Table of Contents
What is the Meaning of Planning?
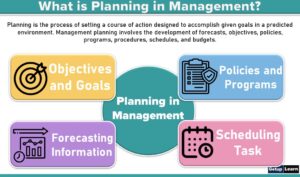
Planning is deciding in advance what is to be done. When a manager plans, he projects a course of action for the future, attempting to achieve a consistent, coordinated structure of operation aimed at the desired result. Below this, we will be learning about the importance of planning.
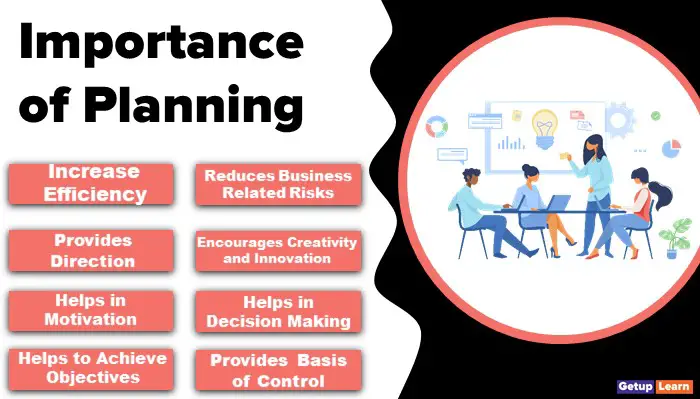
Importance of Planning
Planning increases the efficiency of an organisation. All business organisations would like to be successful, have goodwill in the market, and have higher profits. For attaining these attributes the thinking process has to be very effective.
These are the various importance of planning explained below:
- Increase Efficiency
- Reduces Business Related Risks
- Provides Direction
- Encourages Creativity and Innovation
- Helps in Motivation
- Helps in Decision Making
- Helps to Achieve Objectives
- Provides Basis of Control
Increase Efficiency
Planning makes optimum utilization of all available resources. It helps to reduce wastage and avoids duplication of work.
Planning helps to forecast business-related risks and also helps to take necessary precautions to avoid these risks and prepare for future uncertainties.
Provides Direction
Direction means to give proper information, accurate instructions and guidance to the subordinates. Planning tells us what to do, how to do and when to do it. It helps the organization to achieve its goals through systematic coordination of the employees.
Encourages Creativity and Innovation
Planning helps managers to express their creativity and innovation. It brings satisfaction to the managers and eventually succeeded in the organization.
Helps in Motivation
A good plan provides various financial and non-financial incentives to both managers and employees. These incentives motivate them to work hard and achieve the objectives of the organization.
Helps in Decision Making
A manager makes many different plans. Then they evaluate every course of action and choose the best strategy. So decision-making is facilitated by planning.
Helps to Achieve Objectives
Without Planning each and every activity will be based on trial and error which will give rise to confusion. Every organization has certain targets. Planning helps an organization achieve its aims by avoiding overlapping, confusion and misunderstanding.
Provides Basis of Control
Planning is the first function of management. The other functions like organizing, staffing, directing and controlling etc. are organized for implementing plans. Controlling records the actual performance and compares it with the standards set.
In case the performance is less than the standards set then deviations are ascertained and proper corrective measures are taken to improve the performance in future.
Planning and controlling both are dependent on each other. Planning establishes standards for controlling. Therefore, Planning is necessary for the effective and efficient functioning of every organization irrespective of its size, type and objectives.
Steps in Planning Process
These are the steps in planning process each step is explained well and in easy language which help to understand:
- Establishing Verifiable Goals
- Establishing Planning Premises
- Deciding Planning Period
- Finding Alternative Course of Action
- Evaluating and Selecting a Course of Action
- Implementing Plan
- Measuring and Controlling the Programme
Establishing Verifiable Goals
The first step in planning is to determine the enterprise’s objectives. These are more often set by upper-level managers. The objective may vary from a desired sales volume or growth rate to the development of a new product.
Establishing Planning Premises
Plans are made to operate in the future. The second step in planning is to establish planning premises i.e. assumption on the basis of which plans will be ultimately formulated.
Planning premises are vital to the success of planning as they supply important facts and information related to the future like population trends, economic conditions, production costs, government control etc.
Deciding Planning Period
The next task is to decide the period of the plan whether it’s a yearly plan or a plan which is spread over a longer span of time. The choice of planning period is decided based on the time required in the development of the new product, the time required to recover capital investment and the length of commitments already made.
Finding Alternative Course of Action
The next in planning is to search for and examine an alternative course of action. For Ex-Products may be sold directly to the consumers by the company’s salesman or through exclusive agencies.
Evaluating and Selecting a Course of Action
Having searched for alternative courses, the next step is to evaluate and analyze them in the light of premises and goals and select the best alternative. This is done with the help of quantitative techniques and operations research.
Implementing Plan
The best possible course of action has now to be implemented in other words, putting the plan into action. For this, the managers have to develop derivative plans for each department. A draft version of the action plan should be communicated to inform those directly affected and gain their cooperation.
Measuring and Controlling the Programme
The process of control is a critical part of any plan. Managers need to check the progress of their plans i.e. follow up so that they can take remedial action if the plan is not working as per schedule or change the original plan if it is unrealistic.
Objectives of Organisation
These are the related terms of the objectives of organisation:
Objectives
Objectives may be defined as the goals which an organization tries to achieve. Objectives are the ends towards which the activities of the enterprise are aimed. Objectives provide direction to various activities and serve as a benchmark for measuring the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization.
Strategies
A strategy is a special kind of plan formulated to meet the challenge of the policies of the competitors. Strategy can be shaped by the general forces operating in an industry and the economy. The strategy must be consistent with the external environment.
Policies
Policies may be described as plans which are meant to serve as broad guidelines for decision-making in a firm. Policies exist at various levels of the enterprise. A policy should be definite, positive and clear.
A policy is a standing plan which assists decision-making and should be referred to as a general statement of the established rule.
For example, A firm has a policy of promotion from within the organization. If a vacancy arises; the first preference is given to existing employees.
Procedure
Procedure lays down the manner or method by which work is to be performed in a standard and uniform way. A procedure is a standing plan acting as a means of implementing a policy.
For Example, The sales department lays down a policy to execute all orders within 48 hours. So a procedure has to be followed in a chronological and systematic order to fulfil the orders.
Programmes
Programmes are precise plans which need to be made to discharge a non –repetitive task. The essential ingredients of every programme are time phasing and budgeting. Specific dates should be laid down for the completion of each successive stage of a programme.
For Example, An enterprise has a programme of opening 5 branches in different parts of a country so they have to allocate funds and time period for:
- Securing the necessary accommodation.
- Recruiting personnel to manage the business.
- Arrange the supply of goods that are to be sold through the branches Often a single step in a programme is set up as a project.
Rules
Rules are explicit statement that tells the members of the organization what they can or cannot do. Rules do not allow any room for interpretation because it clearly specifies the action needed to be done in a particular situation. Rules enforce discipline.
For example, The use of Mobile Phones at the workplace during office hours is restricted.
Budgets
Budgets are plans for future periods of time containing statements of expected results in numerical terms. Budgets are very useful for an enterprise.
Being expressed in numerical terms, they facilitate the comparison of actual results with planned ones and serve as a control device. The important budgets are sales budget, production budget, cash budget, Revenue, and Expense Budget.
What is the importance of planning?
Following are the importance of planning given below:
1. Increase Efficiency
2. Reduces Business-Related Risks
3. Provides Direction
4. Encourages Creativity and Innovation
5. Helps in Motivation
6. Helps in Decision Making
7. Helps to Achieve Objectives
8. Provides Basis of Control
What are the steps in planning process?
The following are the steps in planning process:
1. Establishing Verifiable Goals
2. Establishing Planning Premises
3. Deciding Planning Period
4. Finding an Alternative Course of Action
5. Evaluating and Selecting a Course of Action
6. Implementing Plan
7. Measuring and Controlling the Programme.
What are the objectives of organisation?
The following are the objectives of organisation:
4.1 Objectives
4.2 Strategies
4.3 Policies
4.4 Procedure
4.5 Programmes
4.6 Rules
4.7 Budgets.