Table of Contents
Meaning of Entrepreneurship
The meaning of entrepreneurship involves an entrepreneur who takes action to make a change in the world. Whether startup entrepreneurs solve a problem that many struggle with each day, bring people together in a way no one has before, or build something revolutionary that advances society, they all have one thing in common action.

It’s not some idea that’s stuck in your head. Entrepreneurs take the idea and execute it. Entrepreneurship is about the execution of ideas. Entrepreneurship is a complex term that’s often defined simply as running your own business.
But there’s a difference between a “business owner” and an “entrepreneur,” and although one can be both, what distinguishes entrepreneurship is a person’s attitude. Entrepreneurship is a full-time job that requires dedication and hard work.
Entrepreneurs are innovators. They are owners, producers, market creators, decision-takers, and risk-takers. Entrepreneurs are referred to as the fourth ‘Factor of Production’ along with other factors such as land, labor, and capital. They generate employment opportunities so they are the backbone of the nation’s economic progress. They play a very important role in the development of any country.
Factors Affecting Entrepreneurial Growth
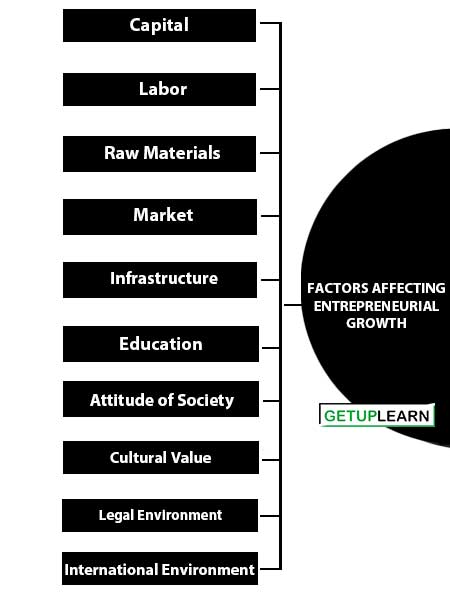
We can categorize factors affecting entrepreneurial growth into two major categories: 1. Economic Factors, 2. Non-Economic Factors:
- Capital
- Labor
- Raw Materials
- Market
- Infrastructure
- Education
- Attitude of Society
- Cultural Value
- Legal Environment
- International Environment
Economic Factors
These are the economic factors affecting entrepreneurial growth:
Capital
Capital is one of the most important factors of production for the establishment of an enterprise. An increase in capital investment in viable projects results in an increase in profits which helps in accelerating the process of capital formation.
Entrepreneurship activity too gets a boost with the easy availability of funds for investment. Availability of capital facilitates the entrepreneur to bring together the land of one, machine of another, and raw materials of yet another to combine them to produce goods.
Capital is, therefore, regarded as a lubricant to the process of production. France and Russia exemplify how the lack of capital for industrial pursuits impeded the process of entrepreneurship and an adequate supply of capital promoted it.
Labor
The easy availability of the right type of workers also affects entrepreneurship. The quality rather than quantity of labor influences the emergence and growth of entrepreneurship. The problem of labor immobility can be solved by providing infrastructural facilities including efficient transportation.
The quality rather than quantity of labor is another factor that influences the emergence of entrepreneurship. Most less developed countries are labor-rich nations owing to a dense and even increasing population. However, entrepreneurship is encouraged if there is a mobile and flexible labor force.
And, the potential advantages of low-cost labor are regulated by the deleterious effects of labor immobility. The considerations of economic and emotional security inhibit labor mobility. Entrepreneurs, therefore, often find it difficult to secure sufficient labor.
Raw Materials
The necessity of raw materials hardly needs any emphasis for establishing any industrial activity and its influence on the emergence of entrepreneurship. In the absence of raw materials, neither any enterprise can be established nor can an entrepreneur emerge.
It is one of the basic ingredients required for production. Shortage of raw materials can adversely affect the entrepreneurial environment. Without an adequate supply of raw materials, no industry can function properly and the emergence of entrepreneurship is adversely affected.
In fact, the supply of raw materials is not influenced by themselves but becomes influential depending upon other opportunity conditions. The more favorable these conditions are, the more likely is the raw material to have an influence on entrepreneurial emergence.
Market
The role and importance of market and marketing is very important for the growth of entrepreneurship. In a modern competitive world, no entrepreneur can think of surviving in the absence of the latest knowledge about the market and various marketing techniques.
The fact remains that the potential of the market constitutes the major determinant of probable rewards from entrepreneurial function. Frankly speaking, if the proof of pudding lies in eating, the proof of all production lies in consumption, i.e., marketing. The size and composition of the market both influence entrepreneurship in their own ways.
Practically, the monopoly in a particular product in a market becomes more influential for entrepreneurship than a competitive market. However, the disadvantage of a competitive market can be canceled to some extent by improvement in the transportation system facilitating the movement of raw materials and finished goods, and increasing the demand for producer goods.
Infrastructure
The expansion of entrepreneurship presupposes properly developed communication and transportation facilities. It not only helps to enlarge the market but expands the horizons of business too. Take, for instance, the establishment of the post and telegraph system and the construction of roads and highways in India.
It helped considerable entrepreneurial activities which took place in the 1850s. Apart from the above factors, institutions like trade/ business associations, business schools, libraries, etc. also make valuable contributions towards promoting and sustaining entrepreneurship in the economy. You can gather all the information you want from these bodies. They also act as a forum for communication and joint action.
Non-Economic Factors
These are the non-economic factors affecting entrepreneurial growth:
Education
Education enables one to understand the outside world and equips him with the basic knowledge and skills to deal with day-to-day problems. In any society, the system of education has a significant role to play in inculcating entrepreneurial values. In India, the system of education prior to the 20th century was based on religion.
In this rigid system, critical and questioning attitudes toward society were discouraged. The caste system and the resultant occupational structure were reinforced by such education. It promoted the idea that business is not a respectable occupation.
Later, when the British came to our country, they introduced an education system, just to produce clerks and accountants for the East India Company, The base of such a system, as you can well see, is very anti-entrepreneurial. Our educational methods have not changed much even today. The emphasis is still on preparing students for standard jobs, rather than marking them as capable enough to stand on their feet.
Attitude of Society
A related aspect to these is the attitude of the society towards entrepreneurship. Certain societies encourage innovations and novelties and thus approve entrepreneurs’ actions and rewards like profits. Certain others do not tolerate changes and in such circumstances, entrepreneurship cannot take root and grow.
Similarly, some societies have an inherent dislike for any money-making activity. It is said, that in Russia, in the nineteenth century, the upper classes did not like entrepreneurs. For them, cultivating the land meant a good life.
They believed that land belonged to God and the produce of the land was nothing but god’s blessing. Russian folk tales, proverbs, and songs during this period carried the message that making wealth through business was not right.
Cultural Value
Motives impel men to action. Entrepreneurial growth requires proper motives like profit-making, acquisition of prestige, and attainment of social status. Ambitious and talented men would take risks and innovate if these motives were strong. The strength of these motives depends upon the culture of the society.
If the culture is economically or monetarily oriented, entrepreneurship would be applauded and praised; wealth accumulation as a way of life would be appreciated. In the less developed countries, people are not economically motivated.
Monetary incentives have relatively less attraction. People have ample opportunities to attain social distinction through non-economic pursuits. Men with organizational abilities are, therefore, not dragged into business. They use their talents for non-economic ends.
Legal Environment
The legal environment affects the business very substantially. If suitable legal arrangements do not exist for safeguarding the interests and powers of the entrepreneurs, businessmen, and other parties related to the business, no one will like to carry out any significant business.
International Environment
The international environment also affects the system. Presently, the waves of globalization and liberalization are flowing throughout the world.
The international environment includes various factors, like mutual relations between various nations, economic policies of the various nations, availability of foreign capital, level of international competition, business activities of multinational companies, conditions of international peace, rules of international trade, etc. The business institutions should manage and operate business activities, considering these factors.
FAQs Section
What are the factors affecting entrepreneurial growth?
The following are factors affecting entrepreneurial growth:
1. Capital
2. Labor
3. Raw Materials
4. Market
5. Infrastructure
6. Education
7. Attitude of Society
8. Cultural Value
9. Legal Environment
10. International Environment.