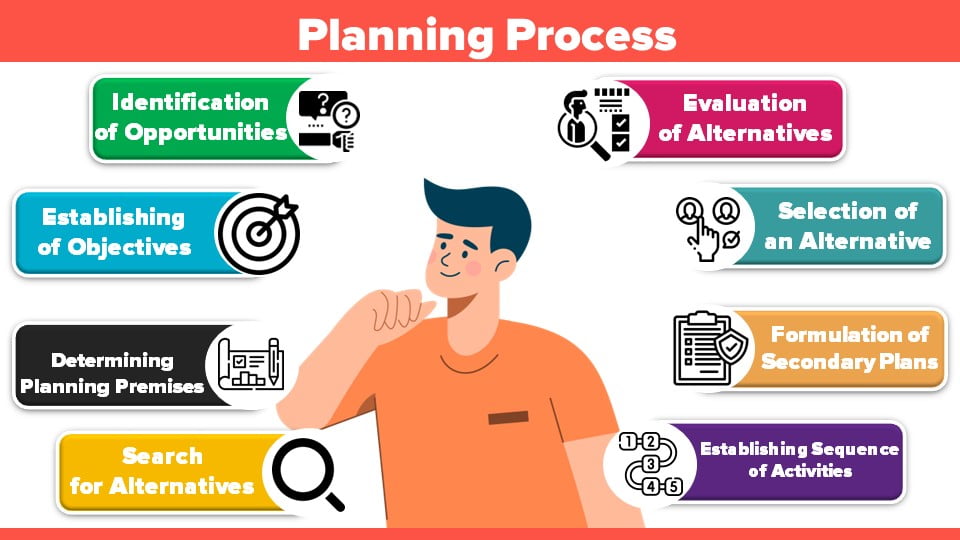
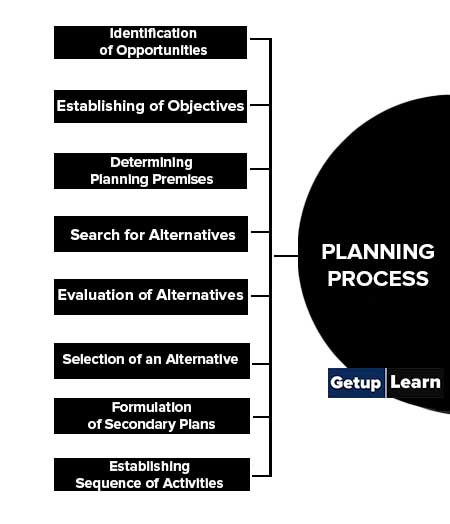
These are the significant steps involved in the planning process of a major organization or enterprise:
- Identification of Opportunities
- Establishing of Objectives
- Determining Planning Premises
- Search for Alternatives
- Evaluation of Alternatives
- Selection of an Alternative
- Formulation of Secondary Plans
- Establishing Sequence of Activities
Identification of Opportunities
This is the beginning of the planning process though it is not part of it. However, this leads to the formulation of plans by providing insight as to whether opportunities exist for taking up particular plans.
The purpose of the identification of opportunities is to enable an organization to adapt to its environment. This is a preliminary stage where analysis of the environment is not done very elaborately but analysis relating to the determination of opportunities is carried out.
Identification of opportunities involves a preliminary look at possible opportunities in order to ascertain whether these opportunities could be exploited by the organization to its advantage.
Establishing of Objectives
It is here that the actual planning process starts. At this stage, the organizational and unit objectives are established. Objectives indicate the end result that is to be achieved and the task to be performed.
Organizational objectives should be laid down in all key result areas. Key result areas help an organization in achieving its objectives. Examples of key result areas for an organization may be profitability, productivity, public responsibility, and so on.
Once the overall objective of an organization is laid, the objectives of lower units can be established. There will always be a hierarchy of objectives in an organization.
Determining Planning Premises
Once the organizational objective is laid down, the next step is to determine the planning premises. Planning premises refer to the limits or conditions under which planning activities will be undertaken. They are assumptions based on Internal and expected environmental conditions.
Internal premises include organizational policies and procedures, various resources, etc., External premises include factors in the task environment like social, political, and technological, competitors’ plans and actions, government regulations, and policies, etc., and Forecasting plays a very vital role in planning premises.
Plans are formulated based on both internal and external factors. Planning premises vary at different levels of planning. At the top levels, it is more external in nature. At the lower level, there is a change from external to internal.
Search for Alternatives
There are several ways through which an objective can be accomplished. The task of management is to search for these alternative ways.
One problem with alternatives is not that of finding alternatives alone, but reducing the number of alternatives so that the most prominent ones may be taken up for evaluation. Through preliminary examination and screening, unwanted alternatives can be eliminated.
Evaluation of Alternatives
At this stage, feasible alternatives are evaluated in order to see how each alternative contributes to the organizational objectives in light of its strength and constraints. Each alternative should be subjected to a close examination to determine its suitability.
Many quantitative techniques are available to evaluate alternatives. Alternatives are evaluated on basis of their cost, limited resources, expected returns risks, and many intangible factors.
Selection of an Alternative
Once the evaluation is over, the most appropriate alternative is selected. Sometimes two or more alternatives may be suitable. Under such a situation the planner may choose more than one alternative. The alternative selected should be the most optimum one under the present circumstances.
Formulation of Secondary Plans
Once the basic plan is determined, the secondary plans are formulated to support it. In an organization, there may be a number of secondary plans which are developed within the framework of the basic overall plans. Basic plans cannot be executed properly unless they are supported by secondary plans.
Establishing Sequence of Activities
In this step, the sequence of activities is established after formulating the basic and secondary plan, in order to put the plan into action. This clearly lays down the pattern of work to be performed and the people who will have to perform it.
8 Types of Plans
Planning is a process and plan is its outcome. The plan is a sort of commitment to accomplish all the activities needed for the attainment of special results, from this point of view there are many plans.
The following study will help in understanding different types of plans:
Objectives
Objectives are those endpoints for the attainment of which all the activities are undertaken. For example, to improve the communication system to hold regular staff meetings and publish a newsletter.
Strategies
Strategies refer to those plans which are prepared in view of the move of the competitors and whose objective is to make possible the optimum utilization of resources.
Policies
Policies are those general statements that are decided for the guidance of the employees while taking decisions. Their purpose is to lay down a limit within which a particular work can be done or a decision taken. Objectives decide what is to be achieved and the policies tell us how it can be achieved.
Procedures
Procedures are those plans which determine the sequence of any work performed. For example, the recovery of money from the debtors can be done in the following order: Writing letters, connecting on the telephone, Meeting personally, and taking legal action.
This is the procedure of collecting money from all the debtors. There is a difference between policies and procedures. There can be two policies of the organization regarding the recovery of money from the debtors. (A) Tight collection policy, and (B) Lenient collection policy.
Under the first policy, an effort is made to recover money from debtors by treating them harshly. Under the second policy, the debtors will be given enough time for the payment of money while treating him leniently.
Methods
Methods are that plan which determines how different activities of the procedure are completed. Methods are not related to all steps but only to one step of the procedure. It is more detailed than the procedure.
There may be many methods to do a particular work. After extensive study, a method has to be selected from which a worker feels minimum fatigue, an increase in productivity and there is a reduction in costs.
Rules
Rules tell us what is to be done and what is not to be done in a particular situation. In the absence of rules, there is no need to take any decision. Whatever is said in the rules has to be followed without any thinking.
For example, the rule No smoking in the factory is applicable to everybody and it must be observed. Provision for punishment in case of non-observing of the rule can also be made.
Budget
Budgets describe the desired results in numerical terms. A budget is that planning which provides detailers about estimated money, material time, and other resources for the achievement of pre-determined objectives of various departments.
For example, the sales department‘s budget gives estimated figures about the type of material that will be purchased, its quantity, the time of purchase and the amount to be spent on it. Similarly, budgets of other departments are also prepared.
Programs
A program means a single-use comprehensive plan laying down the what, how who and when of accomplishing a specific job. Through the program, the managers are informed in advance about various needs so that there is no problem in the future.
The programmers can be of different types-production programs, Training programs Sales promotion programs management development programs, etc.
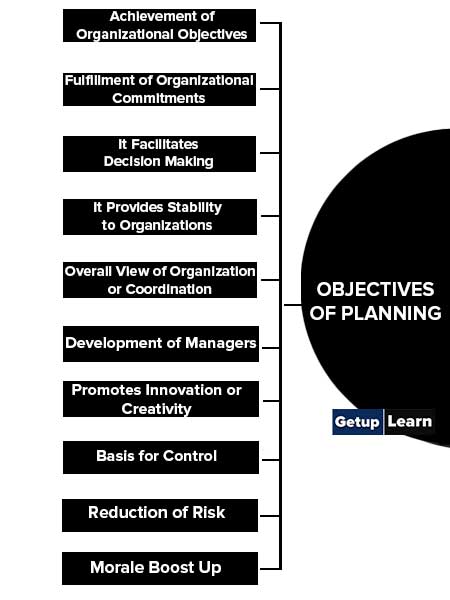
Objectives of Planning
Planning is important because it enables the organization to survive and grow in the dynamic, changing environment. Planning is the basis of the distinction between successful and unsuccessful organizations.
In a dynamic environment, planning helps in scanning environmental changes and forecasting the future. These are the following objectives of planning:
- Achievement of Organizational Objectives
- Fulfillment of Organizational Commitments
- It Facilitates Decision Making
- It Provides Stability to Organizations
- Overall View of Organization or Coordination
- Development of Managers
- Promotes Innovation or Creativity
- Basis for Control
- Reduction of Risk
- Morale Boost Up
- Facilitates Delegation
Achievement of Organizational Objectives
Planning helps the organization achieve its objectives. Planning provides the path for the achievement of organizational goals with minimum waste of time, money, and energy. It bridges the gap between where we are and where we want to go.
Fulfillment of Organizational Commitments
Organizations have long-term and short-term commitments toward society, depending on their nature. A defense organization, for example, has long-run commitments while a retailer is more interested in short-term goals or responsibilities. These commitments or goals of the organization can be fulfilled through planning.
It Facilitates Decision Making
Decision-making is deciding what to do when managers face a problem-solving situation and adopting the best way out of the available courses/ ways of doing it. It is “the process of choosing a course of action from two or more alternatives.
Managers have to make decisions like what to produce and how to produce, what are the organizational resources and how can they are effectively allocated over different functional areas, what are their primary goals profit or social responsibility, and many more. Planning helps to decide a course of action that will solve the specific problem.
It Provides Stability to Organizations
Organizations that plan their operations are more stable than others. Managers foresee risks and prepare the organizations to face them when they occur. Planning precedes all other managerial functions and coordinates them for providing stability to the organization.
Planning before organizing (what kind of organization structure), planning before staffing (what kind of people), planning before direction (what kind of motivation, leadership, and communication system), and planning before control (the controlling techniques to achieve standards of performance) promotes group effort and teamwork to give the right direction to organizational activities.
Overall View of Organization or Coordination
The organization is a structure of relationships where authority and responsibility are clearly defined. Planning coordinates the functions performed by individual members and departments and unifies them into a single goal the organizational goal. It unifies inter-departmental activities so that all departments work according to plans.
Optimum utilization of resources/efficiency of operations: Organizations work with limited resources. Planning allocates these resources over different objectives and functional areas (production, personnel, finance, and marketing) in the order of priority.
This results in the optimum utilization of scarce organizational resources (men, material, money, etc.) and their effective conversion into productive outputs.
Development of Managers
Planning involves imagination, thought, and creativity by managers. Managers develop their conceptual and analytical skills to plan and coordinate organizational activities with the external environment.
Promotes Innovation or Creativity
Planning involves forecasting. Managers foresee the future, analyze the strengths of their competitors and think of new and innovative ways of promoting their products. Planning promotes new ideas, new products, and new relationships and, thus, promotes innovation and creativity.
Basis for Control
Planning frames standards of performance and control ensure the achievement of standards. Controlling involves the measurement of actual performance, its comparison with standard performance, finding deviations, and taking steps to remove the deviations to make better plans for the future. Unless there are plans, there will be no control. Planning is, thus, the basis for control.
Reduction of Risk
Risk is a situation where moderately reliable information is available about the future but it is incomplete. Uncertainty, on the other hand, is a situation where no information is available about the future.
Changes in government policies are a situation of uncertainty while the entry of competitors in the market with better technology represents a situation of risk. Planning helps to reduce risk through forecasting.
Morale Boost Up
If organizational plans succeed and goals are achieved, managers and employees feel satisfied and morally boost up to concentrate on organizational activities. Successful planning, thus, promotes the success of the organization and higher standards in the next planning cycle.
Facilitates Delegation
Well-designed plans enable managers to concentrate on strategic issues and delegate routine/operating activities to lower-level managers. It, thus, facilitates delegation.
Need for Planning
These are the following reasons need for planning:
- Essential for Modern Business
- Related to Performances
- Focus on Objectives
- Proper Allocation of Resources
- Facilitates Control
- Helpful in Decision Making
- Avoiding Business Failures
Essential for Modern Business
The growing complexities of modern business, rapid technological changes, the meaning of economics to international competition, and changes in consumer tastes necessitate.
Planning not only in the current context but also in the future environment. Planning always takes into account all possible features of development.
Planning helps in setting goals for each function and for each employee. The concerns having formal planning have performed better as compared to those where planning is not taken up as a regular activity. Studies have provided that planning has been an instrument in improved performance.
Focus on Objectives
The thrust of formal planning is on setting objectives and providing guidelines for reaching them. Objectives provide a direction and all planning decisions are directed toward achieving them. It ensures maximum utilization of managerial time and effort.
Proper Allocation of Resources
The needs of the organization are anticipated with the help of planning. The acquisition and allocation of resources can be properly planned thus minimizing wastages and ensuring optimal utilization of these resources.
Facilitates Control
Planning can be used to devise a mechanism of control. There can be quantitative targets and their comparison with actual performance can bring to notice any deviations. A periodical review can also help in pointing out low performance.
The deviations in production, sales, profits, etc. may come to light during periodic investigations and remedial action can be taken.
Helpful in Decision Making
Planning is helpful in the process of decision-making. Since planning helps in specifying the actions to be taken for achieving organizational objectives, it serves as a basis for decision-making for the future. The objectives, plans, policies, schedules, rules, etc. serve as guidelines for routine decision-making.
Avoiding Business Failures
Business failures may be due to wrong and unscientific planning. Bad planning may result in the wastage of human and physical resources. The enterprise may not be able to face competition from well-planned units.
Good planning will help in utilizing available resources in the best possible way thus reducing the chances of failure.
Limitations of Planning
Effective planning is not an easy task because there are a number of practical difficulties encountered in the planning process. There are a number of reasons for the failure of planning in practice.
These are the limitations of planning:
- Planning is quite a costly and time-consuming process. time is spent on forecasting, evaluating alternatives, etc. Unlimited amount of By the time a plan is established the environment might change and this requires a complete revision of the plan. Besides this, cost also increases.
- Planning is a future-oriented activity that is based on the forecast. As the period of planning increases, the accuracy of forecasting diminishes. Planning loses its value if reliable and adequate data is not available.
- Planning becomes rigid at times because of internal inflexibilities. This reduces individual initiative and freedom and caused delays in decision-making. Internal inflexibilities like rigid policies and procedures and limited resources affect the planning process.
- External factors beyond the control of an organization affect the effectiveness of planning. These are very difficult to predict and this makes the execution of plans very difficult. External factors like government control, technological change, and trade unions affect the planning process.
- Another important limitation of planning is resistance to change. The human elements in an organization always resist change; they are more concerned about the present rather than the future, which is uncertain. Planning being forward-looking is always affected by this resistance to change.
- The entire planning process may fail if people involved in it do not formulate correct plans. The reasons for the failure of people in planning may be due to a number of reasons like lack of commitment to planning, lack of delegation of authority, excessive reliance on past experience, tendency to overlook premises, etc.
What are the 8 steps in the planning process?
The following is the planning process:
1. Identification of Opportunities
2. Establishing of Objectives
3. Determining Planning Premises
4. Search for Alternatives
5. Evaluation of Alternatives
6. Selection of an Alternative
7. Formulation of Secondary Plans
8. Establishing Sequence of Activities.
What are the 8 types of plans?
The following are the types of plans:
1. Objectives
2. Strategies
3. Policies
4. Procedures
5. Methods
6. Rules
7. Budget
8. Programs.
What are the objectives of planning?
The following are the objectives of planning:
1. Achievement of Organizational Objectives
2. Fulfillment of Organizational Commitments
3. It Facilitates Decision Making
4. It Provides Stability to Organizations
5. Overall View of Organization or Coordination
6. Development of Managers
7. Promotes Innovation or Creativity
8. Basis for Control
9. Reduction of Risk
10. Morale Boost Up
11. Facilitates Delegation.
What is the need for planning?
Following are the some of needs for planning:
1. Essential for Modern Business
2. Related to Performances
3. Focus on Objectives
4. Proper Allocation of Resources
5. Facilitates Control
6. Helpful in Decision Making
7. Avoiding Business Failures.