Table of Contents
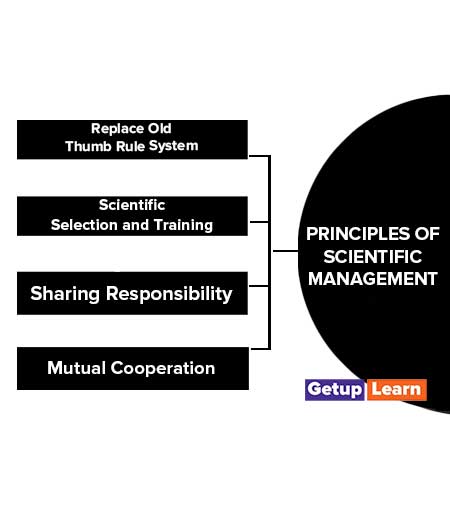
Principles of Scientific Management
Taylor propounded four principles of scientific management. The main principles are discussed below:
- Replace Old Thumb Rule System
- Scientific Selection and Training
- Sharing Responsibility
- Mutual Cooperation
Replace Old Thumb Rule System
Taylor advised that the thumb rule should not be given space in organisations. He was of the view to mean the rule of thumb is guessing, traditional belief without proper reasoning, or rough estimation.
He described that any activity, process or method without a proper justification or reason can be considered a rule of thumb. Therefore, he advised the scientific rules, methods and ways to replace the thumb rule.
Scientific Selection and Training
Taylor propagated this principle in order to replace the system of first come or gate selection method adopted for employee selection in his organisation.
The method was to pair up the skill required to perform the job effectively. He was also of the view that the persons for training should be selected through a scientific method not randomly or bureaucratic manner.
Sharing the responsibility for the outcome was an important principle given by Taylor in scientific management. He advocated that joint activities must have responsibility sharing.
Every member of the team or committee should feel responsible and should be held accountable for the outcome of joint efforts or operations conducted.
Mutual Cooperation
Cooperation between management and workers should be developed in order to implement change in the system.
Mutual confidence can boost the morale level of both management and employees and lead to higher performance and output. In absence of mutual cooperation, the change in the system may lead to inefficiency and indiscipline.
Contribution of Scientific Management
Apart from F. W. Taylor, Henry Gantt, Frank Gilbreth, Lillian Gilbreth, Robert Owen, and Charles Babbage also contributed to the development of the scientific approach to management development.
The major contributions of scientific management to the development of management thoughts are discussed below:
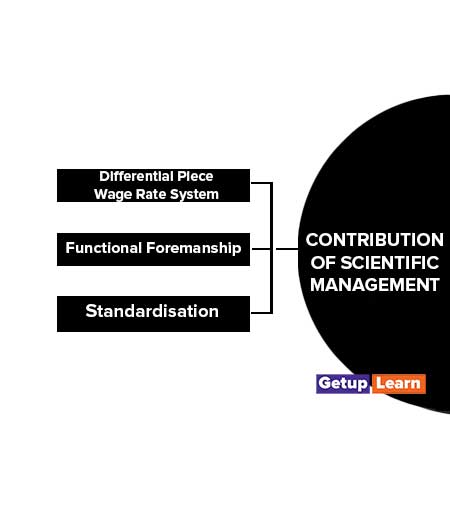
Differential Piece Wage Rate System
F. W. Taylor devised a new wage payment system for workers. He established the main framework of the differential piece wage rate system. He strongly advocated linking wages to productivity to justify the performance appraisal system for employees.
Differential piece wage rate systems encourage employees to increase their performance in order to get more wages thus producing more.
For Example:
Piece wage rate system: Rs. 100/ piece for any number of pieces produced Differential piece wage rate system:
- Rs. 100/piece, if the number of pieces produced is less than 100 pieces;
- Rs.150/piece, if the number of pieces produced is more than 100 and less than 150 pieces and
- Rs. 200/ piece, if the number of pieces produces is more than 150 pieces.
Functional Foremanship
Taylor advocated functional foremanship in order to ensure that the job is performed by a specialised person. The functional foremanship also aims to establish a skill-based corridor for career promotion in organisations.
Technical jobs require specific skills to do the specific job, hence need a specialised person to supervise these jobs. The functional foremanship facilitates the route for the process of supervision.
Standardisation
Standardisation of inputs, processes and output was a major contribution of scientific management to the development of management thoughts.
The standardisation of raw materials, tools, performance standards, processes and methods, jobs, wages and so on, contributes to the improvement in productivity. This concept opened new vistas of quality management in organisations.
What are the principles of scientific management?
The following are the principles of scientific management:
1. Replace Old Thumb Rule System
.2 Scientific Selection and Training
3. Sharing Responsibility
4. Mutual Cooperation.
What is the contribution of scientific management?
The following are the contribution of scientific management:
1. Differential Piece Wage Rate System
2. Functional Foremanship
3. Standardisation.