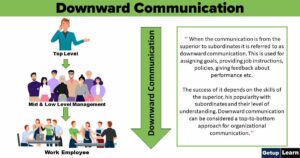
Personality is a set of relatively stable characteristics or dimensions of people that account for consistency in their behavior in various situations. Personality is a major determinant of what will be done and how it will be done in the job where most of the working day is spent interacting with other people.
Table of Contents
Personality Dimensions
In any organization, every individual’s personality reveals how he works with superiors, subordinates, and other people, how an individual adjusts himself to a particular situation, and how he reacts to the changes occurring in the existing jobs or on the new job.
Some of the important personality factors or dimensions that determine what kind of performance will be achieved or what kind of behavior is exhibited at work are:
- Self-Concept and Self-Esteem
- Authoritarianism
- Need Patterns
- Bureaucratic Personality
- Machiavellianism
- Tolerance for Ambiguity
- Locus of Control
- Risk Taking
Self-Concept and Self-Esteem
Self-concept is the way individuals define themselves as who they are and drive their sense of identity. Self-esteem is the degree of respect; liking or disliking an individual has for him. It is a measure of self-confidence and respect for one’s abilities and motivation.
It denotes the extent to which an individual regards himself as capable, successful, important, and worthy. People with high self-esteem are very friendly, and affectionate, find it easy to form interpersonal attachments, and find good in other people.
They tend to take on more challenging assignments and contribute significantly to their organization if the organization rewards them suitably for their efforts. They are high performers. Low self-esteem people are usually critical of others, are generally depressed, and blame others for their own failure. They contribute to poor performance, which in turn leads to low self-esteem.
A closely related term to authoritarianism is “dogmatism” which refers to the rigidity of a person’s beliefs. Authoritarianism refers to blind acceptance of authority. Authoritarian people believe in obedience and respect for authority. They believe that there should be status and power differences among people in the organization.
The individual with a high authoritarian personality is intellectually rigid, judgmental of others, deferential to those above and exploitative of those below, distrustful, and resistant to change. They rightly adhere to conventional values, are conservative, endorse parental control for keeping the family together, are concerned with toughness and power, are close-minded, and are generally less educated.
Where the job demands sensitivity to the feelings of others, tact, and the ability to adapt the complex and changing situations, persons with high-authoritarian personalities would be negatively related to performance.
Need Patterns
Every individual has needs for achievement, affiliation, autonomy, and dominance at work. People with:
- High need for achievement engage themselves totally in work in order to feel proud about their achievements and success.
- High need for affiliation work with great cooperation with others.
- High need for autonomy prefers to work in an environment where the supervision is less.
- A high need for dominance is effective in an environment where they can enforce their legitimate authority.
Bureaucratic Personality
This kind of person has respect for rules and regulations. Thus, on this account, it differentiates from an authoritarian person whose respect for authority is blind.
Bureaucratic persons are not innovative; even not ready to take risks and they keep themselves at ease while following other directions. They value subordination, rules, conformity, and impersonal and formal relationships. In routine and repetitive work, they are better supervisors.
Machiavellianism
It refers to the manipulation of others as a primary way of achieving one’s goals and gaining and keeping control of others. The extent to which an individual is Machiavellian is measured by the Mach Scale. People with high scores on the Mach scale have high self-confidence and self-esteem.
They are cool and calculating, logical in assessing the system around them. They have no hesitation in using others or taking advantage of others in order to serve their own goals, are willing to twist and turn facts to influence others, and try to gain control of people, event, and situations by manipulating the system to their advantage.
As they thoughtfully and logically approach their situation, they are skilled in influencing others. They are successful in exploiting structured situations and vulnerable people.
Tolerance for Ambiguity
Because of rapid changes, an individual has to work in an environment that is full of uncertainty. They should develop a high level of tolerance for ambiguity.
People or managers with high tolerance levels of ambiguity can work effectively without much stress. But people with low tolerance for ambiguity can work effectively in structured work settings but it is difficult for them to work in changed conditions.
Locus of Control
It is the extent to which individuals believe that they control their own lives or that external forces control their lives. In other words, the degree to which people believe that they are masters of their own fate The individual with an ‘internal locus of control’ believes that he is the master of his own destiny.
He believes that his internal traits determine what happens in a given situation and he controls events concerning his own life. The person with this kind of personality seeks opportunities for advancement and relies more on their ability and judgment at work. The study proves that persons with an internal locus of control are highly confident. They use their own wisdom and energy while working on projects.
Risk Taking
This shows the willingness of individuals to take or avoid risks. It shows how long a manager takes to make a decision and how much information he requires before taking a decision. High-risk taker takes rapid decisions with less available information. The propensity to assume risk is dependent upon the nature of the job.
An accountant performing auditing activities should be risk averse; on the other hand in the expectation of higher returns a high risk-taking propensity results from high performance for a stock trader‘s brokerage firm. As a general saying is higher the risk, the higher the return.
Personality Assessment Tests
These are some of the more common personality assessment tests:
Subjective Test
This includes interviews, observations, case studies, etc. A person is interviewed and observed carefully to judge his capabilities and capacities.
Sometimes a person is also judged with the help of case studies and autobiographies. The judgment and critical remarks about the case studies and autobiographies help in judging the personality of a person.
Objective Tests
It includes a questionnaire, K.G. Aggregation, etc. These kinds of tests give stress on the mental ability, capabilities rather than on personal appearance of a person.
Projective Test
In this, test like WAT (Words Association Test) and TAT (Thematic Aptitude Test) is conducted. These tests play a major role in analyzing the personality of a person. These tests comprise words and pictures. And the person is judged by his/her reaction to the picture and words. All these tests have been devised to assist the personality of the person in the most effective manner.