Table of Contents
- 1 How is price and output determined under perfect competition?
- 2 Meaning and Characteristics
- 3 Price and Output Determination During Short Period Under Perfect Competition
- 4 Price and Output Determination During Long Period Under Perfect Competition
- 5 Price and Output Determination Under Imperfect Competition During Short Period
- 6 Price and Output Determination Under Imperfect Competition During Long Period
- 7 Conclusion or Summary
- 8 FAQ Related Price and Output Determination Under Perfect Competition
How is price and output determined under perfect competition?
Perfect competition refers to a market situation where there are a large number of buyers and sellers dealing in homogenous products. Under perfect competition, there are no legal, social, or technological barriers to the entry or exit of organizations. Sellers and buyers are fully aware of the current market price of a product. Therefore, none of them sells or buy at a higher rate.
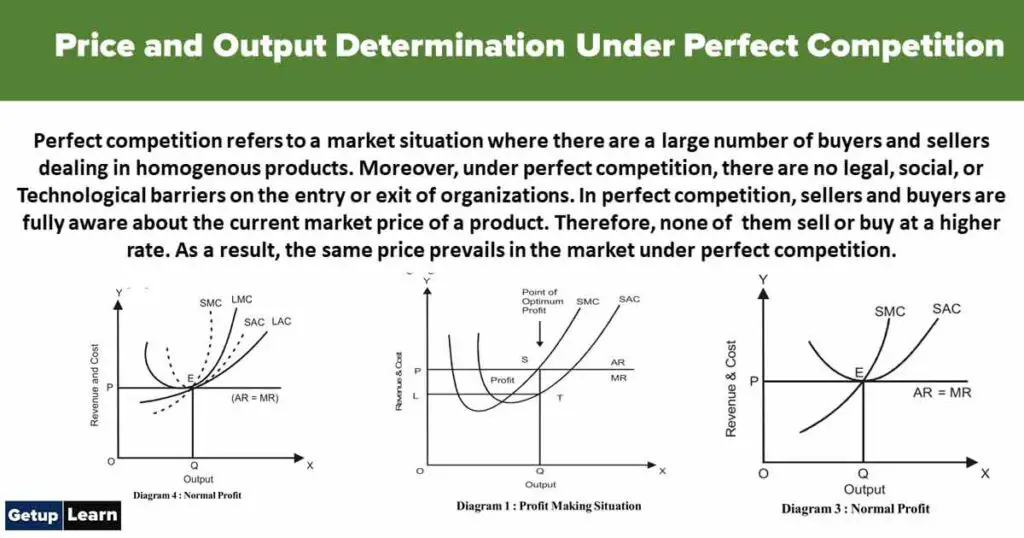
As a result, the same price prevails in the market under perfect competition. The buyers and sellers cannot influence the market price by increasing or decreasing their purchases or output, respectively. The market price of products in perfect competition is determined by the industry. This implies that in perfect competition, the market price of products is determined by taking into account two market forces, namely market demand and market supply.
Study in detail price and output determination under perfect competition given below.
Meaning and Characteristics
Perfect competition is a market structure in which the following characteristics are found:
- A large number of buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous product
- Free entry and exist of firms in an industry
- Perfect knowledge of market conditions
- Perfect mobility of factors of production
- No transport cost
- Firm is a price taker
- Price, average revenue and marginal revenue are equal (P=AR=MR) and they are horizontal to OX–axis.
Under perfect competition, there is a large number of buyers and sellers and they jointly affect the total demand and supply of the goods and services produced by an industry. The product produced under perfect competition is identical in shape, colour, packing, weight, quality etc.
All the units of the product are homogeneous. All the firms are free to enter and exit the industry in this market. When existing firms are earning profit other firms will be attracted and when existing firms are incurring losses then some of them will leave the industry. Thus there are no restrictions on the entry and existence of firms in the industry.
Perfect knowledge of market conditions is another characteristic of the market. Buyers and sellers are aware of the product, price and quantities offered. All the factors of production – land, labour, capital, entrepreneur and organisation have the perfect mobility whenever they are getting higher remuneration elsewhere.
Under perfect competition, there is no transport cost because the whole market is adjacent. Firms are price takers and the price is determined by the total demand and total supply of the product in the industry. Whatever price is determined by industry is accepted by individual firms and accordingly they make decisions regarding the quantity of output.
Price, average revenue and marginal revenue are the same and they are horizontal to OX-axis because the price of the product remains constant for buyers and sellers.
Price and Output Determination During Short Period Under Perfect Competition
The price and output determination is done by the industry as a whole and the individual firm accepts it. There are three situations during a short period under this market structure as given under:
Profit Making Situation
Under perfect competition during short period some firms earn profit as shown in the following diagram:
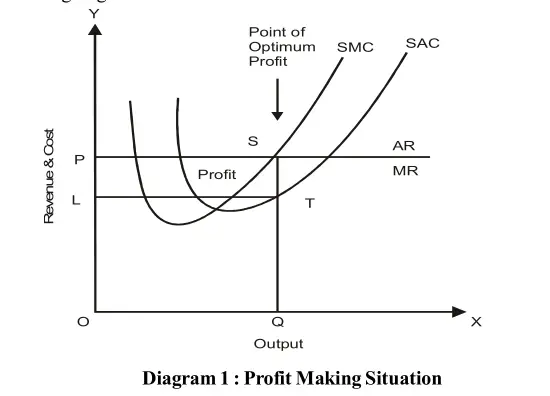
The industry is shown on the left side wherein SS is the total supply and DD is the total demand for the product. The point of E is the equilibrium of industry where the supply curve intersects the demand curve. The price is OP and the quantity of output is OQ. The right side diagram is of an individual firm where AR and MR are average revenue and marginal revenue and they are equal to price (P=AR=MR).
AC and MC are average cost and marginal cost curves of the firm. The point of equilibrium of the firm is at the point where MC cuts the MR curve from below. The average and marginal revenue curves are above the AC and MC curves. The price and output of the firm are OP and OQ respectively. The average profit earned by the firm is (AR-AC)ST and the total profit is PLTS.
Loss Incurring Situation
During a short period, some firms may incur losses when their AC and MC curves are above their AR and MR curves at equilibrium points as shown in diagram 2.

The point of equilibrium of industry is at the E point which indicates the price determined by the total demand (DD) and total supply (SS) where OP is price and OQ is output. The right side of the diagram depicts the P=AR=MR and AC and MC cost curves of the firm. Cost curves are above the revenue curves (AR & MR) which shows the firm is incurring a loss, OP is price, OQ is output, average loss (AC– AR) is ST and total loss is RPTS.
Normal Profit
During short period under perfect competition some firms may earn normal profit which is the situation of neither profit nor loss as shown in diagrams 3.
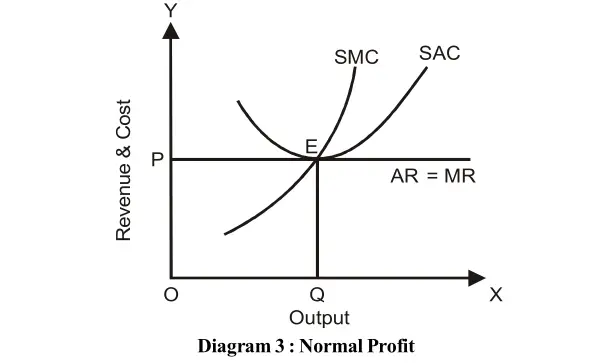
The point of equilibrium of industry is at E, price is OP and output is OQ, the same price is accepted by the firm. Price, revenue and costs are shown on OY-axis while output is on OX-axis. The price is OP and output is OQ and the point of equilibrium of the firm is at point E where P=AR=AC=MR=MC. This firm is called optimum firm during short period under perfect competition because it has optimum utilisation of its resources.
Price and Output Determination During Long Period Under Perfect Competition
There is free entry and exit of the firms in an industry. If existing firms are earning an abnormal profit, more firms will be attracted to the industry, production will increase and the price of the product will fall and profit will be evaporated. On the other hand, if firms are incurring loss no firm would like to stay in the industry for the long period and they will leave the industry.
The number of firms will decrease, the output will decrease and the price of the product will increase thereby the loss incurring situation will be converted into normal profit. Thus there will be neither profit nor loss simply normal profit will be earned by the firms in the industry and normal profit is part of the cost. Price and output during long period under perfect competition are shown in the following diagram:
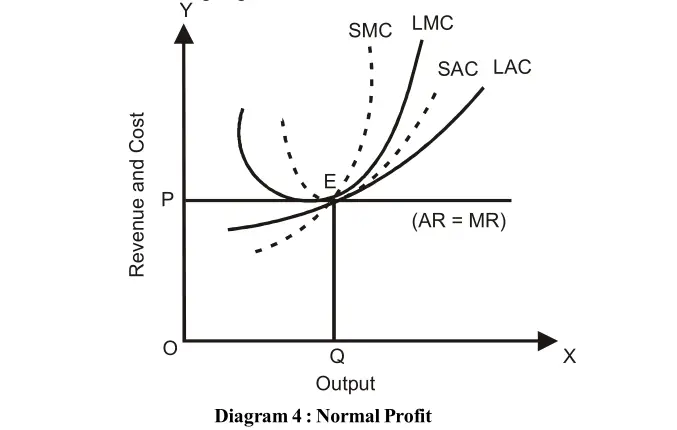
The price and output in the industry are OP and OQ respectively. They are determined by the total demand (DD) and total supply (SS) and the point of equilibrium of industry is at point E. While the point of equilibrium of firm is at Point E1. Price is OP and output is OQ.
At point E long-run average cost (AC) is equal to long-run average revenue (AR), long-run marginal cost is equal to long run marginal revenue and price (P=AR=AC=MR=MC). This is a situation of normal profit during long period and the firm is called the ‘optimum firm’.
Price and Output Determination Under Imperfect Competition During Short Period
Imperfect competition is that market structure wherein the following characteristics exist:
This market structure is also called monopolistic competition and this is a market having some of the characteristics of perfect competition and some of the characteristics of a monopoly market. Under imperfect competition, there is a large number of buyers and sellers.
ll the firms are free to enter as well as free to exist the industry under imperfect competition. If the firms are earning profit other firms will be attracted and the volume of production will increase. When the films are incurring loss they can continue during short period expecting that in the long run, they will earn profit.
But in the long run, no firm would like to stay as there is no restriction on their existence. Thus the firms will leave the industry. Another characteristic of this market structure is product differentiation. Product is differentiated in the form of shape, size, colour, quality, wrapper etc. Consumers know that the product of a particular firm is different from the product of other firms.
Non-price competition is also another characteristic of imperfect competition. This characteristic deals with sales promotion and marketing strategy. Firm spending on advertisement and sales promotion will attract more customers in comparison to other firms spending less on this item. Thus the firm spending more will compete successfully and consumers/buyers will have attachment with the product.
There are three situations of firms under imperfect competition during the short period as given under:
Profit Making Situation
When the firm’s average cost and marginal cost curves are below its average revenue and marginal revenue curves, the firm is earning profit as shown in the following diagram:
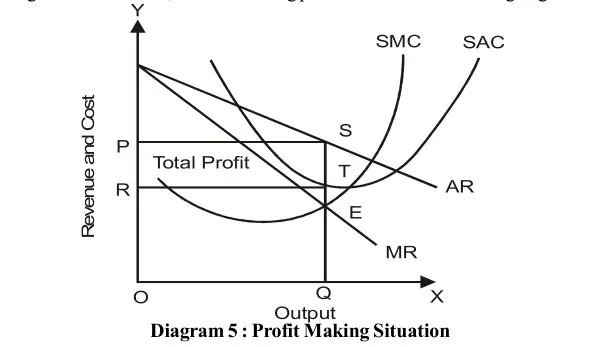
The above diagram clearly shows that AR and MR are revenue curves and AC and MC are cost curves of the firm. The point of equilibrium of the firm is E where the MC curve cuts the MR curve from its below. The price and output are OP and OQ respectively. The average profit (AR-AC) is ST while the total profit is PRTS.
Loss Incurring Situation
When a firm’s Cost Curve (AC) is above the Average Revenue (AR) then the firm is incurring a loss as shown in diagram 6:
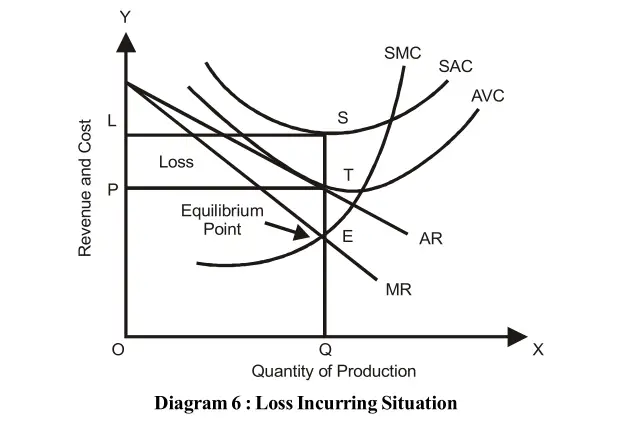
The diagram shows that point of equilibrium is E where MR=MC, price OP and output is OQ. The AC is above the AR. The average loss (AC–AR) is ST and the total loss is LPTS. The firm is incurring losses.
Normal Profit
When the AC curve is tangent to the AR curve of the firm, the situation is normal profit as shown in diagram 7:
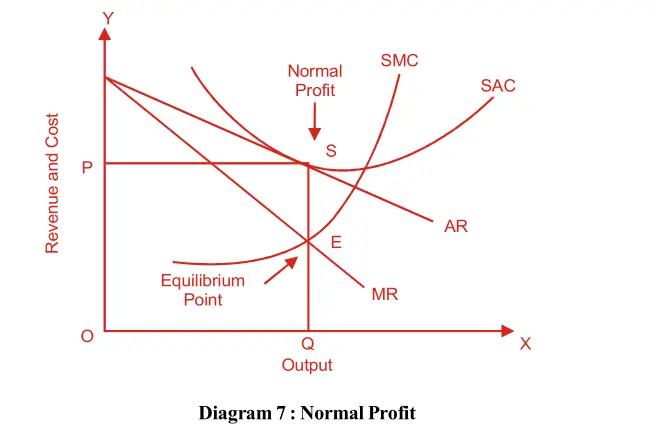
The diagram shows the point of equilibrium E where MR=MC. The AC curve is tangent to the AR curve at the S point. Price is OP and output is OQ.
Price and Output Determination Under Imperfect Competition During Long Period
Free entry and exit of firms in the industry is one of the characteristics of imperfect competition. During the long period when firms are earning profit more firms will be attracted and there will be more productivity, the price of output will decline and thereby profit-earning situation will be converted into normal profit.
On the other hand, when firms are incurring loss they cannot carry on production for long period and they leave the industry thereby production decreases and the price will increase and the loss incurring situation will be converted into normal profit. Thus under imperfect competition, there will be neither profit nor loss but simply normal profit as shown in diagram 8:

Price, revenue and costs are shown on OY-axis while output is shown on OX-axis. The E point shows the point of equilibrium where the firm’s MC=MR. Price is OP and output is OQ while the AC is tangent to AR at point S which clearly indicates the situation of normal profit during a long period.
Conclusion or Summary
Price and output determination under perfect competition and imperfect competition during short period and long period reveals that during short period under perfect competition, profit, loss and normal profit situation are found as firms have no say in price determination as it is dictated by the industry and an individual firm is a price taker and takes decision regarding the quantity of output.
During long period firms earn normal profit under perfect competition as there is free entry and exit of firms in industry. All the characteristics of perfect competition are imaginary and unrealistic. Imperfect competition is a realistic market structure and all the characteristics of the market are found in real life namely product differentiation, non-price competition, free entry and exist of firms in industry and a large number of buyers and sellers in the market.
Under imperfect competition during a short period price and output, determination reflects three situations – profit, loss and normal profit decided by the costs and revenue curves of the firm. During a long period there is neither profit nor loss under imperfect competition because of the free entry and exit of firms in the industry. Thus there will be normal profit only.
How price and output is determined under perfect competition in the long run?
There is free entry and exist of the firms in an industry. If existing the firms are earning abnormal profit, more firms will be attracted to the industry, production will increase and the price of the product will fall and profit will be evaporated. On the other hand if firms are incurring loss no firm would like to stay in the industry in the long period and they will leave the industry. Number of firms will decrease, output will decrease and the price of the product will increase thereby the loss incurring situation will be converted into normal profit.
How are perfect competition prices determined under perfect competition?
Price and output determination under perfect competition and imperfect competition during a short period and long period reveal that during the short period under perfect competition, profit, loss and normal profit situation are found as firms have no say in price determination as it is dictated by the industry and an individual firm is a price taker and takes a decision regarding the quantity of output. During long period firms earn a normal profit under perfect competition as there is free entry and exit of firms in the industry. All the characteristics of perfect competition are imaginary and unrealistic.