Table of Contents
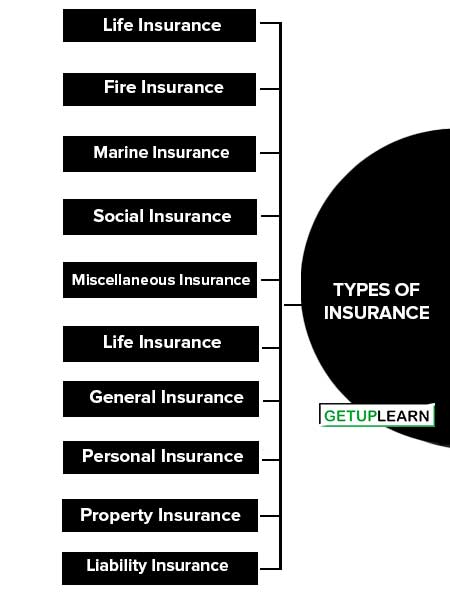
Types of Insurance
We can categorize types of insurance into three bases of types of insurance: 1. On the Basis of the Nature of the Business, 2. On Basis Business Point of View, On Basis Risk Point of View:
- Life Insurance
- Fire Insurance
- Marine Insurance
- Social Insurance
- Miscellaneous Insurance
- Life Insurance
- General Insurance
- Personal Insurance
- Property Insurance
- Liability Insurance
- Fidelity Guarantee Insurance
On Basis of Nature of Business
The following are the types of insurance on the basis of the nature of business:
Life Insurance
Life insurance may be defined as a contract in which the insurer, in consideration of a certain premium, either in a lump sum or by other periodical payments, agrees to pay the assured, or to the person for whose benefit the policy is taken, the assured sum of money, on the happening of a specified event contingent on the human life.
A contract of life insurance, as in other forms of insurance, requires that the assured must have at the time of the contract an insurable interest in his life upon which the insurance is affected. In a contract of life insurance, unlike other insurance, interest has only to be proved at the date of the contract, and not necessarily present at the time when the policy falls due.
Fire Insurance
Fire insurance is a contract to indemnify the insured for distribution of or damage to property caused by fire. The insurer undertakes to pay the amount of the insured’s loss subject to the maximum amount stated in the policy.
Fire insurance is essentially a contract of indemnity, not against accident, but against loss caused by accident. It is becoming very common in fire insurance policies to insert a condition, called the average clause, by which the insured is called upon to bear a portion of the loss himself.
The main object of this clause is to check under-insurance and to encourage full insurance. It impresses upon the property-owner for the need of having his property accurately valued before insurance. Regarding insurable interest, the insured must have an insurable interest in the subject matter both at the time of affecting the policy and at the time of loss.
The risk in a fire insurance policy commences from the moment of the cover note, the deposit receipt, or the interim protection is issued and continues for the term covered by the contract of insurance. It may even date back; if the parties so intend. The rate of premium varies to the degree of hazard or risk involved.
Marine Insurance
A contract of marine insurance is an agreement whereby the insurer undertakes to indemnify the assured in a manner and to the extent thereby agreed, against marine losses, that is, the losses incidental to marine adventure. There is a marine adventure when any insurable property is exposed to marine perils.
Marine perils also known as perils of the seas means the perils consequent on, or incidental to, the navigation of the sea or the perils of the seas, such as fire, war perils, pirates, robbers, thieves; captures, jettisons, barratry and any other perils which are either of the like-kind or may be designed by the policy.
There are different types of marine policies known by different names according to the manner of their execution or the risk they cover. They are voyage policy, time policy, valued policy, unvalued policy, floating policy, and wager or honor policy.
Social insurance has been developed to provide economic security to weaker sections of society who are unable to pay the premium for adequate insurance. The following types of social insurance:
-
Sickness Insurance: In this type of insurance medical benefits, medicines and reimbursement of pay during the sickness period, etc. are given to the insured person who fell sick.
-
Death Insurance: Economic assistance is provided to dependants of the assured in case of death during employment. The employer can transfer such liability by getting an insurance policy against employees.
-
Disability Insurance: There is a provision for compensation in case of total or partial disability suffered by factory employees due to accidents while working in factories. According to Employees Compensation Act, the responsibility to pay compensation is vested with the employer. But the employer transfers his liability to the insurer by taking the group insurance policy.
-
Unemployment Insurance: In case an insured person becomes unemployed due to certain specific reasons, he is given economic support till he gets employment.
- Old-age Insurance: In this category of insurance, the insured or his dependents is paid, after a certain age, economic assistance.
For the last few years, the Indian Government has extended the scope of Social Insurance. Under the concept of social justice, this scheme is now extended to Daily-wages earners, Rickshaw pullers, Landless laborers, Sweepers, Craftsmen, etc. through different insurance plans.
Miscellaneous Insurance
The process of fast development in society gave rise to a number of risks or hazards. To provide security against such hazards, many other types of insurance also have been developed. The important among them are:
- Vehicle insurance on buses, cars, trucks, motorcycles, etc., and made compulsory so that the losses due to accidents can be claimed by the insurance company.
- Personal accident insurance by paying an annual premium of Rs.12 on a policy worth Rs.12,000. In case of accidental death or total/partial disability, a fixed amount as per conditions of insurance, is paid to the insured.
- Burglary insurance (against theft, decoity, etc.).
- Legal liability insurance (insurance whereby the assured is liable to pay the damages to property or to compensate the loss of personal injury or death. This is in the form of fidelity guarantee insurance, automobile insurance, and machines, etc.).
- Crop insurance (crops are insured against losses due to heavy rains and floods, cyclones, droughts, crop diseases, etc.) (vi) Cattle insurance (Insurance for indemnity against the loss of cattle from various kinds of diseases).
In addition to the above, insurance plans are available against crime, medical insurance, bullock cart, jewelry, cycle-rickshaw, radio, T.Vs., etc.
On Basis Business Point of View
The following are the types of insurance on the basis business point of view:
Life Insurance
According to the Life Insurance Act, of 1938, life insurance refers to the contract of insurance on human life, under which if any individual’s death, other than an accident, or happening of any event concerning human life, a certain amount is guaranteed to be paid to assured or his/her legal representative.
According to the terms of the contract the assured should pay the premium, the rate of which may differ according to human life. The act also provides for:
- Payment of double or triple rate of accidental benefits, as per terms of the contract.
- Annuity on human life.
- Superannuation allowance, and annuity from the funds created for granting assistance to such persons.
General Insurance
General insurance business refers to fire, marine, and miscellaneous insurance business whether carried on singly or in combination with one or more of them, but does not include capital redemption business and annuity certain business. (According to Sec.3(g) of the General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act, 1972).
On Basis Risk Point of View
The following are the types of insurance on a basis risk point of view:
Personal Insurance
Personal insurance refers, to the loss of life by accident, or sickness to an individual who is covered by the policy. The insurer undertakes to pay the sum insured on the happening of a certain event or on the maturity of the period of insurance.
This insurable sum is determined at the time of affecting the policy and includes life insurance, accident insurance, and sickness insurance. Life insurance contains the element of investment and protection, while accidental, sickness, or health insurance contain the element of indemnity only.
Property Insurance
A contract of property insurance is a contract of indemnity. Proof by the assurance of loss is an essential element of property insurance.
The policies of insurance against burglary, home-breaking or theft, etc. fall under this category. The assurance is required to protect the insured property. After the loss has taken place, the assured is usually required to notify the police as to losses.
Liability Insurance
Liability insurance is the major field of general insurance whereby the insurer promises to pay the damage to property or to compensate the losses to a third party. The amount of compensation is paid directly to the third party. The fields of liability insurance include workmen’s compensation insurance, third-party motor insurance, professional indemnity insurance, and third-party liability insurance, etc.
In liability insurance, there may be various reasons for the arising of liability; viz. accident to a worker at the workplace, defective goods, explosion in the factory during the process of production, formation of poisonous gas within the factory, due to the uses of chemicals and other such substances in the manufacturing process.
Fidelity Guarantee Insurance
In this type of insurance, the insurer undertakes to indemnify the assured (employer) in consideration of certain premiums, for losses arising out of fraud, or embezzlement on the part of the employees. This kind of insurance is frequently adopted as a precautionary measure in cases where new and untrained employees are given positions of trust and confidence.
FAQs About the Types of Insurance
What are the types of insurance?
These are the types of insurance:
1. Life Insurance
2. Fire Insurance
3. Marine Insurance
4. Social Insurance
5. Miscellaneous Insurance
6. Life Insurance
7. General Insurance
8. Personal Insurance
9. Property Insurance
10. Liability Insurance.