Table of Contents
-
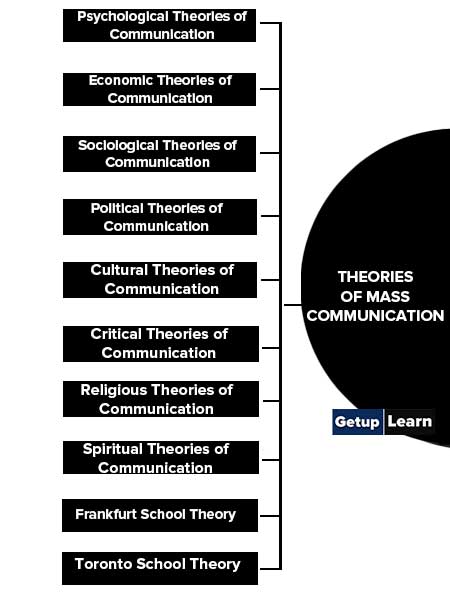
1 Theories of Mass Communication
- 1.1 Psychological Theories of Communication
- 1.2 Economic Theories of Communication
- 1.3 Sociological Theories of Communication
- 1.4 Political Theories of Communication
- 1.5 Cultural Theories of Communication
- 1.6 Critical Theories of Communication
- 1.7 Religious Theories of Communication
- 1.8 Spiritual Theories of Communication
- 1.9 Frankfurt School Theory
- 1.10 Toronto School Theory
- 2 FAQs About Theories of Mass Communication
Theories of Mass Communication
A theory is meant is to raise the output. Colloquially, we may call somebody a theoretical or theoretician his theory is outdated or irrelevant and not problem-solving. But if a theory is relevant, problem-solving output raising, then it must be respected.
A theory depends on time, place, and circumstances. As a seed can’t be sprouted in all the seasons except, its own particular time, similarly a theory can’t be applied all the time or all through the year. Again a seed can’t be shown in all the places of the world. An American seed can’t be sown on Indian soil, because it may not germinate or may not sprout.
Even the seed of an apple produced in Kashmir, may not sprout or germinate in the soil of Haryana. Similarly, a seed depends on the circumstances. If a seed of winter is sown even in winter but suddenly there is heavy rain during the winter, then the entire seeds will be destroyed. Thus as a seed depends on time, place, and situation, so is the case with theory.
When we study an American or British theory, whether it is sociology or psychology or economics or political science or anthropology, or communication, we often fail to apply it to the prevailing socio-economic, political, and cultural circumstances of India. As far as communication theories are concerned, Indians have hardly developed any theory.
There are only a handful of Indian communication theories like, ‘Sadharikaran’, Sahridayas’, ‘Sambhaost’, ‘Nirveda’, ‘Glani’, ‘Rasa’, etc. All these Indian theories could not grow even on Indian soil. Despite the fact, that these theories have been developed by Indians like Prof. I.P.Tewari, Prof. J.S.Yadava, and Prof. Gupta, due to time and situation, they could not grow in our own land.
Unfortunately, most of the models and theories in social sciences have been developed by western social experts and are taught in India. No doubt, some of them are universally applicable. But a majority of them are not applicable in India whether it is economics or political science or sociology or anthropology or communication.
But due to the extremely poor education system in India and equally adverse circumstances, there is a complete dearth of Indian theories on what to talk about communication or mass communication, even in other matured and older social sciences, the situations are similar. But now there are only two ways out:
- Hybridization of western theories
- Developing our own original theories
Hybridization of Western theories means these western concepts may be Indianised and made useful for solving Indian problems just like hybridization is performed in biotechnology. Second, now with the growth of Indian research circumstances, the universities and institutions may focus on developing our own Indian and indigenous theories.
There are so many communication theories like magic-bullet theory, agenda-setting theory, two-step flow theory, multi-step flow theory, diffusion of innovation theory, uses and gratification theory, selective exposure, selective perception, and selective retention theory, etc.
- Psychological Theories of Communication
- Economic Theories of Communication
- Sociological Theories of Communication
- Political Theories of Communication
- Cultural Theories of Communication
- Critical Theories of Communication
- Religious Theories of Communication
- Spiritual Theories of Communication
- Frankfurt School Theory
- Toronto School Theory
Psychological Theories of Communication
This relates to human behavior and is also described as behavioral theory. In such theories, we generally discuss the theory of perception, theory of individual difference, theory of audience attention, theory of audience attitude, conflict theory, consensus theory, theory of mental defense mechanism including the theory of rationalization, theory of sublimation, theory of repression, theory of regression, theory of identification, theory of cognitive dissonance, cognitive theory, theory of learning, theory of retention, theory of persuasion, theory of recall, social influence theory.
Economic Theories of Communication
These theories of communication relate to the economic aspects like inequality, poverty, development, communism, socialism, capitalism, etc. Such theories include the communist theory of communication, the Marxist theory of communication, the Neo-Marxist theory, the capitalistic theory of communication, the crony capitalistic theory of communication, corporate culture theory, the advertising theory, etc.
Sociological Theories of Communication
These theories of communication relate to the sociological aspects like social responsibility theory, social identity theory, social information processing theory, social interaction theory, social judgment theory, social penetration theory, family communication theory, etc.
Political Theories of Communication
These theories of communication relate to political issues like political communication theory, political economy theory, propaganda theory, etc.
Cultural Theories of Communication
These theories of communication pertaining to cultural issues like cultural contacts theory, cultural identity theory, cultural performance theory, cross-cultural adaption theory, co-cultural theory, etc.
Critical Theories of Communication
These theories of communications relate to critical observation or critical assimilation of the theory or model or paradigm. Examples, critical discourse analysis, critical race theory, critical communication pedagogy, critical constructivism, critical cultural studies, critical ethnography, etc.
Religious Theories of Communication
These theories of communication pertaining to religious issues like dutifulness, Buddhism, Jainism, Hinduism, Islamism, Christianity, Sikhism, etc. Examples, Buddhist communication theory, Hindu communication theory, Chinese harmony theory, religious communication theory, etc.
Spiritual Theories of Communication
These theories of communication relate to spiritual issues like self-knowledge, self-exploration, knowledge of God, meditation, etc. Examples, metacommunication theory, self-categorization theory, self-disclosure theory, value studies theories, spiritual theory, etc.
Frankfurt School Theory
This is an extension of critical theories. This is because the Frankfurt school is a group of critical theorists who joined the Institute of Social Research, Frankfurt University, Germany from 1923 to 1933. The theories of this school dealt with a Marxist analysis of social and economic processes.
Then they accessed the role of the individual and the group in relation to these processes. The experts of this school focused their studies on communication relating to the historical, social, and economic processes. The expert theorists of Frankfurt school are: Max Horkheimer, Theodor WeisengrundAdorono, Walter Benjamin, Herbert Marcuse, Leo Lowenthal and JurgenHabermas.
Toronto School Theory
This school has developed theories relating to human communication, human culture, and the human mind. That is why this school is described as “the theory of the primacy of communication in the structuring of the human cultures and structuring of the human mind.” The school originated from the works of Eric A.
Havelock and Harold Innis in the 1930s grew to prominence with the contributions of Edmund Snow Carpenter, NorthopFyre, and Marshall McLuhan. Eric Havelock’s pioneering work in the transitions from orality to literacy, as an account of communication, seriously influenced the media theories of Marshall McLuhan and Harold Innis.
Harold’s theories of political economy, media, and society had a significant influence on critical media theory. His work along with Marshall McLuhan offered groundbreaking Canadian perspectives on the function of communication technologies as key agents in social and historical change. Their joint work developed a theory of history in which communication is central to social change and transformation.
FAQs About Theories of Mass Communication
What are the theories of mass communication?
The following are the theories of mass communication:
1. Psychological Theories of Communication
2. Economic Theories of Communication
3. Sociological Theories of Communication
4. Political Theories of Communication
5. Cultural Theories of Communication
6. Critical Theories of Communication
7. Religious Theories of Communication
8. Spiritual Theories of Communication
9. Frankfurt School Theory
10. Toronto School Theory.