Table of Contents
What is a Project Report?
A project report is a report that provides all the necessary details of the unit proposed to be established either for the manufacture of a product or for rendering a service. It is also used as a tool for anticipating and solving problems that may creep in during the course of running the project at a later stage. It is nothing but a blue-print of all those activities that an entrepreneur proposes to engage in.
The project report is an essential document for procuring financial assistance from financial institutions and banks and also to fulfill other formalities for the implementation of the project.
Therefore, the report should provide a complete framework for the presentation of all information that would be required by financial institutions for appraising the project. It would also enable the entrepreneur to know how much money, material, and manpower would be required to set up the project. Thus, a project report for an entrepreneur is very similar to a guide map for a traveler.
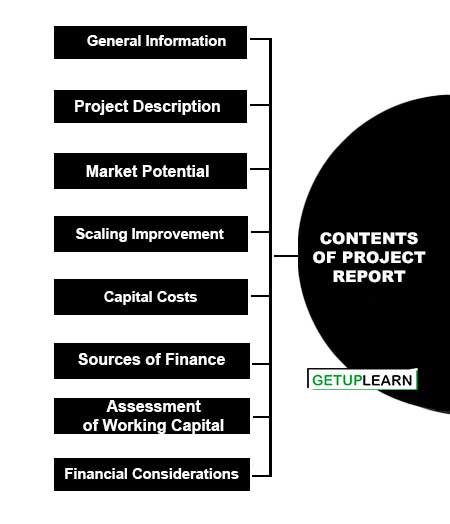
Contents of Project Report
A project report may be prepared in different ways by different entrepreneurs. There is no standard pattern for it. However, it must contain all the information necessary to appraise it and make a financial decision by lending institutions.
The amount of information to be furnished in the report depends upon the size of the unit, the nature of production, and the amount of finance required. The following guidelines will help an entrepreneur to prepare a report generally for establishing a small-scale unit. The relevant information should be given under the following heads:
- General Information
- Project Description
- Market Potential
- Capital Costs
- Sources of Finance
- Assessment of Working Capital Requirements
- Financial Considerations
- Economic and Social Considerations
General Information
To start with, some basic information should be provided. These include:
- Name and address of the entrepreneur.
- Qualification, experience, and capabilities of the entrepreneur.
- Profile of the industry to which the project belongs.
- Constitution and organizational structure of the enterprise whether sole trader or partnership and if partnership, whether registered or not.
- Registration certificate from the Directorate of Industries DIG. whether obtained or to be obtained.
- Range of products to be manufactured and their utility.
- Competitive advantages of the proposed product over its substitutes.
Project Description
Under this head, a brief particulars of the project should be given in the report. Generally, the particulars relate to the following:
- Site
- Infrastructure
- Raw Materials
- Skilled Labour and Personnel Requirements
- Consumables Utilities
- Disposal of Waste
- Transportation and Communication
- Machinery Equipment & Common Facilities
- Manufacturing Process and Technology
- Balancing of Plant and Quality
- Research and Development
Market Potential
It is vital that the prospective entrepreneur should state in his project report the potentialities for the marketing of his products. It is preferable to prepare a detailed market survey report providing information about demand and supply position, competitors’ position, price expected, etc.
It is advisable to obtain a few letters from future clients, and machinery/raw material suppliers to make the project report more credible. However. the following aspects relating to market potential should be given in the report:
- Demand and Supply Position
- Cost and Price Position
- Marketing Strategy
- After-Sales Services
- Seasonality and Demand
Capital Costs
An estimate of the capital expenditures to be incurred by the unit on various items should be given in the report. This estimation should be scientific, realistic, and accurate, since, many units are found to be running serious problems due to faulty and inadequate estimates of funds requirements made at the initial stage.
The various components of capital items may relate to the following:
- Land and building costs
- Costs of plant and machinery
- Installation charges
- Other miscellaneous assets like furniture and fixtures, vehicles,
- Tools, patterns, etc.
- Preliminary expenses and preoperative expenses
- Contingency provision against future rise in price or to meet
- Unforeseen expenditures
- Margin for working capital
Sources of Finance
The report should also include probable sources of finance. They include:
- Owner’s contribution towards the proposed venture,
- Capital subsidies from State/Central Governments if any,
- Loans and deposits proposed to be raised,
- Credit limits expected from financial institutions,
- Finance from friends and relatives,
- Adequacy of total funds available to meet the total cost of the project.
Assessment of Working Capital Requirements
As already stated, while estimating the capital costs, the margin for working capital has to be taken into account, since, no unit can function without the availability of adequate working capital finance.
Hence, the estimate of the working capital requirements should be made and shown with the total cost of the project itself. Even though some formats for working capital assessment have been designed, most entrepreneurs have n tendency to present their working capital requirements’ in their own way.
It leads to the recasting of these estimates as per the requirements of financing agencies. This is a waste of time and creates more problems. Hence, entrepreneurs are advised to present the data in the prescribed form. The working capital calculation involves the following:
- Expenditures to be incurred on raw material stock,
- Expenses on goods under process,
- Costs involved in finished goods stock,
- Expenses on stores and spares,
- Expenses of a recurring nature are mostly in the form of monthly expenses.
Financial Considerations
The proposed project would earn sufficient livelihood only when it is financially sound and the products to be taken up for production are profitable. Moreover, the project must be able to retrieve the investments made within its life cycle.
For this purpose, a projected profit and loss account should be prepared. It would indicate likely sales revenue, cost of production, other expenses, and profit. All these estimates should be made on a realistic basis.
It is also desirable to mention the abatement costs, i.e. the costs to be incurred for controlling the environmental damage like pollution, effluents, emissions, etc. The abatement cost will involve the value of the additional engineering and technology needed for treating effluents and emissions.
Again, the soda-economic benefits that may accrue should also be specifically stated in the report. The examples of some of these benefits are given below:
-
Promotion of Employment: The member of persons proposed to be employed in relation to the employment situation of that area may be mentioned.
-
Import Substitution: The extent to which and the manner in which the proposed unit would achieve import substitution and the probable benefits that may be expected can be mentioned in the report.
-
Promotion of Ancillaries: Whether the unit promote ancillary units to meet its sub-contracting requirements in case the unit requires sub-contracting functions’? H must be specifically given in the report.
-
Export Potentials: Whether the unit has export potential and to what extent its products could be exported to other countries should be mentioned in the report.
-
Utilization of Local Resources: The possibility of utilizing local resources, which are presently a waste, should be stated in the report.
- Development of the Area: To what extent the establishment of the unit will bring out an overall development of the local area should also be mentioned in the report.
FAQs About the Project Report
What are the contents of the project report?
These are the contents of the project report:
1. General Information
2. Project Description
3. Market Potential
4. Capital Costs
5. Sources of Finance
6. Assessment of Working Capital Requirements
7. Financial Considerations
8. Economic and Social Considerations.