Table of Contents
What is a Certificate of Deposit?
A certificate of deposit is a document of title to depositors of funds that remain on deposit at the bank for specified period at a specified rate of interest. They are unsecured, negotiable short term instruments in bearer form.
They are introduced in June 1989 and only scheduled commercial banks were allowed to issue Certificates of deposit initially. It was only in 1992 that financial institutions were permitted to issue certificates of deposits. The term of a CD generally ranges from one month to five years. Further, the minimum amount of a CD is fixed at Rs.25 Lakh in the denomination of Rs.5 Lakh.
Features of Certificate of Deposits
The following are the features of certificate of deposits:
- CDs are is highly safe for investors as the default risk in them is almost negligible, Thus, they are considered as risk-less and safe securities.
-
Certificate of deposits is highly liquid and marketable and hence investors can buy or sell it whenever they desire to do so.
- It has an added advantage for investors who are willing to invest in it, as they are transferable from one party to another which cannot be done with term deposits.
- It is a time deposit that restricts holders from withdrawing funds on demand, however if an investor wants to withdraw the money, this action will often incur a penalty.
- A certificate of deposits may be payable to the bearer or registered in the name of the investor. Investors can resell bearer CD’s more easily than registered CD’s and so most certificates of deposits are issued in bearer form. Certificate of deposits can be one of the alternatives for a investor if he or she does not want to invest in term deposits.
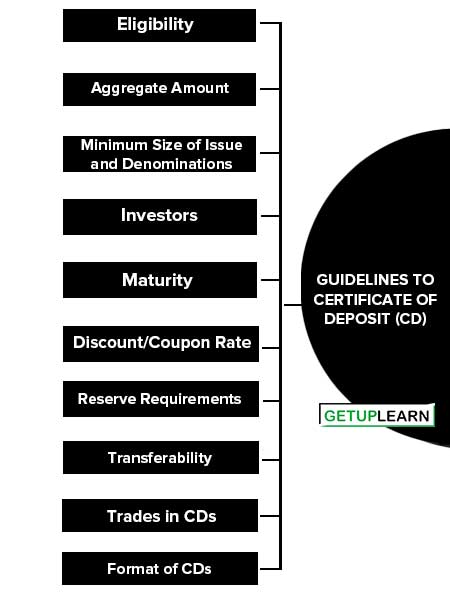
Guidelines to Certificate of Deposit (CD)
The main guidelines to certificate of deposit (cd) are:
- Eligibility
- Aggregate Amount
- Minimum Size of Issue and Denominations
- Investors
- Maturity
- Discount/Coupon Rate
- Reserve Requirements
- Transferability
- Trades in CDs
- Loans/Buy-Backs
- Format of CDs
- Security Aspect
- Payment of Certificate
Eligibility
CDs can be issued by (i) scheduled commercial banks {excluding Regional Rural Banks and Local Area Banks}; and (ii) select All-India Financial Institutions (FIs) that have been permitted by RBI to raise short-term resources within the umbrella limit (prescribed in paragraph 3.2 below) fixed by RBI.
Aggregate Amount
Banks have the freedom to issue CDs depending on their funding requirements. An FI can issue CD within the overall umbrella limit prescribed in the Master Circular on Resource Raising Norms for FIs, issued by DBOD and updated from time-to-time.
Minimum Size of Issue and Denominations
Minimum amount of a CD should be Rs.1 lakh, i.e., the minimum deposit that could be accepted from a single subscriber should not be less than Rs.1 lakh, and in multiples of Rs. 1 lakh thereafter.
Investors
CDs can be issued to individuals, corporations, companies (including banks and PDs (Primary Dealers) trusts, funds, associations, etc. Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) are allowed to subscribe to CDs, but only on non- repatriable basis, a condition, clearly stated on the Certificate of deposit. Such CDs cannot be endorsed to another NRI in the secondary market.
Maturity
The maturity period of CDs issued by banks should not be less than 7 days and not more than one year, from the date of issue. But FIs can issue CDs for a period not less than 1 year and not exceeding 3 years from the date of issue.
Discount/Coupon Rate
CDs may be issued at a discount on face value. Banks / FIs are also allowed to issue CDs on floating rate basis provided the methodology of compiling the floating rate is objective, transparent and market-based. The issuing bank / FI is free to determine the discount / coupon rate.
The interest rate on floating rate CDs would have to be reset periodically in accordance with a pre-determined formula that indicates the spread over a transparent benchmark. The investor should be clearly informed of the same.
Reserve Requirements
Banks have to maintain appropriate reserve requirements, i.e., cash reserve ratio (CRR) and statutory liquidity ratio (SLR), on the issue price of the CDs.
Transferability
CDs in physical form are freely transferable by endorsement and delivery. CDs in demat form can be transferred as per the procedure applicable to other demat securities. There is no lock-in period for the CDs.
Trades in CDs
All OTC trades in CDs shall be reported within 15 minutes of the trade on the FIMMDA reporting platform.
Loans/Buy-Backs
Banks / FIs cannot grant loans against CDs. Furthermore, they cannot buy-back their own CDs before maturity. However, the RBI may relax these restrictions for temporary periods through a separate notification.
Format of CDs
Banks / FIs should issue CDs only in dematerialised form. However, according to the Depositories Act, 1996, investors have the option to seek certificate in physical form. Accordingly, if an investor insists on physical certificate, the bank / FI may inform the Chief General Manager, Financial Markets Department, Reserve Bank of India, Central Office, Fort, about such instances separately.
Security Aspect
Since CDs in physical form are freely transferable by endorsement and delivery, it will be necessary for banks/FIs to see that the certificates are printed on good quality security paper and necessary precautions are taken to guard against tampering with the document. They should be signed by two or more authorised signatories.
Payment of Certificate
Since CDs are transferable, the physical certificates may be presented for payment by the last holder. The question of liability on account of any defect in the chain of endorsements may arise. It is, therefore, desirable that banks take necessary precautions and make payment only by a crossed cheque. Those who deal in these CDs may also be suitably cautioned.