Table of Contents
What is Electronic Data Interchange?
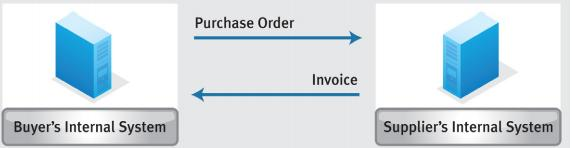
As its name implies, EDI is exchange/interchange of data (and information) in electronic format (soft copy only). It refers to exchange of business related documents (agreements, spreadsheets, presentations) between business organizations.
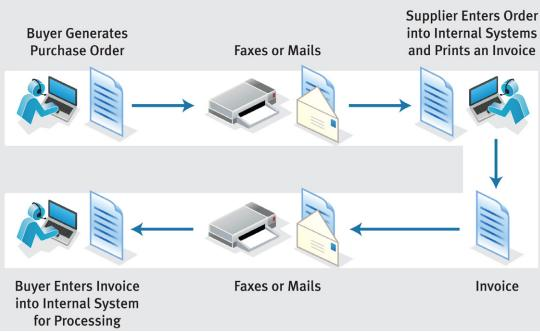
It replaces the old method of data exchange whereby documents (in hard copy form) are exchanged between business organizations through mailing, faxing, sending by courier etc.
Business organizations exchanging information via EDI are called trading partners. Business organizations use specific and agreed formats of documents, based on widely accepted standards. Though, they are allowed a little bit of flexibility that fits their business needs.
The documents to be shared may include agreements, purchase orders, summarized reports, advance shipment notices, and invoices, product catalogs, quotations etc. Data interchange happens over a network which may be an intranet, Value Added Network (VAN), or Internet.
History of Electronic Data Interchange
Electronic Data Interchange was developed in the 1960s as a means of speeding up the movement of documents pertaining to shipments and transportation. ANSI (American National Standards Institute) has approved a set of EDI standards, it is known with the name“X.12 standards”.
A similar standard developed by the United Nations is EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange For Administration, Commerce and Trade). ANSI X.12 is commonly used in North America whereas EDIFACT is more popular in the rest of world.
EDI surely offers many benefits. The major one being the speed at which documents, data and information can be shared or sent from one office to another. Sending an email needs few seconds only. It also gives the advantage that business transactions can happen faster.
E-commerce websites are heavily using EDI. For example, when a customer purchases a product online, he is sent invoice immediately on his email address.
Types of EDI
There are three basic types of EDI. These are explained next:
Batch EDI
Batch EDI is the most popularly used EDI system. It is ideal for transfer of electronic documents of similar type on regular basis.
It requires minimum efforts on the behalf of the data entry computer operator. This type of EDI system is good for the organizations whereby there are high quantities of repetitive information, and it is tried to reduce the volume of information to be conveyed.
Event Driven EDI
Event Driven EDI is an enhancement of Batch EDI. It is also known as customer-driven EDI. In this case, EDI processing is initiated by some predetermined criteria like the receipt of a Purchase Order or a request for product catalog from Trading Partner etc.
It integrates the data with other internal data processing systems of the organization. Applications start exchanging message sets as soon as they are created or received. It starts a detailed cascade effect which initiates and automates other processes as a result of the request from a customer.
Interactive EDI
In this type of Electronic Data Interchange, participating systems are designed to reduce the response delay and documents are exchanged online in real time as soon as a transaction completes. It is also called real time EDI. It consists of applications exchanging EDI directly within a pre-programmed context.
Interactive EDI (IEDI) takes messages in the form of a whole series of pairs of conversational messages that allows a person with an EDI requesting system to interrogate a host system for information in real-time. Interactive EDI is still at its initial stage.
Benefits of EDI in E Commerce
There are many benefits of implementing EDI. These benefits can be categorized into:
- Direct Benefits
Direct Benefits
- Major benefit is that data is communicated faster and more accurately. Speed comes from electronic means of data communication. Accuracy comes from the agreed upon common standards and from the fact that data does not have to be keyed-in again and again.
- EDI significantly reduces the volume of paper used and handled in the office. It results in cost savings. EDI results in paper-less or at least “less paper” office. Less use of paper needs smaller storage space, fewer efforts to search particular information etc.
- With EDI transactions, many expenses associated with paper printing, storage, filing, reproduction, and document retrieval etc. are all reduced.
- Less use of manual records also reduces the chances of misuse of office information and stealing of important data. Documents in electronic format are not only easier to take care of, rather, they are more secure and safe. Use of cryptography may make these documents unreadable and use of security measures like password etc. may save the document from unauthorized access.
Strategic Benefits
- Competitive edge is maintained and enhanced.
- Better customer and supplier relations through more effective and faster communication and exchange of information.
FAQs Section
What is EDI?
As its name implies, EDI is exchange/interchange of data (and information) in electronic format (soft copy only). It refers to exchange of business related documents (agreements, spreadsheets, presentations) between business organizations.
What are types of EDI in E commerce?
There are three basic types of EDI:
1. Batch EDI
2. Event Driven EDI
3. Interactive EDI.
