Table of Contents
- 1 What are Barriers to Communication?
- 2 Types of Barriers to Communication
-
3 How to Overcome Barriers of Communication
- 3.1 Eliminating Differences in Perception
- 3.2 Use of Simple Language
- 3.3 Reduction and Elimination of Noise Levels
- 3.4 Active Listening
- 3.5 Emotional State
- 3.6 Simple Organizational Structure
- 3.7 Avoid Information Overload
- 3.8 Provide Constructive Feedback
- 3.9 Proper Media Selection
- 3.10 Flexibility in Meeting the Targets
- 4 FAQ Related to Barriers to Communication
What are Barriers to Communication?
The communication process is disturbed by certain obstacles which obstacles are called “Barriers to communication.’’ In other barriers to communication are anything that tries to be a hindrance in the communication process between sender and receiver.
Table of Contents
No fixed classification of the barriers to communication is possible. However, for the purpose of easy understanding of their nature, we may classify them into four categories.
Types of Barriers to Communication
The various types of barriers to communication are given as follows:
- Physical or Environmental Barriers
- Physiological or Biological Barriers
- Semantic Barriers or Language Barriers
- Personal Barriers
- Emotional Barriers
- Socio-Psychological Barriers
- Cultural Barriers
- Organisational Barriers

Physical or Environmental Barriers
These are environmental factors that limit the sending and receiving of messages. Often the term Noise is used as a blanket term to refer to this kind. They include distance, noise, breakdown of communication media, faulty mechanical equipment, etc. Many barriers arise in the surroundings or our environment. These barriers create problems or confusion in communication.
Physical barriers may include:
- Noise
- Time and Distance
- Wrong Choice of Medium
- Surroundings
- Inadequacy of Message Design/poorly Expressed Message
Noise
It is the first major barrier to communication. Communication gets disturbed by the noise that occurs at the transmission level. For example, the noise of traffic around a school obstructs the flow of information between a student and a teacher. Similarly, poor signal while talking over cell phone or using public address system or watching TV also disrupts communication. Bad weather conditions may also sometimes cause barriers to communication.
Time and Distance
These may also obstruct the smooth flow of information. For example, time differences between two different countries may affect communication between two people. Another example will be two people working in two different shifts may face problems in communicating effectively. Improper seating arrangement in a class also may act as a barrier to the process of communication.
Wrong Choice of Medium
This can cause a barrier to communication if the sender uses the wrong channel for the transmission of the message with is improper for the audience. For example, if an expert uses a powerpoint presentation for the uneducated factory workers then they will be unable to understand it.
Surroundings
Adverse or extreme weather conditions like, too hot or too cold, their surroundings do have a direct effect on the effectiveness of communication. As environment causes a psychological effect like, too hot weather will cause restlessness and humidity, whereas too cold weather makes a person feel lazy to communicate.
Inadequacy of Message Design/poorly Expressed Message
No matter how clear the idea is in the mind of the sender, it may still get affected by the use of poorly chosen words, long sentences, complex words, poor organization of ideas, use of jargon.
Physiological or Biological Barriers
Physiological barriers are related to a person’s health and fitness. These may arise due to disabilities that may affect the physical capability of the sender or the receiver. Proper functioning of the vocal cords, hands, fingers, eyes is necessary for effective communication. For example:
- Speaking can adversely affected by stammering, fumbling, utterance of improper sounds due to defective vocal organ.
- Listening can be ineffective as a result of defective hearing
- Writing can be failed due to hand injury, numbness, etc.
- Reading can be affected due to poor eyesight.
Semantic Barriers or Language Barriers
The term ‘semantic’ refers to the systematic study of the meaning of the words. Semantic barriers are barriers related to language. They cause obstructions in the process of receiving or understanding the message during the process of encoding or decoding ideas and words. The most common semantic barriers are listed below:
- Misinterpretation of Words
- Use of Technical Language
- Vocabulary Deficiency
- Multiple Meaning of the Words in a Different Contexts
Misinterpretation of Words
Different people mean different meanings while using the same word.
Use of Technical Language
It is often found that technical people use technical language, which is related to their profession which is known as jargon. For eg: A manager handed over an important document to a new assistant and told him to burn it( here burn means copy in another computer.)
But the new assistant took a different meaning to the word burn and literally burn it with a match stick. Doctors, lawyers, etc. use a language that a layman cannot understand that, due to a lack of knowledge of that language.
Vocabulary Deficiency
Vocabulary deficiency of both the sender and the receiver may cause semantic barriers to communication.
Multiple Meaning of the Words in a Different Contexts
Different words are used in different ways as per the need/ message. For instance consider the word, ‘out’ in the following sentences:
- Get out of here
- Something is out of order in my car
- The truth got out at last
- He really stands out in his class.
- The workers are going out on strike
Personal Barriers
Differences in the personal and psychological makeup of individuals may create barriers between people. They arise from the judgments, emotions and social values of people. The following are some of the most common personal barriers.
Attitudes and Opinions
Assumptions and negative feelings about the receiver, such as hostility may have an effect on the message. In a typical superior-subordinate relationship, a subordinator may or may not ask questions, may even withhold information due to fear.
Some supervisors may not be open to suggestions and feedback as they presume that their subordinates are not capable of advising them. This creates indifference between them and subordinates do not feel motivated. Attitude thus becomes a barrier to communication.
Lack of Self-Confidence
Lack of self-confidence either on the part of the sender or the receiver while communicating may be a barrier to it.
Emotional Barriers
Emotional barriers are associated with sentiments and emotions:
Blocked Mind
A blocked mind considers only limited information and ignores or rejects additional information. An individual who has a blocked mind is rigid and dogmatic. He resists all contradictory communication and pays a deaf ear to new ideas.
Bias and Prejudice
If closed-minded people are asked for reasons for rejecting a message, they may reveal prejudices. They react with anger and give a sharp rebuff who try to argue with them. This acts as a barrier to communication.
Emotions
One’s state of mind plays an important role in act of communication. If the sender is worried, excited, afraid, nervous, then he will not be able to organize his message properly. Similarly, if the receiver is not in a proper state of mind, he may misinterpret the message.
Socio-Psychological Barriers
They are similar to perceptional barriers:
Selective Perception
This means that the receiver selectively sees and hear based on their needs, motivations, experience and expectations. In communication, this tendency means that they hear what they want to hear and ignore other relevant information.
Status Consciousness
Differences in status and power between the sender and the receiver may constitute another barrier. The subordinate feel very jittery, nervous in front of the supervisor and the supervisors may be reluctant to pass complete information.
Prejudices
People who are not open to discussions, new ideas, viewpoints and have a closed mind may be a great barrier to communication.
Halo Effect
Sometimes the listener may be too much in awe of or completely distrust a speaker. When there is a lack of sufficient trust, confidence and faith between the communicating parties, selective listening takes place. In these situations, several types of ‘noise’ enter the communication process. Similarly things like distrust, threat, fear are vital barriers to effective communication.
Physical Appearance
The receiver may not like the sender’s physical appearance, voice, pronunciation, accent, use of grammar or mannerisms. This may cause the receiver to discard the content. Communicator’s mood also influences his capacity to communicate, for eg: he may be tired, sleepy, bored, etc.
Cultural Barriers
Culture shapes the way we think and behave. Each group categorized on the basis of nationality, ethnicity, race, religion, etc. has its own distinctive culture. Cultural differences often cause communication differences. It arises when individuals in one social group have developed different norms, values, or behaviours to individuals associated with another group.
The same category of words, phrases, symbols, actions colours means different things to different cultures. For eg: In western countries black colour is associated with mourning, while in the far east white is the colour of mourning. In the U.S people love to be called by their first name, while in Britain, people are addressed by their last name.
Organisational Barriers
The factors are internal to the organization which adversely affect the flow of communication arc called on barriers. This includes:
Complex Organizational Structure
A complex org structure has long communication channels which are subject to the breakdown of communication.
Too Many Levels in the Organization
As the message has to pass through many levels, there are chances of distortion, delays or total failure of the message.
Time and Timeliness
Time pressures can be a serious obstacle as messages are hastily and inadequately communicated by managers.
How to Overcome Barriers of Communication
Barriers disrupt communication and interfere with understanding. They must be overcome if communication has to be effective.
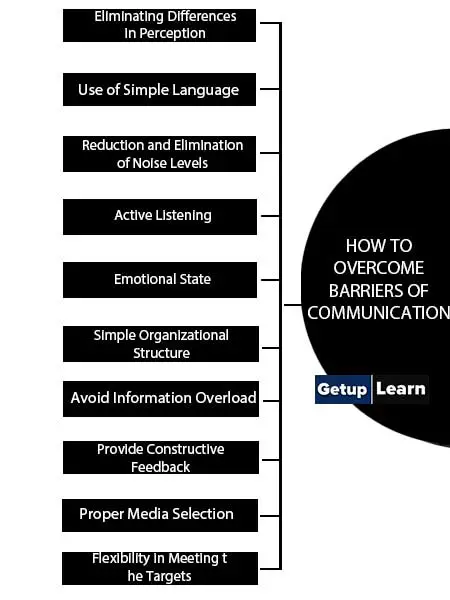
And there are the following points of how to overcome barriers of communication:
- Eliminating Differences in Perception
- Use of Simple Language
- Reduction and Elimination of Noise Levels
- Active Listening
- Emotional State
- Simple Organizational Structure
- Avoid Information Overload
- Provide Constructive Feedback
- Proper Media Selection
- Flexibility in Meeting the Targets
Eliminating Differences in Perception
Within the organization when individuals are recruited, their performance, qualifications, skills, abilities, knowledge, attitude should be taken into consideration; there should be proper training and development programs, employee selection procedures and individuals should possess effective communication skills especially regarding the English language, they should be fluent in English, in speaking as well as in writing.
Use of Simple Language
While communicating no matter what language, the use of words should be understandable, clear and simple; usage of complicated words might make an individual perplexed and such words should be avoided.
Reduction and Elimination of Noise Levels
Noise is the most common barrier which occurs everywhere, for instance, when family members are communicating at home, constant noise comes from busy neighbourhoods, or at the workplace too while working on the computers, people may get engaged in informal conversations, hence that leads to the emergence of noise levels. It is necessary to identify the sources of noise and then formulate measures in order to eliminate those sources.
Active Listening
The receiver should listen to the speaker with awareness and in a considerate manner; he/she should respond by asking questions, the speaker should always be aware of the fact that the listener understands everything that he is saying and this overcomes the barrier to effective communication.
Emotional State
During communication, the speaker is required to make effective use of body language and not depict one emotional state; for example, if the speaker is upset due to some reason then he should not portray his distress in his speech, the listeners might misinterpret the information if it is delivered by a speaker in a distressed mood.
Simple Organizational Structure
The hierarchical levels within the organization should be optimum in number; the operations and functions implemented within the organization, the leadership skills, a span of control, authority, rules, policies should be organized appropriately and put into operation in an effective manner.
Avoid Information Overload
Employers, as well as the employees, should not overload themselves with work; they should manage their work for the day accordingly, extended working hours should be avoided and employees should also take out time during their working hours to listen to the subordinates and workers grievances; they should practice effective time management skills.
Provide Constructive Feedback
While making provision of feedback to the employees and subordinates, negativity should be avoided and feedback should always be delivered in a constructive manner; negative feedback is stated to be a barrier to effective communication. The content of the feedback can be negative if the superior feel that there have been some misinterpretations, but it should be communicated in a constructive manner with a positive attitude.
Proper Media Selection
The medium of communication should be proper; if it is a simple message or just a minor notice, it can be delivered either through a face to face conversation or through a telephone; information that is complicated and lengthy should be delivered in a written manner for example, through letters, notices, newspapers or electronic mail, therefore proper media selection also leads to effective communication.
Flexibility in Meeting the Targets
Employees, when they are employed within an organization, should work towards accomplishing the desired goals and objectives, they should not be put under pressure to complete a particular assignment within a particular time period, in other words, they should be allowed sufficient time, especially when the task is extensive; in accomplishing the organization’s goals and objectives, it is essential to have effective means of communication and flexibility should be allowed in a meeting of the targets.
What are the 5 communication barriers?
Most commons communication barriers are Environmental Barriers, Biological Barriers, Language Barriers, Personal Barriers, Emotional Barriers, Socio-Psychological Barriers, Cultural Barriers, Organisational Barriers etc.
What are the 7 barriers to communication?
Types of barriers to communication are Environmental Barriers, Biological Barriers, Language Barriers, Personal Barriers, Emotional Barriers, Socio-Psychological Barriers, Cultural Barriers, Organisational Barriers etc.
What is the best way to overcome barriers?
And there are the following points of how to overcome barriers of communication:
1. Eliminating Differences in Perception
2. Use of Simple Language
3. Reduction and Elimination of Noise Levels
4. Active Listening
5. Emotional State
6. Simple Organizational Structure
7. Avoid Information Overload
8. Provide Constructive Feedback
9. Proper Media Selection
10. Flexibility in Meeting the Targets etc.