Table of Contents
- 1 What is Formal Organisation?
- 2 Meaning of Formal Organisation
- 3 Definition of Formal Organisation
- 4 Characteristics of Formal Organisation
- 5 Functions of Formal Organisation
- 6 Principles of Formal Organisation
- 7 Importance of Formal Organisation
- 8 Advantages of Formal Organisation
- 9 Disadvantages of Formal Organisation
- 10 Features of Formal Organisation
- 11 Difference Between Formal and Informal Organisation
-
12 FAQ Related to Formal Organisation
- 12.1 What is a formal organisation example?
- 12.2 What are the characteristics of formal organisation?
- 12.3 What are the functions of formal organisation?
- 12.4 What are the principles of formal organisation?
- 12.5 What is the importance of formal organisation?
- 12.6 What are the advantages of formal organisation?
- 12.7 What are the disadvantages of formal organisation?
What is Formal Organisation?
The formal organisation is a system of well-defined Jobs, each bearing a definite measure of authority, responsibility, and accountability, the whole consciously designed to enable the people of the enterprise to work most effectively together in accomplishing their objectives.
The formal organisation is characterized by being will-defined, found by delegation, and relatively stable.
Meaning of Formal Organisation
The formal organisation refers to the structure of jobs and positions with clearly defined functions and relationships as prescribed by the top management. This type of organisation is built by the management to realize the objectives of an enterprise and is bound by rules, systems, and procedures.
Everybody is assigned a certain responsibility for the performance of the given task and given the required amount of authority for carrying it out.
The formal organisation is built around four key pillars. They are:
- Division of Labour
- Scalar and Functional Processes
- Structure
- Span of Control
Thus, a formal organisation is one resulting from planning where the pattern of structure has already been determined by the top management.
Definition of Formal Organisation
These are the definitions of formal organisation by the author:
[su_quote cite=”Sharma and Sadona”]They defined ‘formal organisation‘ means: “The organisation as deliberately planned, designed and duly sanctioned by the competent authority[/su_quote]
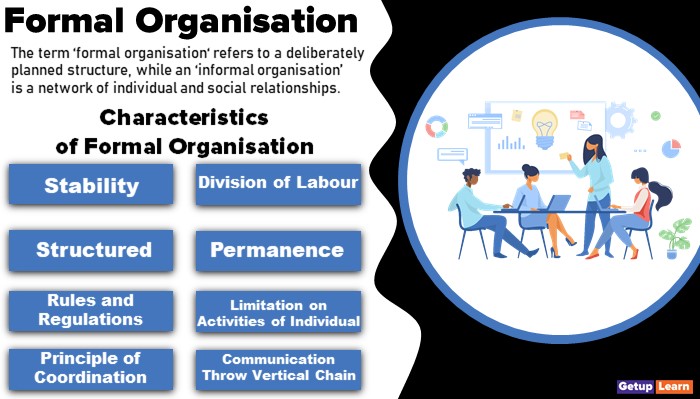
[su_quote cite=”Getuplearn”]The term ‘formal organisation‘ refers to a deliberately planned structure, while an ‘informal organisation’ is a network of individual and social relationships.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Chester I. Barnard”]He defined formal organisation as “a system of consciously coordinated activities or forces of two or more persons”. A formal organisation is deliberately designed to achieve some particular objectives. It refers to the structure of well-defined jobs, each bearing a definite measure of authority, responsibility, and accountability.[/su_quote]
The structure is consciously designed to enable the people of the organisation to work together for accomplishing common objectives. Thus, the formal organisation is more or less an arbitrary structure to which the individual must adjust.
It tells him to do certain things in a specified manner, to abbey orders from designated individuals, and to cooperate with others. Coordination also proceeds according to a prescribed pattern in the formal organisation structure.
Characteristics of Formal Organisation
These are the characteristics of formal organisation:
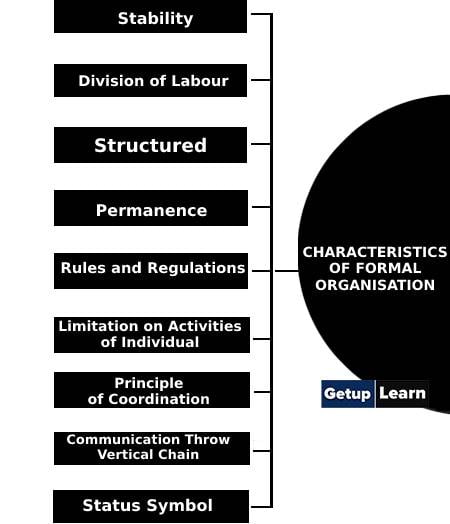
- Stability
- Division of Labour
- Structured
- Permanence
- Rules and Regulations
- Limitation on Activities of Individual
- Principle of Coordination
- Communication Throw Vertical Chain
- Status Symbol
Stability
An important characteristic of a formal organisation is its stability. Therefore, the formal organisation grows and expands with the passage of time.
Division of Labour
The structure of the formal organisation is based on jobs to be performed by the individual, and not vice versa. Roles are hierarchical and work is assigned to individuals on the basis of expertise and capability.
Structured
A formal organisation is structured and organized to accomplish the organisational mission. One exponent has remarked that the “absence of structure is illogical, cruel, wasteful, and inefficient”.
Because of this feature, the roles and responsibilities of individuals in an organisation are clearly defined.
Permanence
As the organisation is structured, it has continuity of operations. They last for a long time and grow over a period of time.
Rules and Regulations
Formal organisations follow rules and regulations. Individuals working in formal organisations do not perform activities, according to their whims. Rather, they act according to the rules and regulations framed by the organisation.
For example, if a cooperative bank has to sanction a loan to a Panchayat for its development, the manager of the bank has to follow guidelines before sanctioning the loan.
Limitation on Activities of Individual
Every individual in a formal individual is assigned specific duties & responsibilities. This is true regulation for every personnel.
Principle of Coordination
Strict observance of the principle of coordination: The coordination between different departments in an organisation is strictly maintained to achieve the most efficient result.
Communication Throw Vertical Chain
Messages are communicated through the vertical chain: Normally in a formal organisation, the vertical communication chain is followed so that the chain of command & its unity is maintained.
Status Symbol
A formal organisation is a separate social entity. The activities have a separate entity from the individuals performing those activities.
Functions of Formal Organisation
These are the functions of formal organisation:
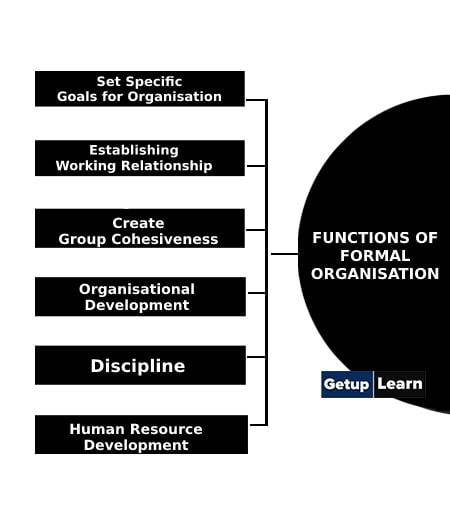
- Set Specific Goals for Organisation
- Establishing Working Relationship
- Create Group Cohesiveness
- Organisational Development
- Discipline
- Human Resource Development
Set Specific Goals for Organisation
A formal organisation has to set specific goals for the personnel working in it. By achieving the goals individually achieved the organisation as a whole will be benefited in achieving the eventual goals.
Establishing Working Relationship
In a formal organisation, the primary goal is to establish an efficient working relationship & to establish a clear chain of command. An effective work relationship is the most important thing for the goals.
Create Group Cohesiveness
It creates a sense of cohesiveness & belongings among the groups of personnel working in a formal organisation. The employee’s inter-personnel interaction is important for the functioning of an organisation.
Organisational Development
A formal organisation works on organisational development by testing all the rules, regulations & the chain of activities as a present. The organisation detects any problem & works to change them if necessary for better service.
Discipline
Discipline within an organisation is important to get the best result of it. Organisational management has to find a proper way to achieve proper discipline.
Human Resource Development
It helps in other human resources development activities such as recruitment, promotions, career planning and development, and manpower planning. The important part of an organisation is its employees.
A formal organisation gives the opportunity to treat the human resources within the organisation. The development & improvement of human resource is easy in a formal organisation,
Principles of Formal Organisation
A formal organisation works to achieve some specific goals regarding the organisation. These are the principles of formal organisation:
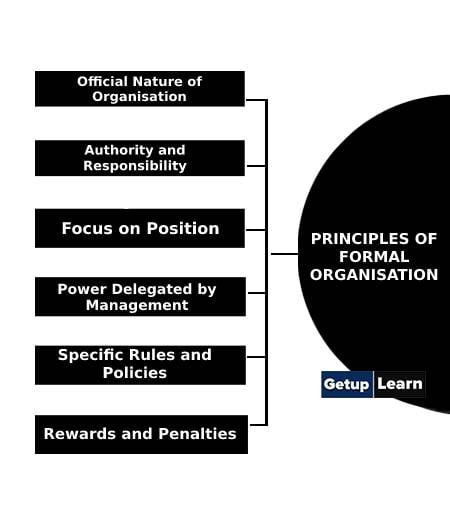
- Official Nature of Organisation
- Authority and Responsibility
- Focus on Position
- Power Delegated by Management
- Specific Rules and Policies
- Rewards and Penalties
Official Nature of Organisation
The organisation must be legal & official in all respect. It should be recognizable in its respective industry of operating in an official manner.
The formal organisation emphasizes clear delegation of authority & a specific set of responsibilities for a specific position.
Focus on Position
A formal organisation focuses on the position of personnel & its position regarding the organisation rather than the personnel him/her.
Power Delegated by Management
The formal organisation management delegates the power regarding every position of personnel & specific power sets for specific authority.
Specific Rules and Policies
The rules & policies regarding a formal organisation are specific & should be always followed in terms of performing activities for achieving organisational goals.
Rewards and Penalties
A formal organisation has to have a systematic way of rewarding personnel based on their good services and also needs to have a penalty system outlined to prevent carelessness & recklessness from the employees.
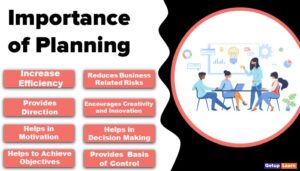
Importance of Formal Organisation
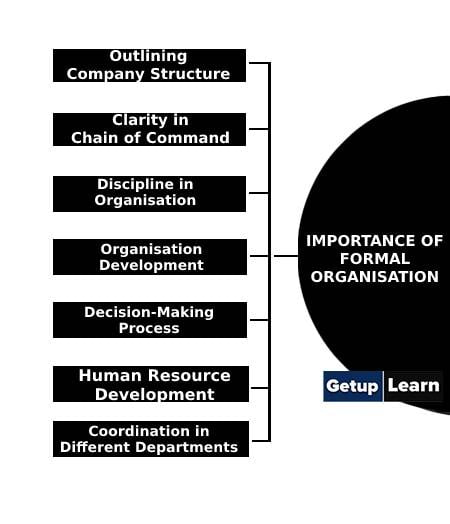
These are the importance of formal organisation:
- Outlining Company Structure
- Clarity in Chain of Command
- Discipline in Organisation
- Organisation Development
- Decision-Making Process
- Human Resource Development
- Coordination in Different Departments
Outlining Company Structure
It provides a basic structure for the division of work and responsibilities. Without such a structure it will be very difficult for employees to agree between themselves on the duties and responsibilities of each, and such difficulties multiply in geometric proportions with the increasing size of the organisation. A formal organisation is helpful & strict in the ways a company will act upon.
Clarity in Chain of Command
It generates clarity on what support and input each employee can expect from others, and in turn what is expected of him by others.
In a formal organisation, the chain of command is clearly drawn so that personnel in the organisation can follow them as per requirement & ordered to do so. In a formal organisation, the chain of command is strictly followed to achieve the company goal.
Discipline in Organisation
It promotes discipline in the organisation. In a formal organisation, the rules & regulations are clear & organized, so the presence of discipline is there. This discipline itself influences the efficiency of the organisation.
Organisation Development
It makes it easier to review and revise the organisation with changing requirements. The world is changing every day & so is the environment in which the organisation is operating.
To keep up with the ever-changing environment the organisation needs to develop embracing changes. In a formal organisation, the process of development becomes easier.
Decision-Making Process
It provides a structure for laying down pay scales and taking other decisions linked to organisational levels. A formal organisation is the logical distribution of resources to achieve the company goal in the most efficient manner. Any decision-making regarding the organisation is easy &easy to implement.
Human Resource Development
It helps in other human resources development activities such as recruitment, promotions, career planning and development, and manpower planning.
The important part of an organisation is its employees. The development & improvement of human resources is easy in a formal organisation.
Coordination in Different Departments
An organisation consists of different departments to carry out various activities and contributes to the ultimate function of the organisation.
In a formal organisation, all the departments are well outlined along with their activities. So it is easy to relate & co-ordinate. Thus a formal organisation is easier to manage.
Advantages of Formal Organisation
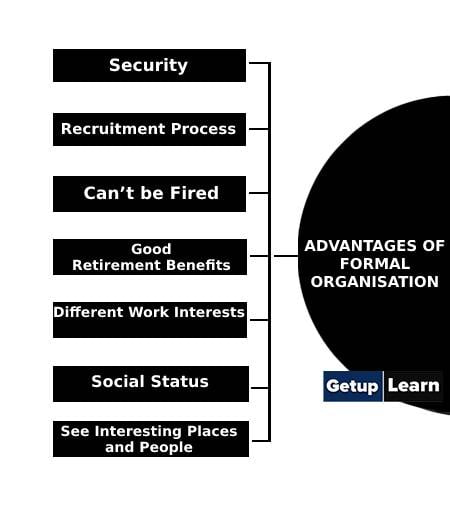
The advantages of formal organisation can be enlisted under two aspects:
- Security
- Recruitment Process
- Can’t be Fired
- Good Retirement Benefits
- Different Work Interests
- Social Status
- See Interesting Places and People
Financial Aspect
Security
A formal organisation is more established & the entity of the company is not dependent on individual losses. So working in such an organisation provides secured financial support to the employees & the employees working here are more devoted to work.
Slow but steady promotions in a formal organisation the promotion may not be rapid due to a chain of command but with certain seniority in the organisation with sufficient performance, personnel is sure of a promotion.
Recruitment Process
Commissioned ranks open to men and women graduates: A formal organisation will always put preference to recruiting graduates or highly educated personnel, in this way creating job opportunities for this class of people.
Can’t be Fired
After recruiting a person a formal organisation tries its best to develop the personnel. In many cases, the personnel is not generally fired depending on a few personal mistakes.
Good Retirement Benefits
The organisation of such value will arrange a plan for the employees so that they can retire with benefits.
Social Aspect
Different Work Interests
Many different branches appeal to different interests: A formal organisation has many different departments to perform various activities.
So a person has a wide range of options from which he/she can choose depending on individual interest & skill level. So as a person, there is an option in this type of organisation on the choice of profession.
A formal organisation has specific positions & position names that bear the status of the person in the organisation. These posts are familiar in the environment the company is operating & often works as a social status symbol.
By working in a formal organisation the person has to way to achieve such a position & thus achieve a high social activity.
See Interesting Places and People
By working in a formal organisation a person gets to meet many different people with different views & values. By interacting with these variations a person will learn more about working in such an environment.
Disadvantages of Formal Organisation
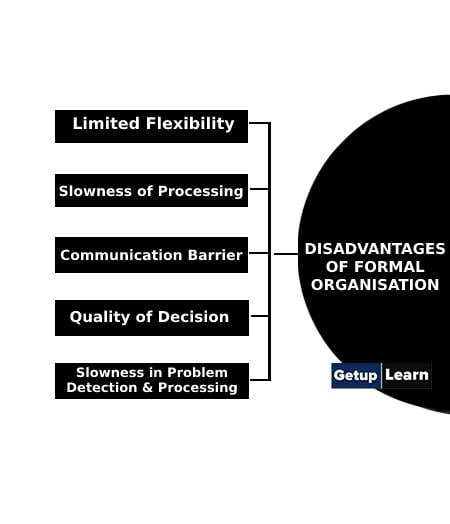
These are the following disadvantages of formal organisation:
- Limited Flexibility
- Slowness of Processing
- Communication Barrier
- Quality of Decision
- Slowness in Problem Detection & Processing
Limited Flexibility
As this type of organisation is very specific in every activity there is very little margin for flexibility & spontaneous decision-making in the company. Such practices in the company can demotivate the employees.
Slowness of Processing
In a formal organisation performing a task needs many formal procedures. Such formalities often slow down the implementation of decision-making.
Communication Barrier
As in a formal organisation, a task needs the coordination of different departments so the communication needs to be clear in this process. Any kind of miscommunication may lead to ultimate inefficiency.
Quality of Decision
Sometimes the quality of the decision made by the top management may not be most compatible with the company but the chance of correction is very scarce.
Slowness in Problem Detection & Processing
As every procedure goes through a lot of formalities any problem detected at the operation level cannot be instantly corrected. The right process will take some time to detect the problem & correct & its implementation. In such a process the organisation may suffer financial loss.
Features of Formal Organisation
These are the features of formal organisation explained below:
- A formal organisational structure is laid down by the top management to achieve organisational goals.
- A formal organisation prescribes the relationships among the people working in the organisation.
- The organisation structure is consciously designed to enable the people of the organisation to work together for accomplishing the common objectives of the enterprise.
- Organisational structure concentrates on the jobs to be performed and not the individuals who are to perform jobs.
- In a formal organisation, individuals are fitted into jobs and positions and work as per managerial decisions. Thus, the formal relations in the organisation arise from the pattern of responsibilities that are created by the management.
- A formal organisation is bound by rules, regulations, and procedures.
- In a formal organisation, the position, authority, responsibility, and accountability of each level are clearly defined.
- The organisational structure is based on the division of labour and specialization to achieve efficiency in operations.
- A formal organisation is deliberately impersonal. The organisation does not take into consideration the sentiments of organisational members.
- The authority and responsibility relationships created by the organisation structure; are to be honoured by everyone.
- In a formal organisation, coordination proceeds according to the prescribed pattern.
Difference Between Formal and Informal Organisation
Following are quick notes differences between formal and informal organisation:
| Formal Organisation | Informal Organisation |
| It has defined objectives that will save the organisation and make it stable. | It does not have objectives but inspires of friendship, fame, respect, and unity. |
| It is established with a particular process. | It appears spontaneously. |
| In this, the members are bound together with authority relations. | In this, the member has duty, authority, and responsibility. |
| It can be shown in an organisational chart. | It cannot be shown in an organisational chart. |
| In this, the work for achieving the organisational goal is identified. | In this, the work for achieving the organisational goal is not identified. |
What is a formal organisation example?
The formal organisation is a system of well-defined Jobs, each bearing a definite measure of authority, responsibility, and accountability, the whole consciously designed to enable the people of the enterprise to work most effectively together in accomplishing their objectives.
What are the characteristics of formal organisation?
Following are the points of characteristics of formal organisation:
1. Stability
2. Division of Labour
3. Structured
4. Permanence
5. Rules and Regulations
6. Limitation on Activities of Individual
7. Principle of Coordination
8. Communication Throw Vertical Chain
9. Status Symbol.
What are the functions of formal organisation?
The following are the functions of formal organisation:
1. Set Specific Goals for the Organisation
2. Establishing Working Relationship
3. Create Group Cohesiveness
4. Organisational Development
5. Discipline
6. Human Resource Development,
What are the principles of formal organisation?
The following are the principles of formal organisation:
1. Official Nature of Organisation
2. Authority and Responsibility
3. Focus on Position
4. Power Delegated by Management
5. Specific Rules and Policies
6. Rewards and Penalties.
What is the importance of formal organisation?
Following are the importances of formal organisation:
1. Outlining Company Structure
2. Clarity in the Chain of Command
3. Discipline in the Organisation
4. Organisation Development
5. Decision-Making Process
6. Human Resource Development
7. Coordination in Different Departments
What are the advantages of formal organisation?
The following are the advantages of formal organisation:
1. Security
2. Recruitment Process
3. Can’t be Fired
4. Good Retirement Benefits
5. Different Work Interests
6. Social Status
7. See Interesting Places and People
What are the disadvantages of formal organisation?
The following are the disadvantages of formal organisation;
1. Limited Flexibility
2. Slowness of Processing
3. Communication Barrier
4. Quality of Decision
5. Slowness in Problem Detection & Processing.