Table of Contents
Scope of International Marketing
These are the following scope of international marketing explained below:
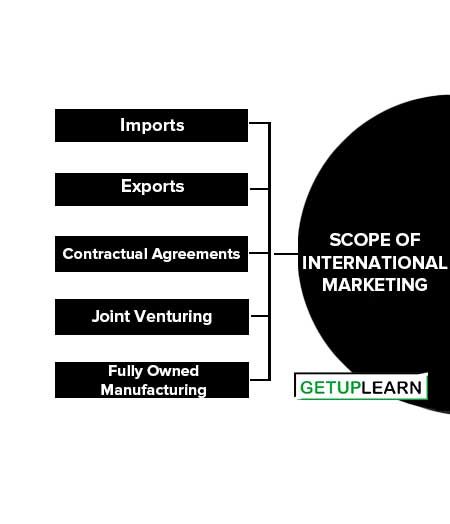
Imports
This is the easiest form of International Marketing a company can get into – Importing from one country and selling in the domestic market.
This is attainable solely in an exceeding state of affairs wherever there’s demand within the domestic marketplace for foreign merchandise or services. Companies also localize the imported product depending on the needs of the market.
Exports
Opposite of importation and mercantilism, firms export their finalized product to international markets or on to their different franchises in far-flung markets wherever they will sell the product to their localities for generating huge revenues.
Contractual Agreements
Whenever business moves on the far side their domestic boundaries, its scope of international marketing exposes it to greater chances of doing a lot more business.
The market expands, the consumer base expands and even volumes and profits expand. Companies grow exponentially by going into written agreement agreements with many different partners overseas.
Joint Venturing
Two brands will close and enter a possible market. The investments, profit or losses are pre-decided in terms of both value and time period. At times it’s useful for firms to enter into a squad for raising the scope of international selling as a result of barriers to new entrants in foreign markets.
A local partner will sway be vastly helpful for doing business not solely operationally but conjointly from a domestic understanding of the market dynamics.
Fully Owned Manufacturing
With relatively a better level of engagement within the foreign soils, companies can own fully owned manufacturing in a country. The company will use this facility to sell products at intervals in the country or export to close nations. Owning a totally owned production helps the firm’s management quality.
Difference Between Domestic and International Marketing
Though fundamentally international marketing operations look like domestic marketing operations, yet some important distinctions can be perceived following an in-depth insight. The corporations having expertise in domestic business will in all probability have a foothold whereas diversifying into international operations.
Keeping this in mind, a leading management guru, Micheal E. Porter has ascertained that corporations desiring to flourish and achieve success globally should try at being successful within the domestic market 1st. Most firms like IBM, Coca-Cola, Unilever, Proctor and Gamble, Suzuki, and Sony operating globally in fact started initially as domestic companies.
As the magnitude of their operations grew, they found it profitable to venture abroad by setting up manufacturing and distribution centres in other countries.
These are the points of difference between domestic and international marketing:
Method of Selling
Marketing is deemed to involve 2 processes viz., technical and social. The technical method basically includes non-human factors like product, price, cost, and brand. But, the social process takes care of human behaviour, customs, attitudes, values etc.
The latter is unique to a national market. Hence, this shows that international selling is completely different from domestic selling. Accordingly, sociological & cultural factors predominate the decision-making with regard to the marketing mix.
Selling Environment
The environmental and operational variables conjointly assume a unique structure in international business. Environmental factors such as economic, politico-legal, geographic, cultural and competition are much more dynamic and uncontrollable in foreign markets as compared to domestic markets.
Different countries have completely different currencies, accounting practices, legislation, interest rates, inflation etc. So, the manageable factors of a firm (marketing mix) have to be compelled to be redesigned in step with the wants of individual countries. The terrible complexness of exchange transactions across nations makes them considerably completely different from domestic business operations.
What are the scope of international marketing?
The following is the scope of international marketing:
1. Imports
2. Exports
3. Contractual Agreements
4. Joint Venturing
5. Fully Owned Manufacturing.