Table of Contents
What is Contract Manufacturing?
A contract manufacturer (CM) is a manufacturer that contracts with a firm for components or products. It is a form of outsourcing.

Contract Manufacturing Business Model
In a contract manufacturing business model, the hiring firm approaches the contract manufacturer with a design or formula. The contract manufacturer will quote the parts based on processes, labour, tooling and material costs. Typically, a hiring firm will request quotes from multiple CMs.
After the bidding process is complete, the hiring firm will select a source, and then, for the agreed-upon price, the CM acts as the hiring firm’s factory, producing and shipping units of the design on behalf of the hiring firm.
Industries that Utilize the Practice
Many industries utilize this process, especially aerospace, defence, computer, semiconductor, energy, medical, food manufacturing, personal care and automotive.
Contract manufacturing includes CNC machining, complex assembly, aluminium die casting, grinding, broaching, gears and forging. The pharmaceutical industry utilizes this process with CMs called Contract manufacturing organizations.
Why Contract Manufacture?
There are many benefits as well as risks to contracting to manufacture. Companies are finding many reasons why they should be outsourcing their production to other companies. However, showing outside of the company does come with many risks attached.
Companies must identify what their core competencies are first before deciding whether or not they should contract manufacture. A company’s core competencies are what make them competitive in the marketplace. If a company allows another company to take control of them, it loses control over that advantage.
When making the decision on whether or not a company should contract manufacture, the company should weigh the benefits and risks associated with it. For small companies, contract manufacturing may not be a good business strategy. For large companies that are trying to grow and extend into new markets, contract manufacturing is likely to be a good choice.
Advantages of Contract Manufacture
These are the advantages of contract manufacture given below:
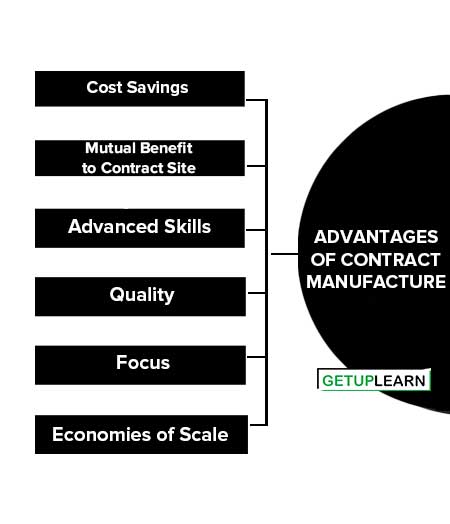
Cost Savings
Companies save on their cost of capital because they do not have to pay for a facility and the equipment needed for production. They can also save on labour costs such as wages, training and benefits. Some companies may look to contract manufacturing in low-cost countries, such as China, to benefit from the low cost of labour.
Mutual Benefit to Contract Site
A contract between the manufacturer and the company it is producing for may last several years. The manufacturer will know that it will have a steady flow of business until then.
Advanced Skills
Companies can take advantage of skills that they may not possess, but the contract manufacturer does. The contract manufacturer is likely to have relationships formed with raw material suppliers or methods of efficiency within their production.
Quality
Contract manufacturers are likely to have their own methods of quality control in place that help them to detect counterfeit or damaged materials early on.
Focus
Companies can focus on their core competencies better if they can hand off base production to an outside company.
Economies of Scale
Contract Manufacturers have multiple customers that they produce for. Because they are servicing multiple customers, they can offer reduced costs in acquiring raw materials by benefiting from economies of scale. The more units there are in one shipment, the less expensive the price per unit will be.
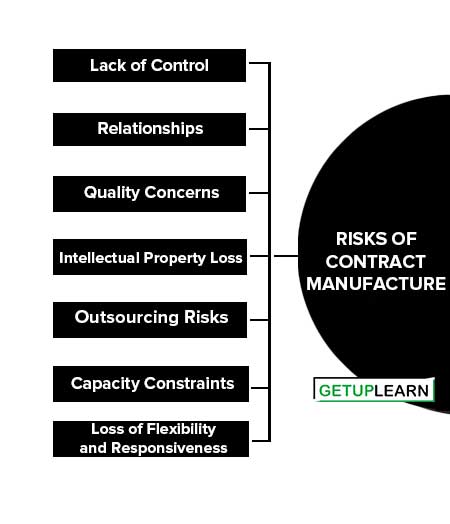
Risks of Contract Manufacture
These are the following risks of contract manufacture:
- Lack of Control
- Relationships
- Quality Concerns
- Intellectual Property Loss
- Outsourcing Risks
- Capacity Constraints
- Loss of Flexibility and Responsiveness
Lack of Control
As soon as a company signs a contract allowing another company to produce their product, they lose a significant amount of control over that product. They can only suggest strategies to the contract manufacturer; they cannot force them to implement them.
Relationships
It is imperative that the company forms a good relationship with its contract manufacturer. The company must keep in mind that it is not the only customer of the manufacturer.
They cannot force them to produce their product before a competitor’s. Most companies mitigate this risk by working cohesively with the manufacturer and awarding good performance with more of their business.
Quality Concerns
When entering into a contract, companies must make sure that the manufacturer’s standards are in line with their own. They should also evaluate the methods by which they test products to make sure the products being produced are of good quality. The company has to rely on the contract manufacturer for having good suppliers that also meet these standards.
Intellectual Property Loss
When entering into a contract, a company is letting someone else in on their formulas or technologies. This is why it is very important that a company not give out any of its core competencies to contract manufacturers. It is very easy for an employee to download such information from a computer and steal it.
The recent uptake in intellectual property loss has companies and government officials struggling to find the best method of security. Usually, it comes down to the integrity of the employees.
Outsourcing Risks
Although outsourcing to low-cost countries has become very popular, it does bring along risks such as language barriers, cultural differences and long lead times. This could make the management of contract manufacturers more difficult, expensive and time-consuming.
Capacity Constraints
If a company does not make up a large portion of the contract manufacturer’s business, it may find that they are de-prioritized over other companies during high production periods. Thus, they may not be able to get the product they need when they need it.
Loss of Flexibility and Responsiveness
Without direct control over the manufacturing facility, the company will lose some of its ability to respond to disruptions in the supply chain. It may also hurt their ability to respond to demand fluctuations, risking their customer service levels.